Potential Project 1: GPCR electronics
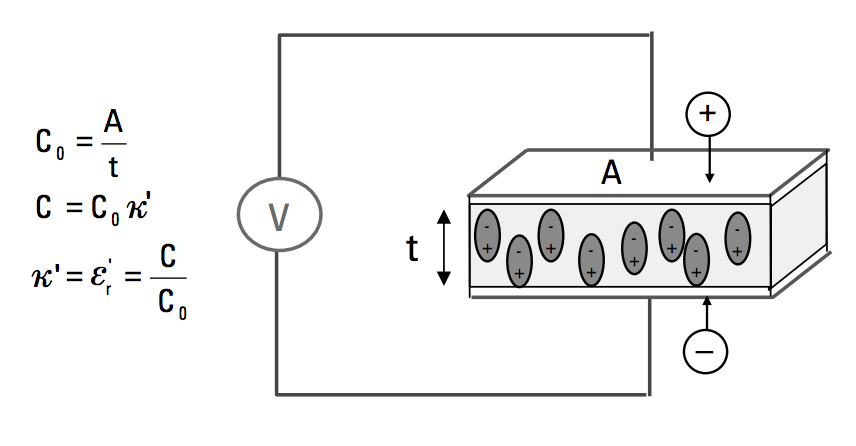
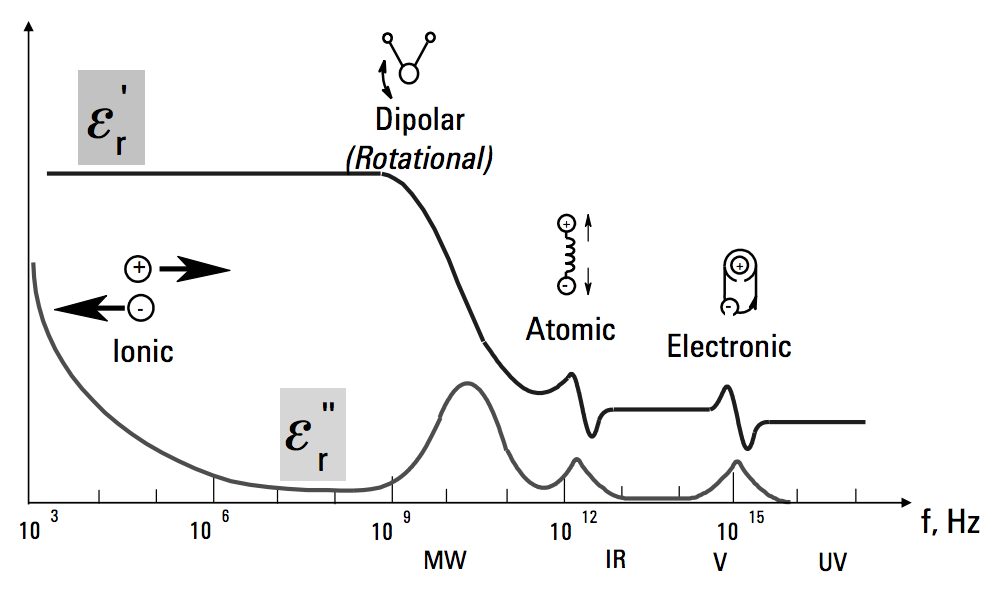
A material is classified as “dielectric” if it has the ability to store energy when an external electric field is applied. If a DC voltage source is placed across a parallel plate capacitor, more charge is stored when a dielectric material is between the plates than if no material (a vacuum) is between the plates. The dielectric material increases the storage capacity of the capacitor by neutralizing charges at the electrodes, which ordinarily would contribute to the external field. The capacitance with the dielectric material is related to dielectric constant. If a DC voltage source V is placed across a parallel plate capacitor (Figure 1), more charge is stored when a dielectric material is between the plates than if no material (a vacuum) is between the plates.
In the image on the right, C and C0 are capacitance with and without dielectric, k' real dielectric constant or permittivity, and A and t are the area of the capacitor plates and the distance between them (Figure 1). The dielectric material increases the storage capacity of the capacitor by neutralizing charges at the electrodes, which ordinarily would contribute to the external field. The capacitance of the dielectric material is related to the dielectric constant as indicated in the above equations.