HTGAA : Hardware
David Kong (MIT), Kristin Ellis (Opentrons), and Julie Legault and Justin Pahara (Amino)
Hardware Assignment
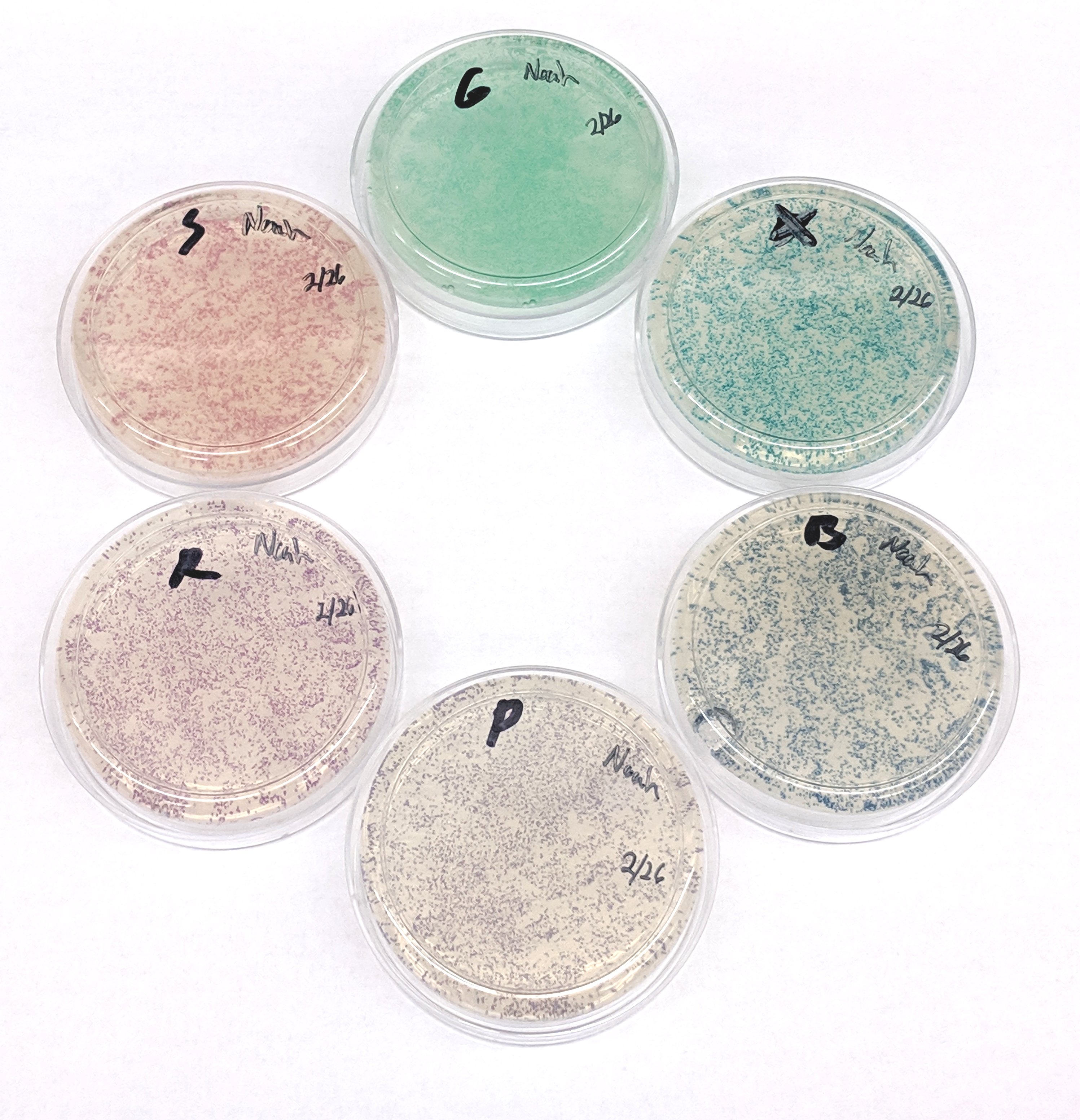
Build and test 'Zap-pore', a DIY electroporator used for transformation. Transform the pBlu plasmid into electrocompetent E coli and plate the cells on LB agar supplemented with ampicillin and X-gal alternatives.
Here is a (non-exclusive) list of hardware projects:
Experiment Execution. Throughput and reproducibility are key limits to what can be accomplished in synthetic biology. Any hardware that accelerates the design, test, build, and learn cycle and/or makes experimental results more reliable and reproducible will have a significant impact on synthetic biology.
Sensors. Data acquisition for biological measurement—from optical density to fluorescence measurements—require sensors. Projects based on novel sensing technologies, or innovative remixes of current sensors, are welcome topics.
Microscopy. The ability to visualize biological systems is one of the most critical enabling technologies for biology. In class, we've learned about a variety of imaging techniques that can enable, for example, expansion microscopy and FISSEQ.
Liquid Handling. We exist in the pipette era of biology. Fluidic machines—from microfluidics to liquid handling robots—can help us realize the longstanding vision of an automated biological future.
Complexity Management. Synthetic biologists constantly manage complexity, from sample tracking to running multiple parallel experiments. Great hardware can help organize and systematize without scaling up confusion.
Bioreactors. Engineered organisms typically require culturing in an in vitro environment. Great hardware can help organisms grow according to experimental parameters and execute their engineered functions.
Bio-printing. We have learned in class about ways to work with biological materials to create structures. From inkjets to larger deposition systems, hardware is critical for precisely spatially orienting bio-materials.
Bio-Made Hardware. Hardware can help synthetic biologists engineer biology, but biology can also be used to engineer hardware. Consider also projects that use genetically engineered machines to create structures, mechanisms, and other devices.
Reading
2003 Synthetic Biology Study by Drew Endy
TABSE: A Tool-Chain to Accelerate Synthetic Biological Engineering http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.467.7189&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Overview on Generic Lab Equipment http://hackteria.org/wiki/Generic_Lab_Equipment