#Robotic Fabrication #Parametric Design #Modularization #GUI |
|---|
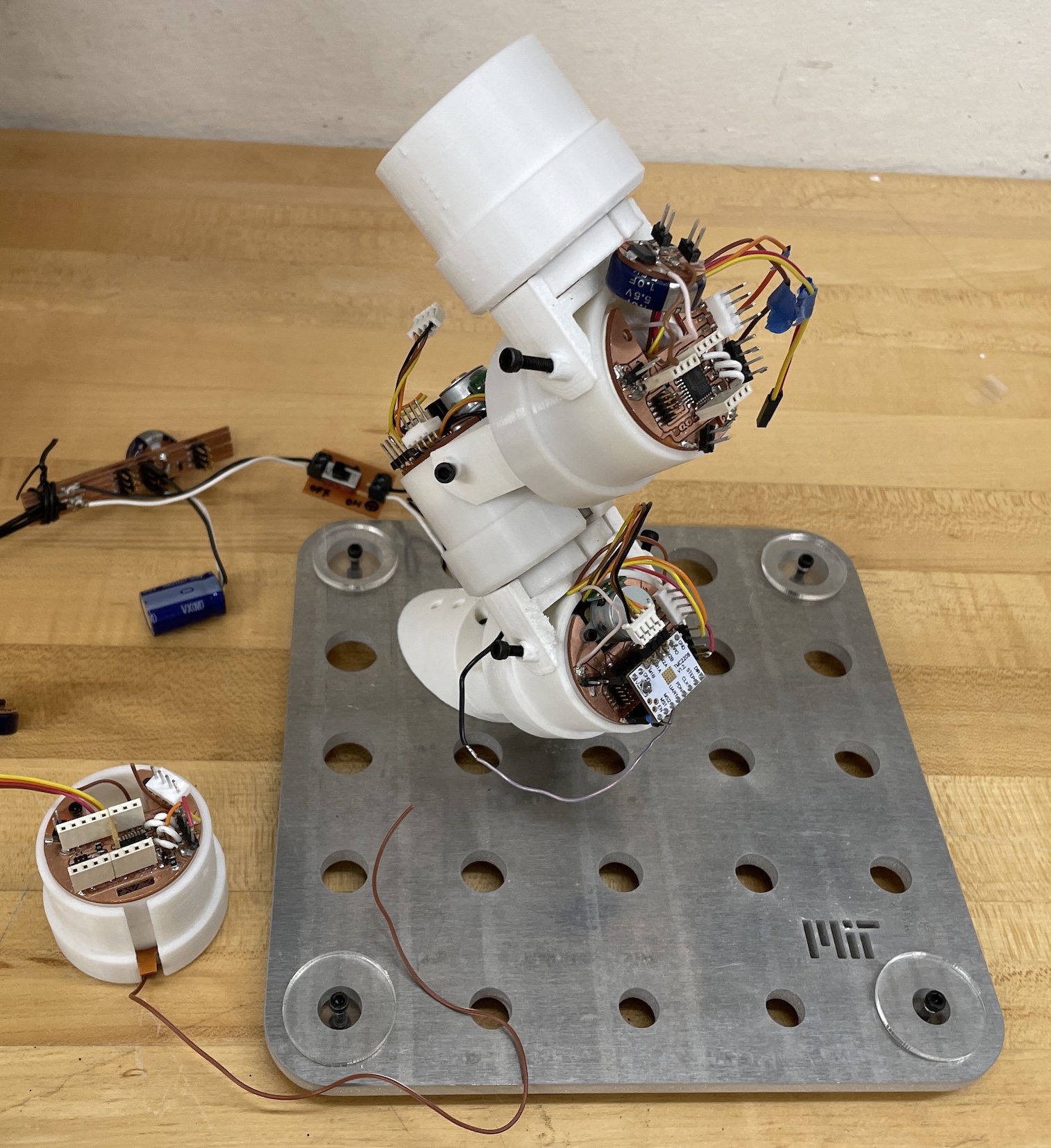
In the design field, designers are looking for a more intuitive way to use robots. In order to meet the need, I decided to develop a modularized versatile robotics system with a parametric design interface and visualization. The robot system may need to be aware of the current configuration when a user assembles some modules. I would use the IoT method to design the robot system; the interface can visualize and control the robot modules in real-time. |
|---|
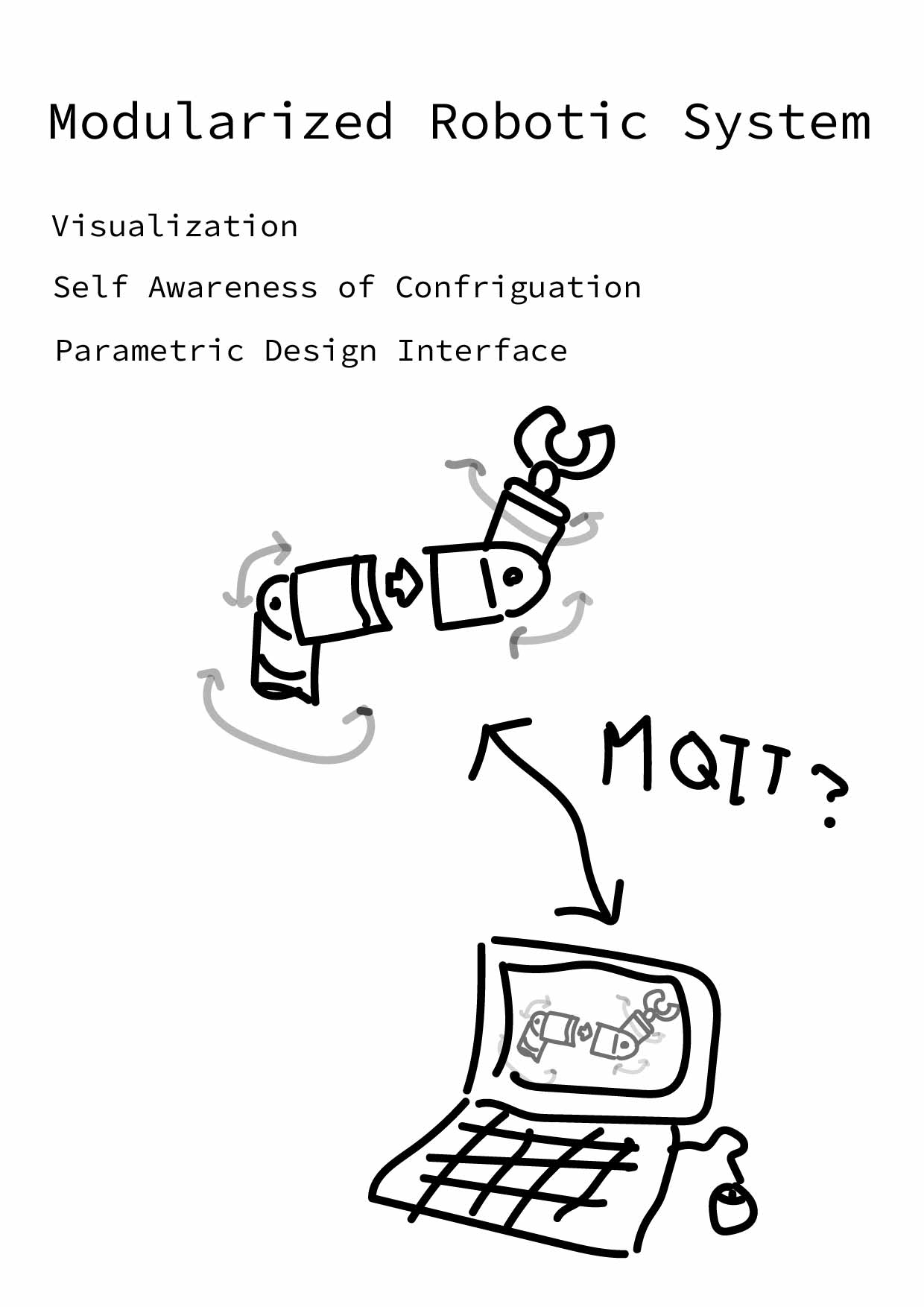
Furthermore, Users can use these modules as a telepresence robotic system since they can be controlled remotely with MQTT. These parts are the same; therefore, users can easily assemble them, reconfiguring them to meet the needs of different scenarios. |
|---|
Therefore, I design the modular robotic systems including three main features: |
|---|
1.Identical units 2.Plug and Play 3.Wireless Control |
|---|
WHY? |
|---|
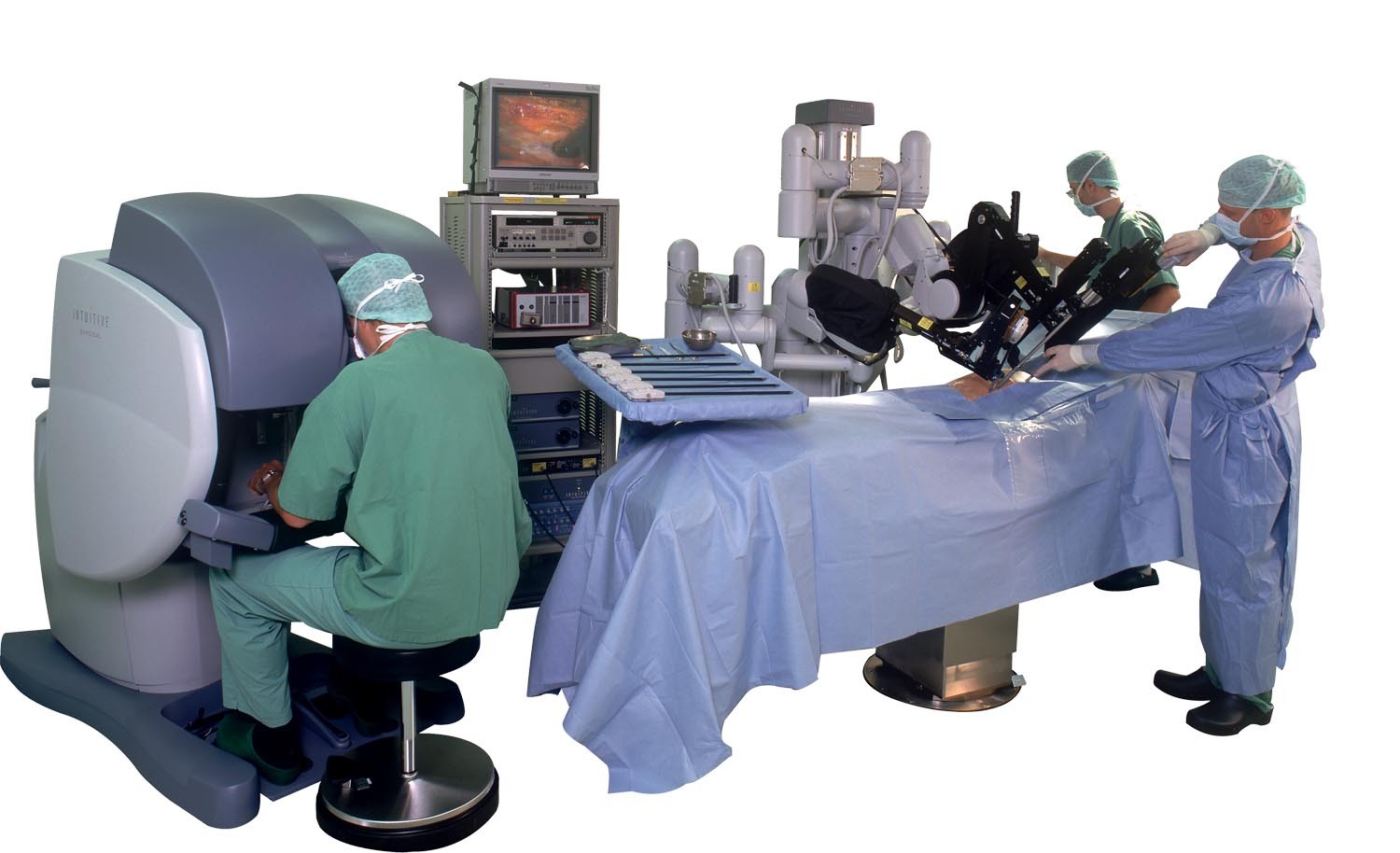
First, current existing industrial robots are difficult to use for creaters. |
|---|
I have some experiences the I was using industrial robots for digital fabrication and art. |
|---|
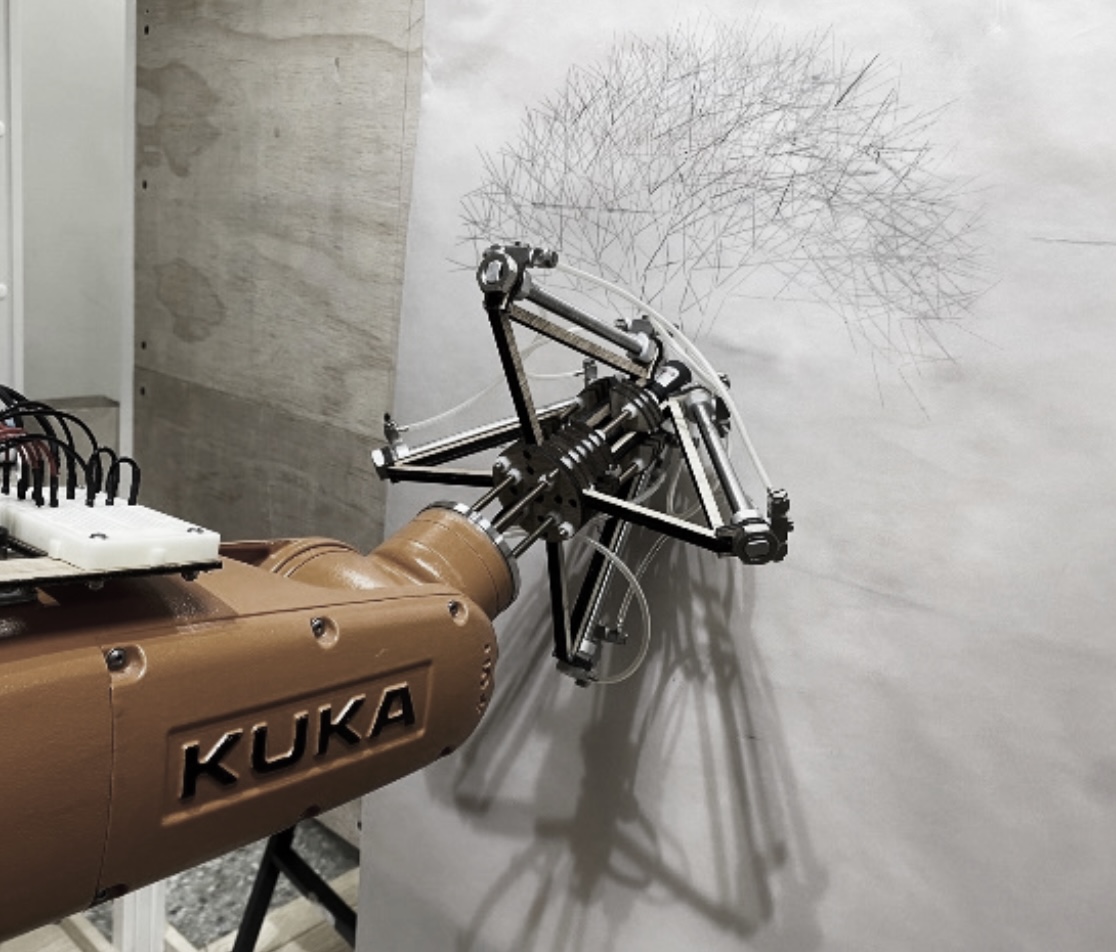

I need to deal with many issues when using current industrial robot arm all the time. |
|---|
In a confined working space, current industrial robotic systems are useless. |
|---|
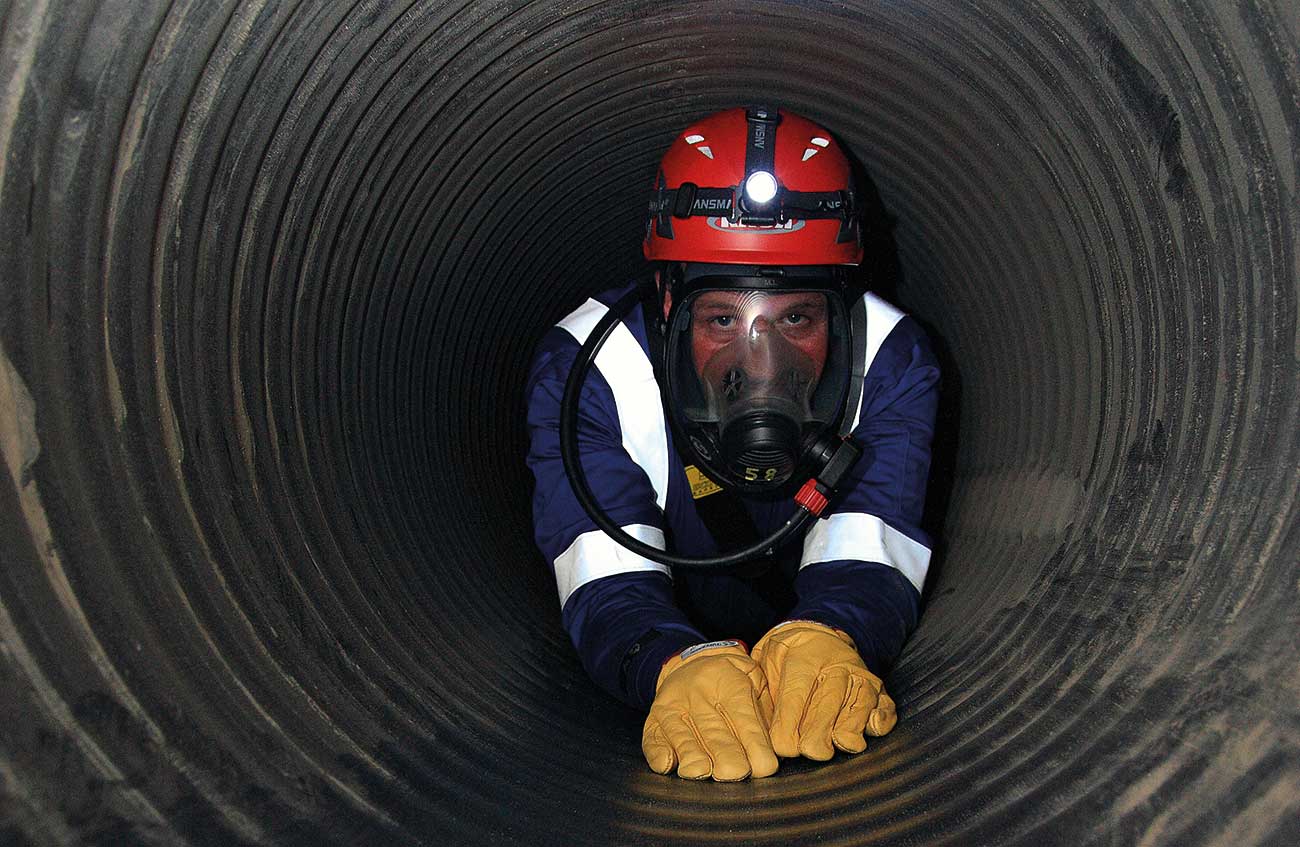

In space, a robot system that is compact and easy to carry andmaintain is crucial. |
|---|
It would be handy to carry and repair these versatile and identical parts because they can be designed to be packed efficiently and changed components. |
|---|

Also, when people have a punch of same modules, it is easy to accumulate using experiences; therefore, it is easier to get helps when encountering problems. |
|---|

Wireless control is useful for remote working |
|---|
Additionally, when we meet online and try to solve some problems, a wireless control robots through the interned could help a lot. |
|---|
I believe it can help to convey ideas as well, the robot can be participants' telepresence hands. |
|---|

|
|---|
|
|---|
The interface I created in Grasshopper, which is able to caculate each modular's angle and send to the robotic system through MQTT |
|---|
It will be easy for users to control the robot intuitively |
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
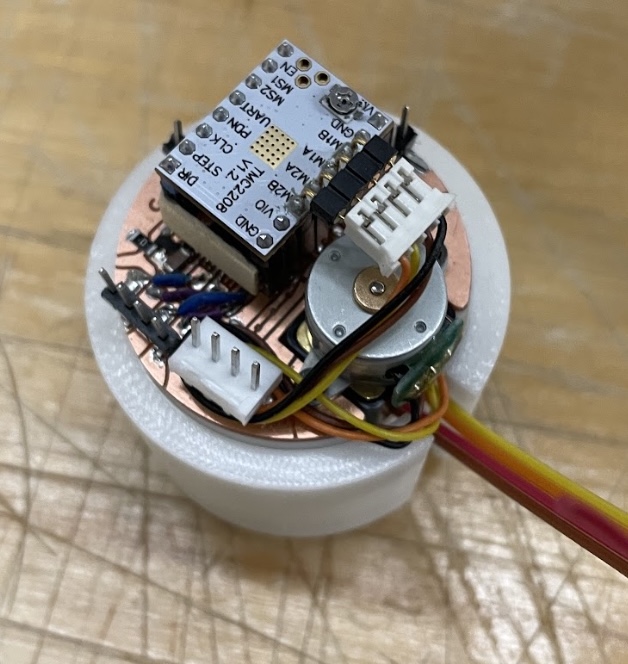
#BOM |
|---|
The section of the robot. |
|---|
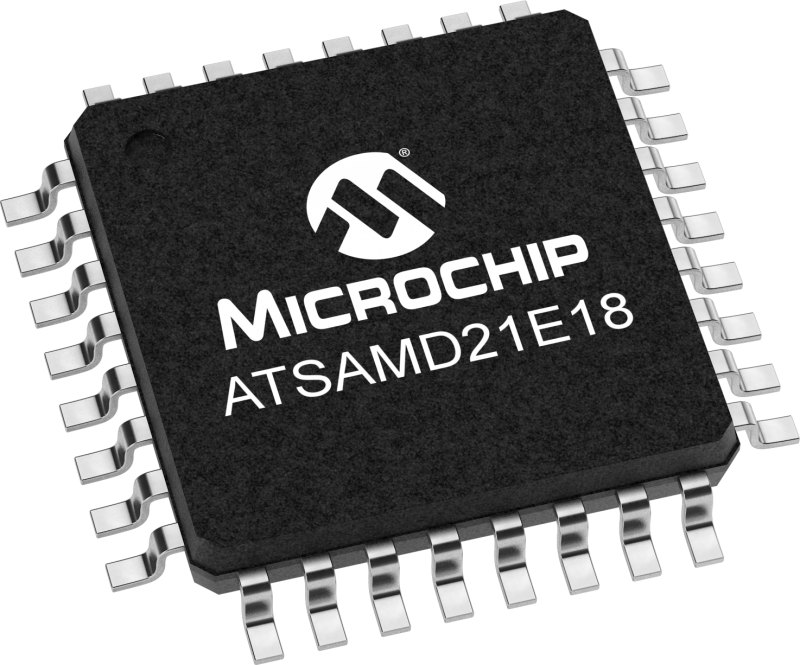
SAMD21E18: MCU with more flash storage to memorize the stepper angle in a non-volatile way |
|---|
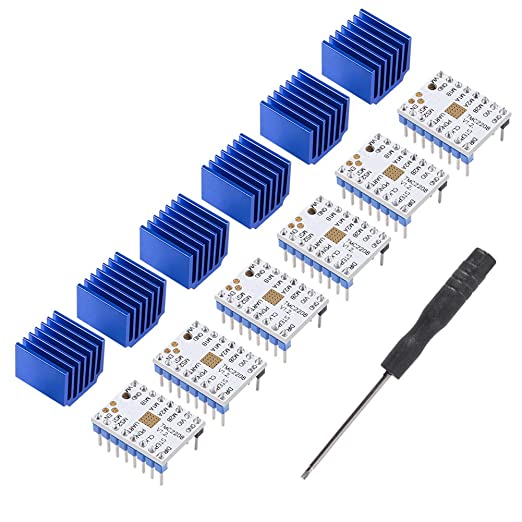

TMC2208: Sepper motor driver |
|---|
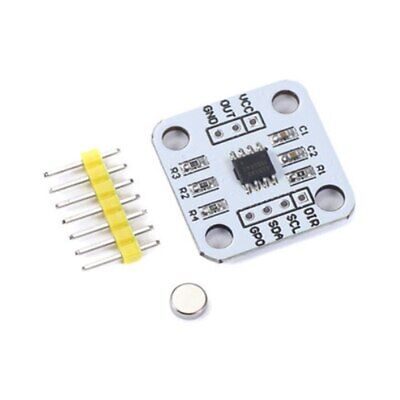

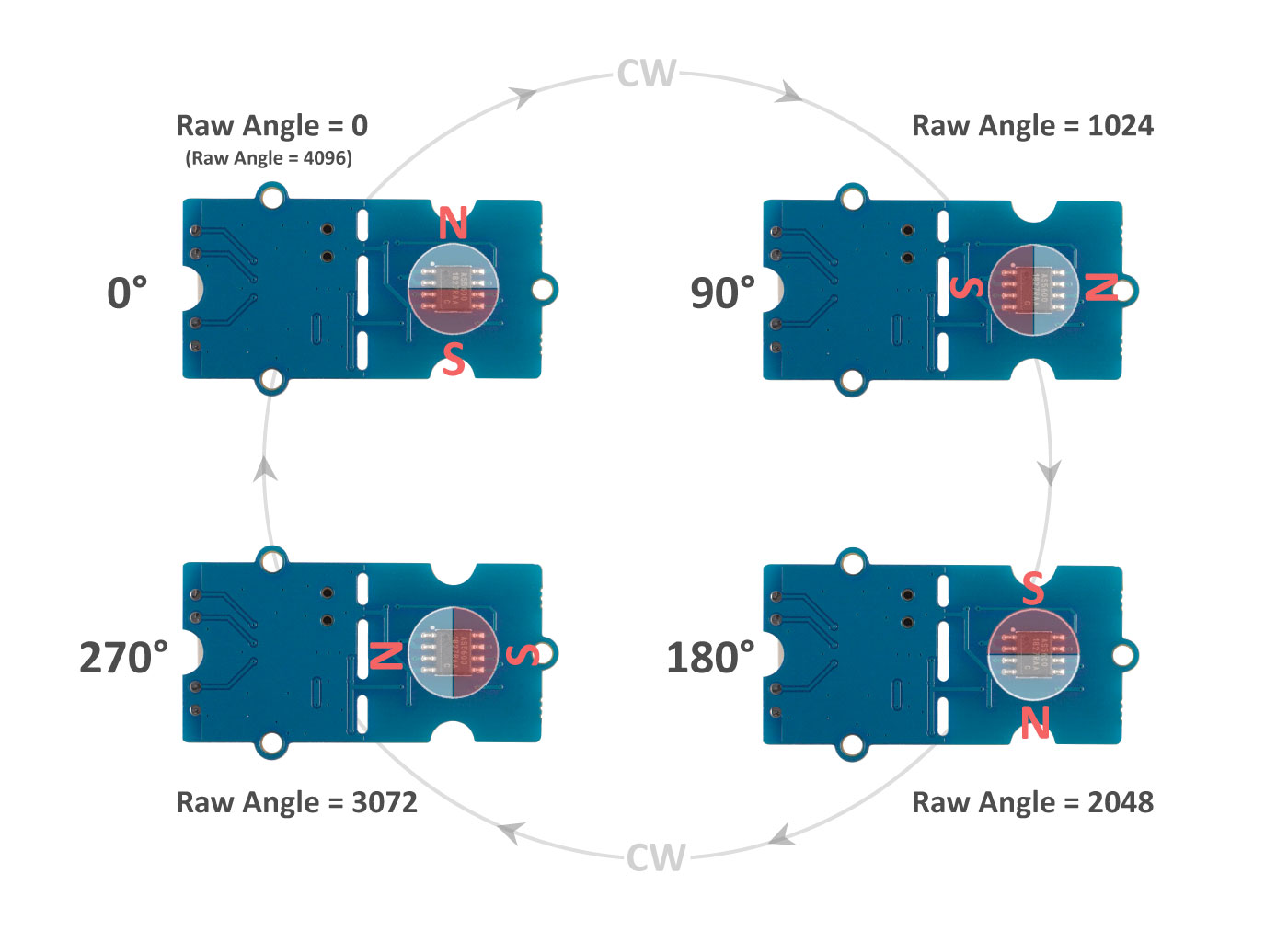
AS5600 is a magnetic encoder magnetic induction angle measurement sensor module, it can output 4096 positions per round |
|---|
Esp8266: wireless control through MQTT |
|---|
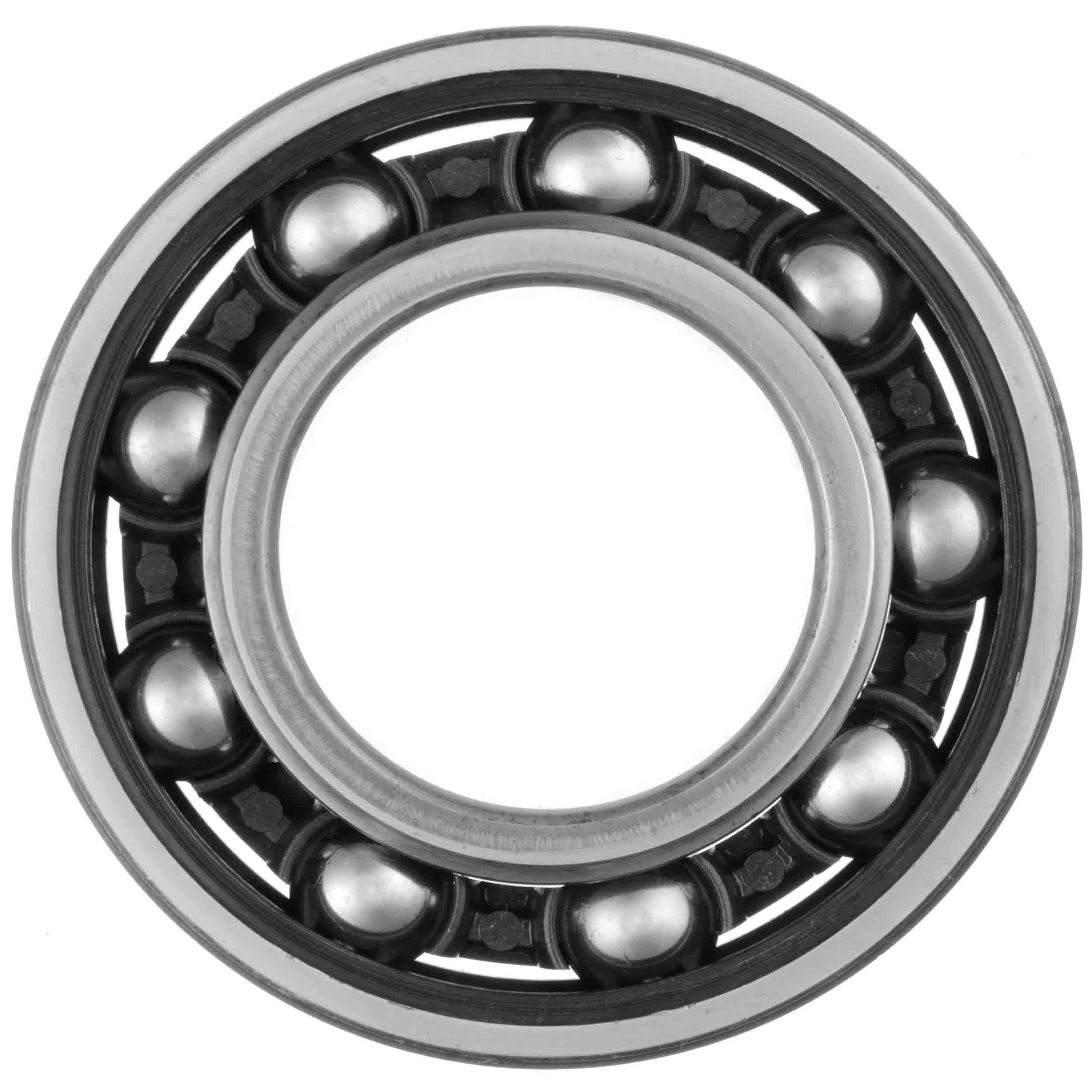

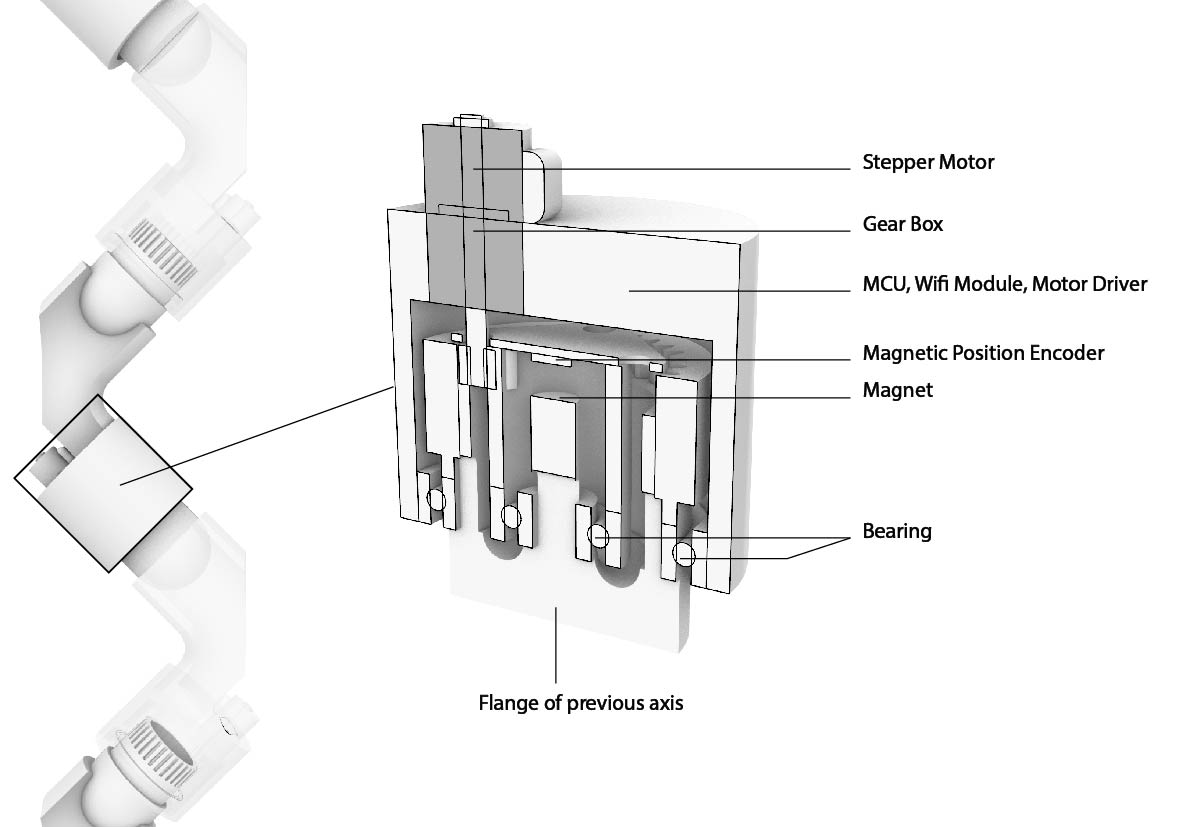
Bearing: in this project, I attempt to make bearings as connectors; therefore, they will be modified to be conductive. |
|---|
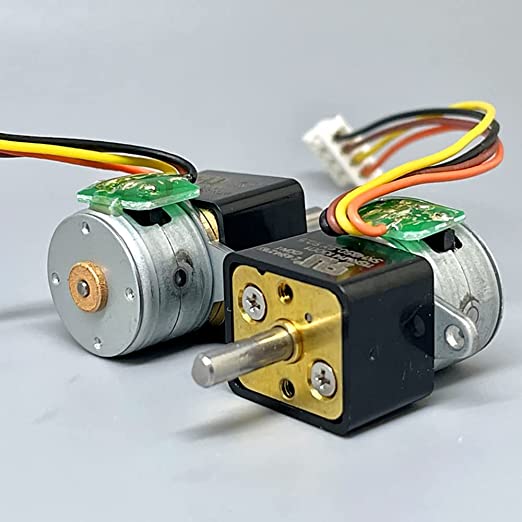

DC 5V 2-Phase 4-Wire Micro Stepper Motor |
|---|
|
|---|
working in progress |
|---|
|
|---|
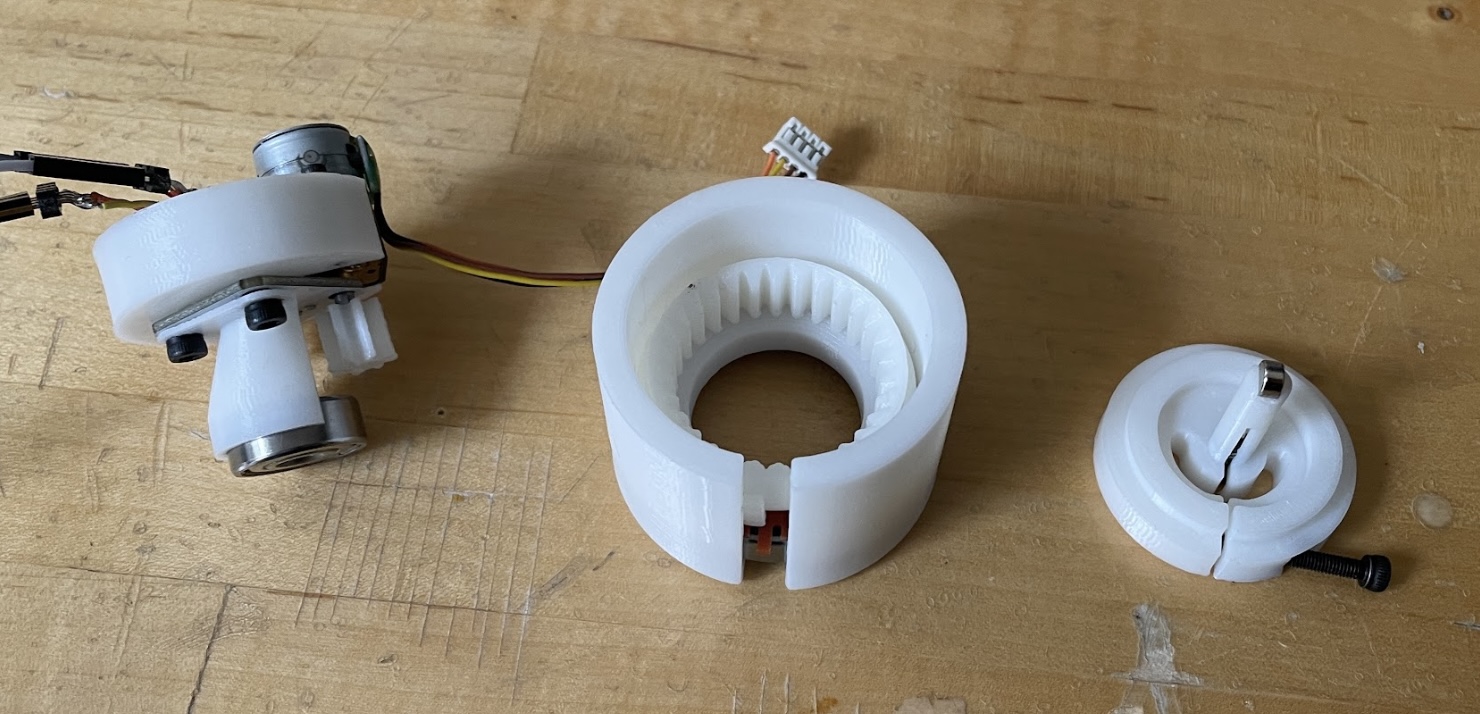
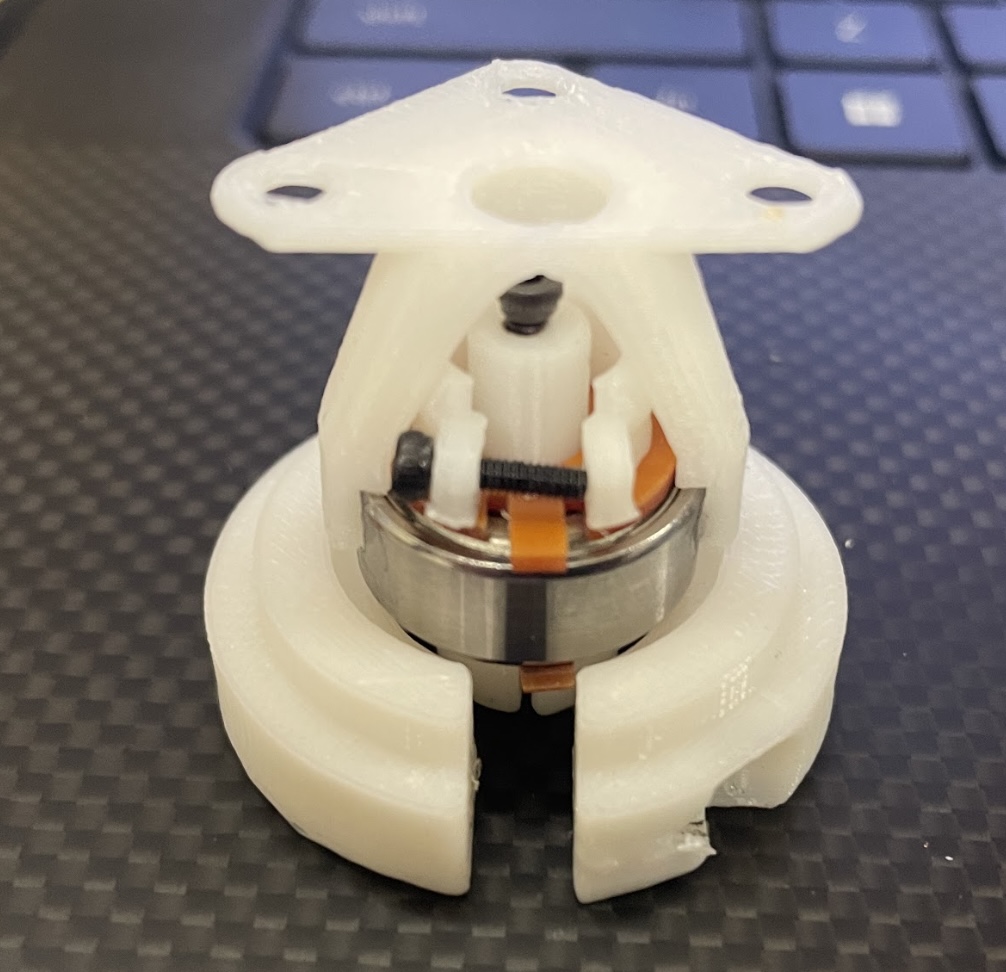
A compact design combines a gearbox, a stepper motor, a rotary encoder, connectors(bearings), Wifi Module, and MCU |
|---|
|
|---|
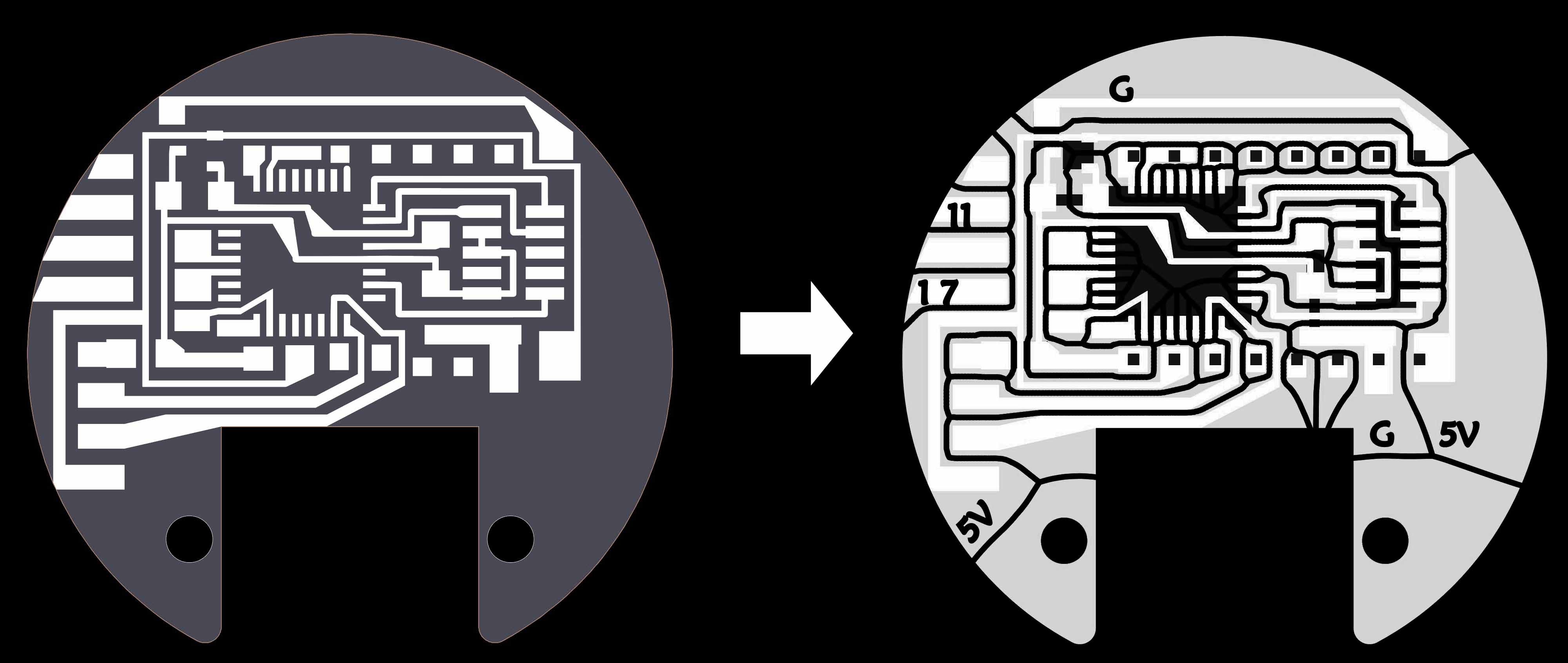
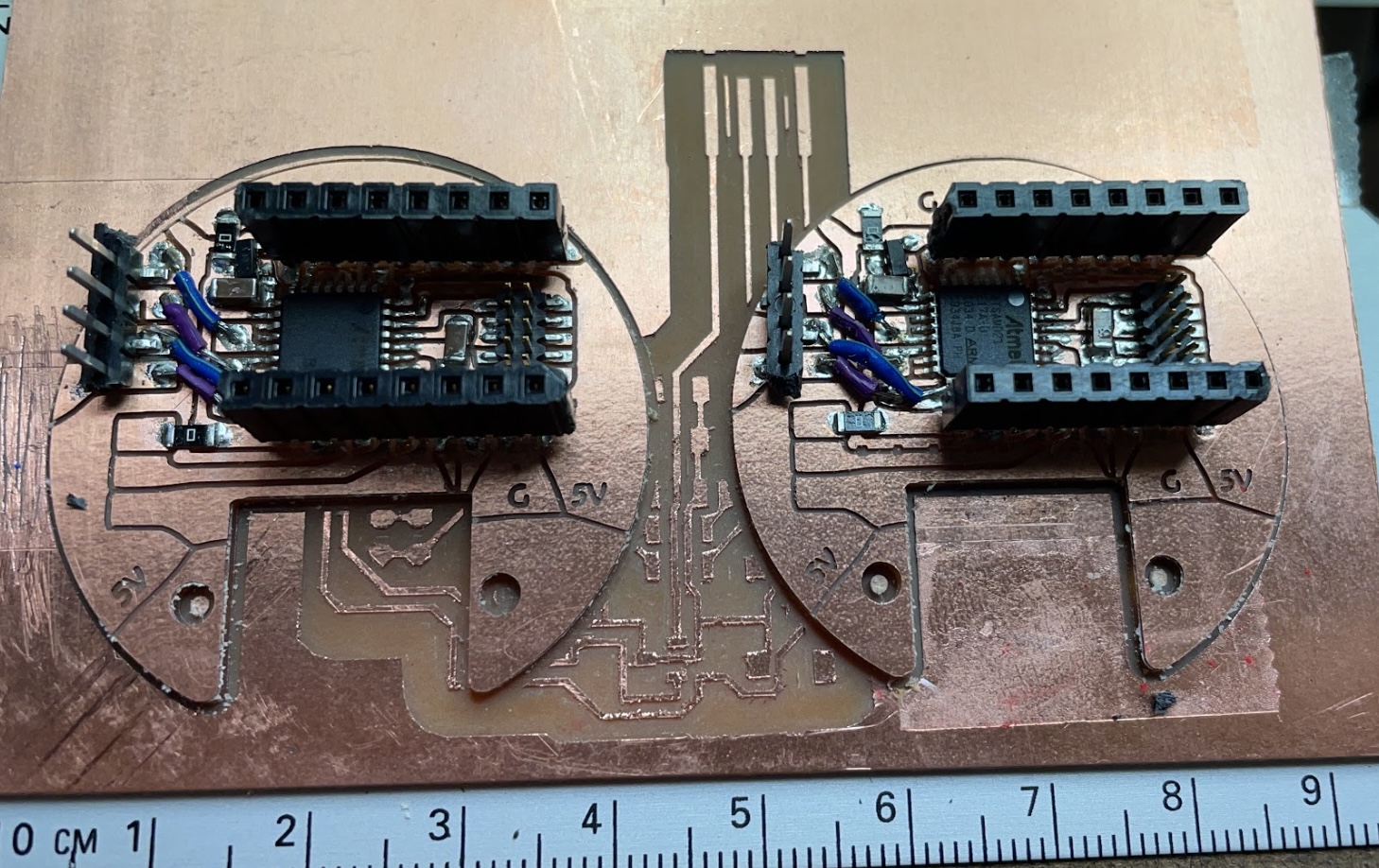
I try to add copper boards to make bearing conductive, using two bearings as GND and 5V to power each system. |
|---|

This mechanism is to press down the copper board to connect inner and outter rings of a bearing. |
|---|
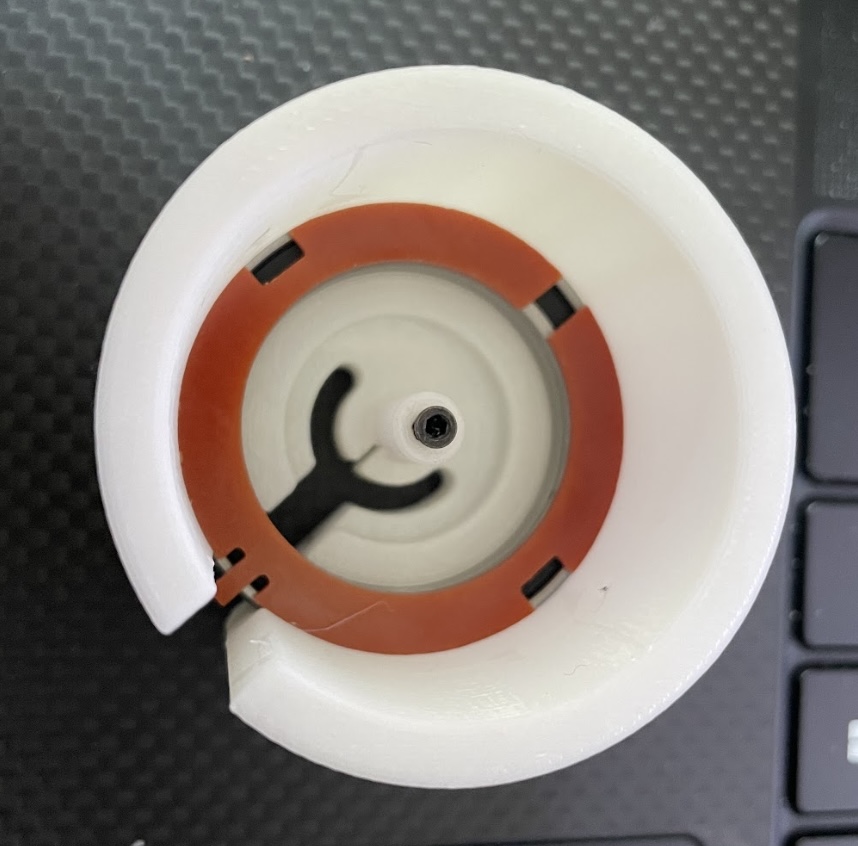

|
|---|

The lubricant in a bearing will make the inner ring and the outer ring insulated; I use a copper-clad PCB to connect them. |
|---|
Rotary encoder test |
|---|
|
|---|

|
|---|
Final Project Video |
|---|
|
|---|
2022 |
|---|