←Index
11/15 Signal Processing
## Week 10:
In this week, we learned how to ...
# Class notes
- The gate resistor is used to slow down the signal to the mosfet.
Networking and Communications
- modularity
- Wired Networks
- asychcronous vs synchronous: synchronous serial is preferred, because it is clocked.
- SPI, used by SD memory cards to read an write lines of data.
- I2C, a lot of sensors use I2C to communicate
- Wireless Networks
- Single Chip Radio
- Antennas: the shape of the Antenna create impedance
- WiFi: Xiao serves a webpage and handles local requests, collaborative multitasking (loop is stoped with async)
- Bluetooth: have profiles, NUS (bluetooth profile from Nordic using UART), How
- WebBluetooth: Serial port through the air
- RFID: Read and Write recoginized with coil
- LoRa: city scale, agricultural Networking
- software radio
- Send Data optically, rgb light
Show and Tell
---
## Idea
- Continue last week's experimentations and add network interface.
# Assignment
- individual assignment: design, build, and connect wired or wireless node(s)
with network or bus addresses and a local interface
- group assignment: send a message between two projects
# 1) PCB for LIG x LCE
Continuing last week's progress, I trouble shooted the pcb board that switches the 12v power supply. Two things I changed:
- break out all the pin of the Xiao ESP32C3. For my previous pcb board, I only broke out one pin of the ESP. That made trouble shooting very unflexible.
- remove the gate resistor and made the flyback diode optional. Just to further remove sources that could cause trouble.
I then designed and milled the boards.
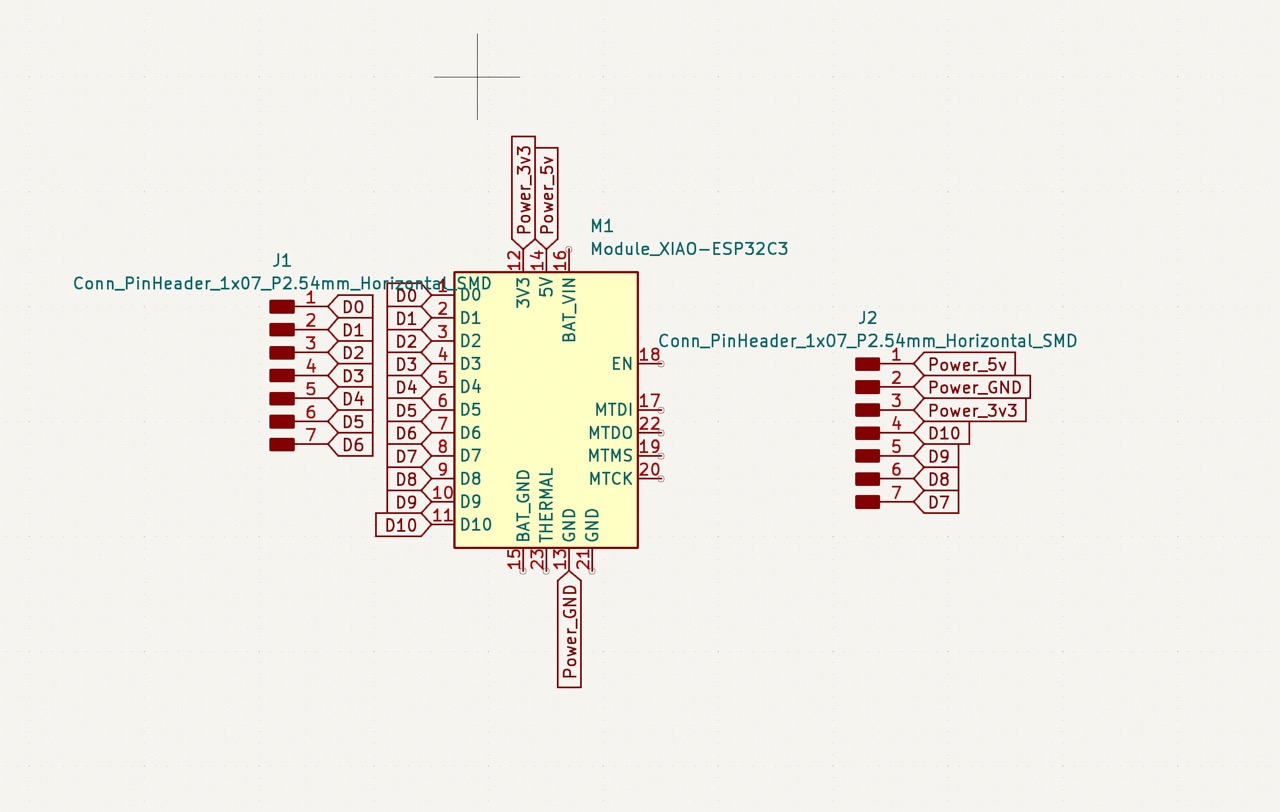
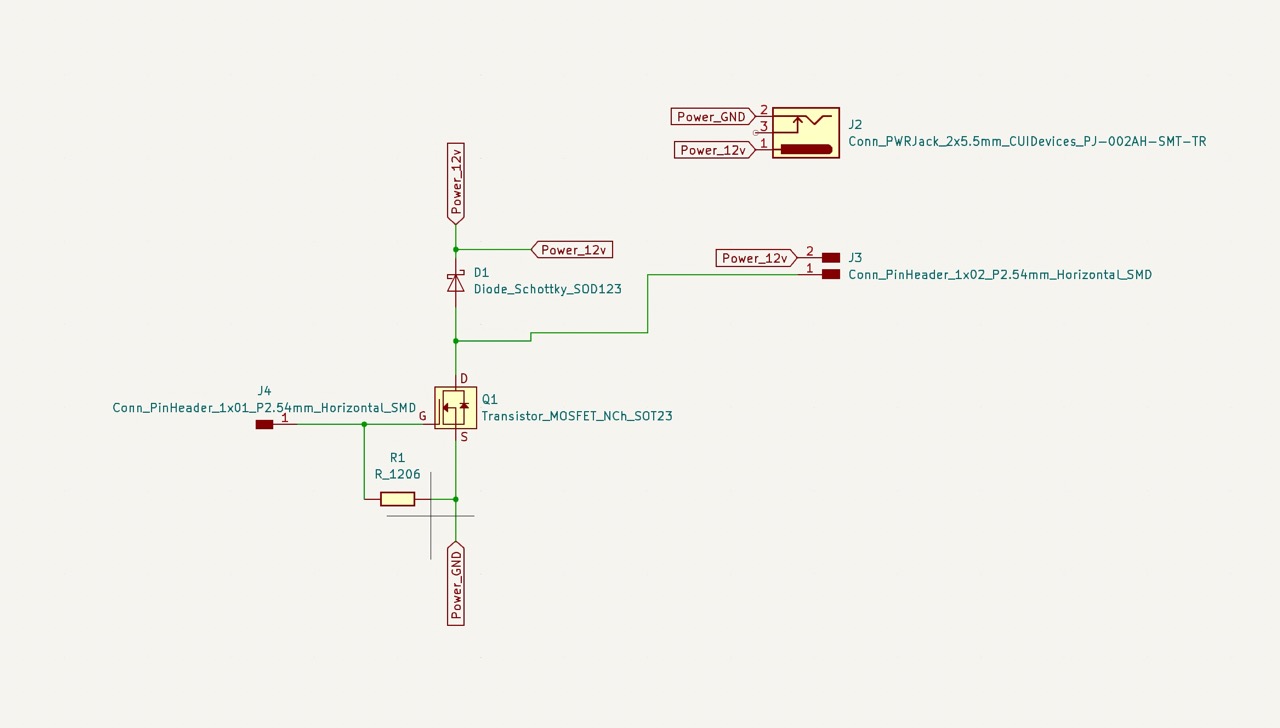
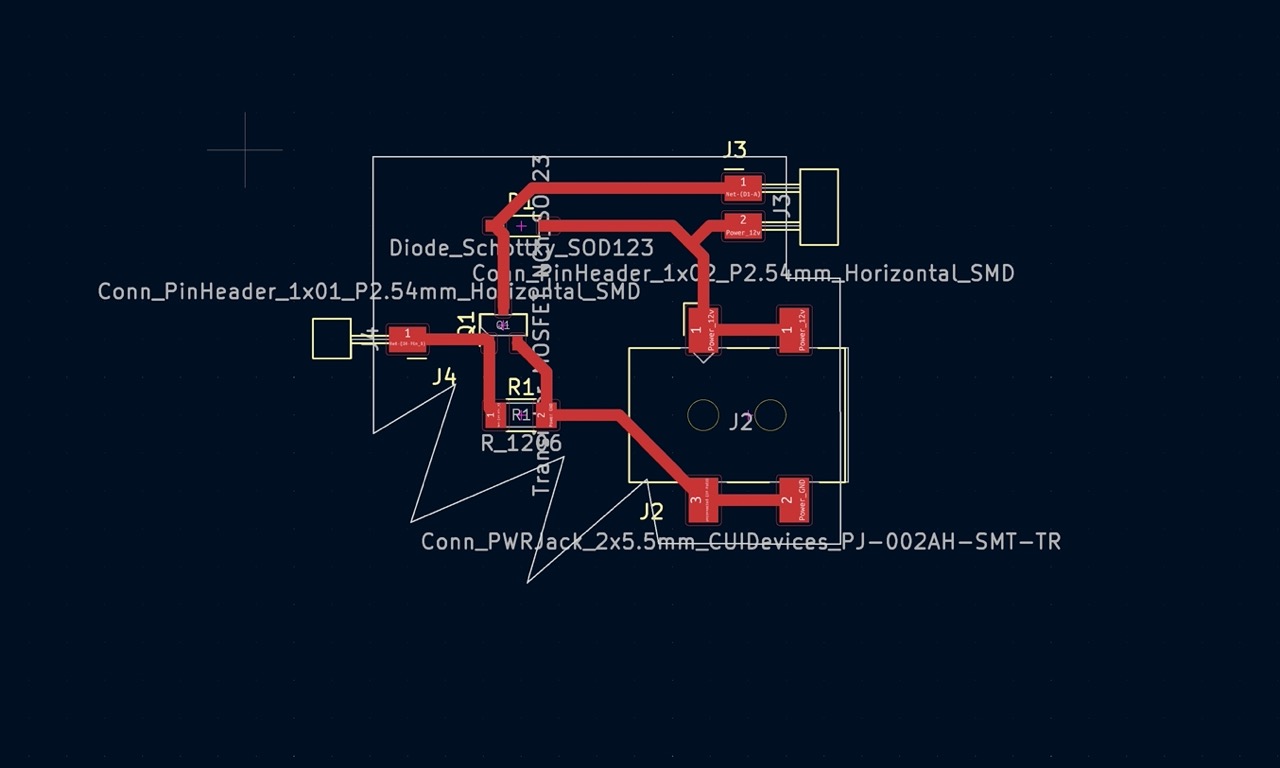
Trouble shoot conclusion:
- Mill the holes of blue prints using 1/32.
- check the direction of power jack. I had the plug in face facing inward.
- Desoldering components with more than 2 legs, it's better to use a hot air to heat up the whole area.
- **When connecting several boards, break out GND on each board so that they can connect to a common GND** I had to add a wire post milling.
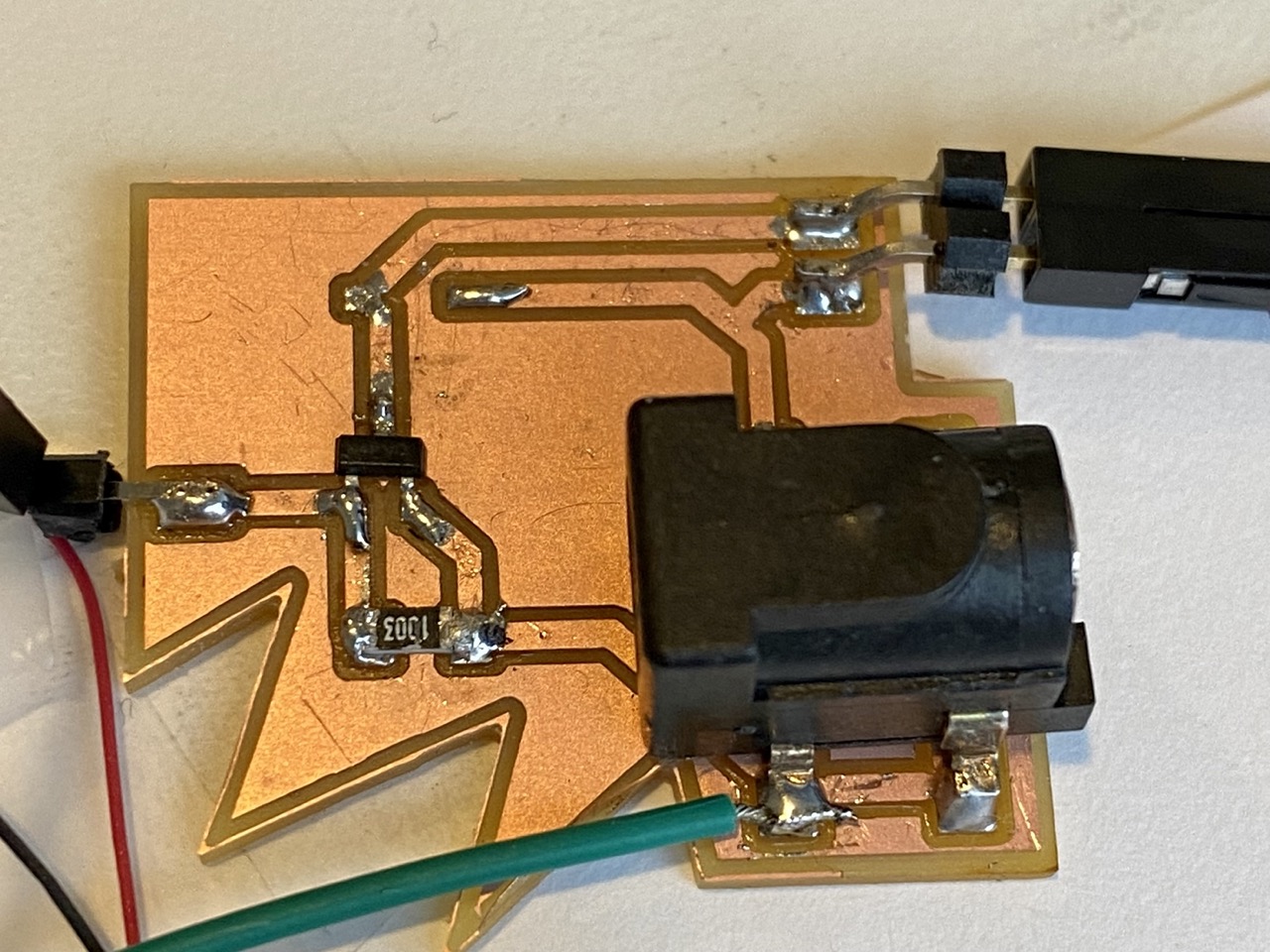
I tested all connections, however, it was still not working. I looked up the [datasheet](https://www.mouser.com/datasheet/2/916/PMV45EN2-1319180.pdf) of the mosfet I used and realised it has a **Vgs of 10v.** I switched the mosfet to a [SI2336DS-T1-GE3](https://www.digikey.com/en/products/detail/vishay-siliconix/SI2336DS-T1-GE3/3748946) and the board worked.
# 2) ESP32 Web Server
With a functioning esp32 switching 12v, I started to work on controling GPIO pin with a web server. This was the [tutorial](https://randomnerdtutorials.com/esp32-esp8266-web-server-physical-button/) I followed and it worked right away.
- remember to connect all devices to the same network.
With everything set, I connected the components: ESP32 hosting a Web Server, mosfet board, 12v power supply, LIGxLCE sheet.
## Next Steps
- use copper plating to make heating frame
---
# Resources
- files
- [wifi btn code](files/wifi_btn.ino)
- Buy your own 1/64 and 1/32 End mills.
---
↳About