This week, we worked on sending a message between two projects. We attempted to make my mouse control the music generator, but it didn’t work as expected.
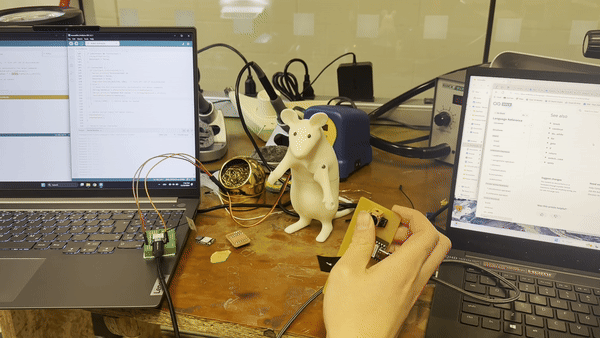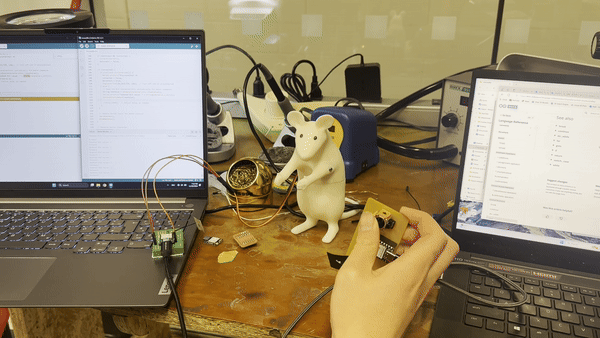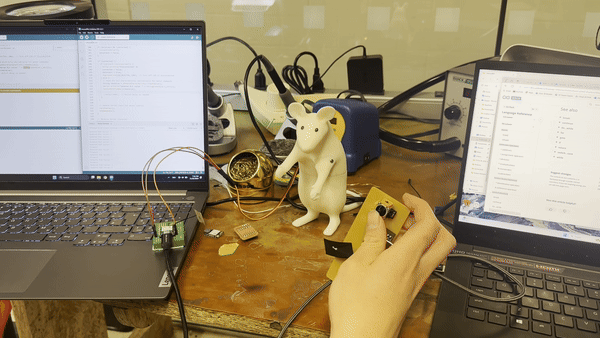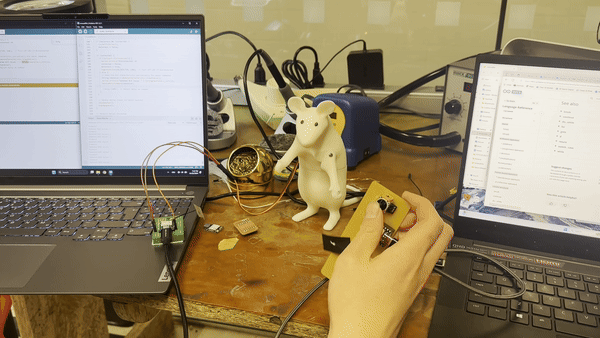
For my independent project, I used a controller to operate a servo motor. First, we attached an antenna to the Xiao ESP C6. I encountered difficulties converting the Arduino RP2040 to the ESP C6 as it required a different library file. With the assistance of ChatGPT, I searched for "servo control with PWM" to resolve the issue.
Servo Control with PWM
const int servoPin = 35; // GPIO pin for the servo signal
const int servoMin = 500; // Minimum pulse width (0 degrees) in microseconds
const int servoMax = 2500; // Maximum pulse width (180 degrees) in microseconds
const int refreshRate = 20000; // Servo PWM signal period in microseconds (50 Hz)
void setup() {
pinMode(servoPin, OUTPUT); // Set the servo pin as output
Serial.begin(115200); // Start Serial communication
Serial.println("Enter a value between 0 and 60:");
}
void loop() {
// Check if data is available from the Serial Monitor
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
String inputString = Serial.readStringUntil('\n'); // Read input until newline
int inputValue = inputString.toInt(); // Convert input to integer
// Validate the input
if (inputValue >= 0 && inputValue <= 60) {
// Map the input value (0-60) to pulse width (500-2500 microseconds)
int pulseWidth = map(inputValue, 0, 60, servoMin, servoMax);
// Generate the PWM signal for the servo
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { // Loop to maintain the 50 Hz signal for 1 second
digitalWrite(servoPin, HIGH); // Set the pin high
delayMicroseconds(pulseWidth); // Wait for the pulse duration
digitalWrite(servoPin, LOW); // Set the pin low
delayMicroseconds(refreshRate - pulseWidth); // Wait for the remainder of the period
}
Serial.print("Input: ");
Serial.print(inputValue);
Serial.print(" -> Pulse Width: ");
Serial.print(pulseWidth);
Serial.println(" us");
} else {
Serial.println("Invalid input. Enter a value between 0 and 60.");
}
}
delay(50); // Small delay for stability
}
Controller Code
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
# Pin configuration
servo_pin = 11 # Replace with the actual pin connected to the servo motor
# Setup GPIO
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # Use physical pin numbering
GPIO.setup(servo_pin, GPIO.OUT)
# Setup PWM
frequency = 50 # Typical servo motors use a 50 Hz frequency
pwm = GPIO.PWM(servo_pin, frequency)
pwm.start(0) # Start PWM with 0% duty cycle
# Helper function to set angle
def set_servo_angle(angle):
"""
Sets the servo to the specified angle.
:param angle: The desired angle (0 to 180 degrees)
"""
duty_cycle = 2 + (angle / 18) # Map 0-180 degrees to 2-12% duty cycle
pwm.ChangeDutyCycle(duty_cycle)
time.sleep(0.5) # Allow the servo to reach the position
pwm.ChangeDutyCycle(0) # Stop sending signal to prevent jittering
try:
while True:
# Move servo to 0 degrees
print("Moving to 0 degrees")
set_servo_angle(0)
# Move servo to 90 degrees
print("Moving to 90 degrees")
set_servo_angle(90)
# Move servo to 180 degrees
print("Moving to 180 degrees")
set_servo_angle(180)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Stopping program")
finally:
pwm.stop() # Stop PWM
GPIO.cleanup() # Clean up GPIO
Motor Code
const int servoPin = A1; // Pin A1 connected to the servo signal wire
// Function to write an angle to the servo motor
void writeServoAngle(int angle) {
// Convert angle (0-180) to microseconds (1000-2000)
int pulseWidth = map(angle, 0, 180, 1000, 2000);
// Send the PWM signal
digitalWrite(servoPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(pulseWidth); // HIGH pulse duration
digitalWrite(servoPin, LOW);
delay(20 - (pulseWidth / 1000)); // Rest of the 20ms period
}
void setup() {
pinMode(servoPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Sweep the servo from 0 to 180 degrees
for (int angle = 0; angle <= 180; angle += 10) {
writeServoAngle(angle);
delay(500); // Wait for servo to reach position
}
// Sweep the servo from 180 to 0 degrees
for (int angle = 180; angle >= 0; angle -= 10) {
writeServoAngle(angle);
delay(500); // Wait for servo to reach position
}
}