<br>
[MAS.865](../../) > [Additive](../index.html) >Inkjet Printing
## Inkjet Printing & Printing Inks
### Classification
#### A. Droplet Formation Method
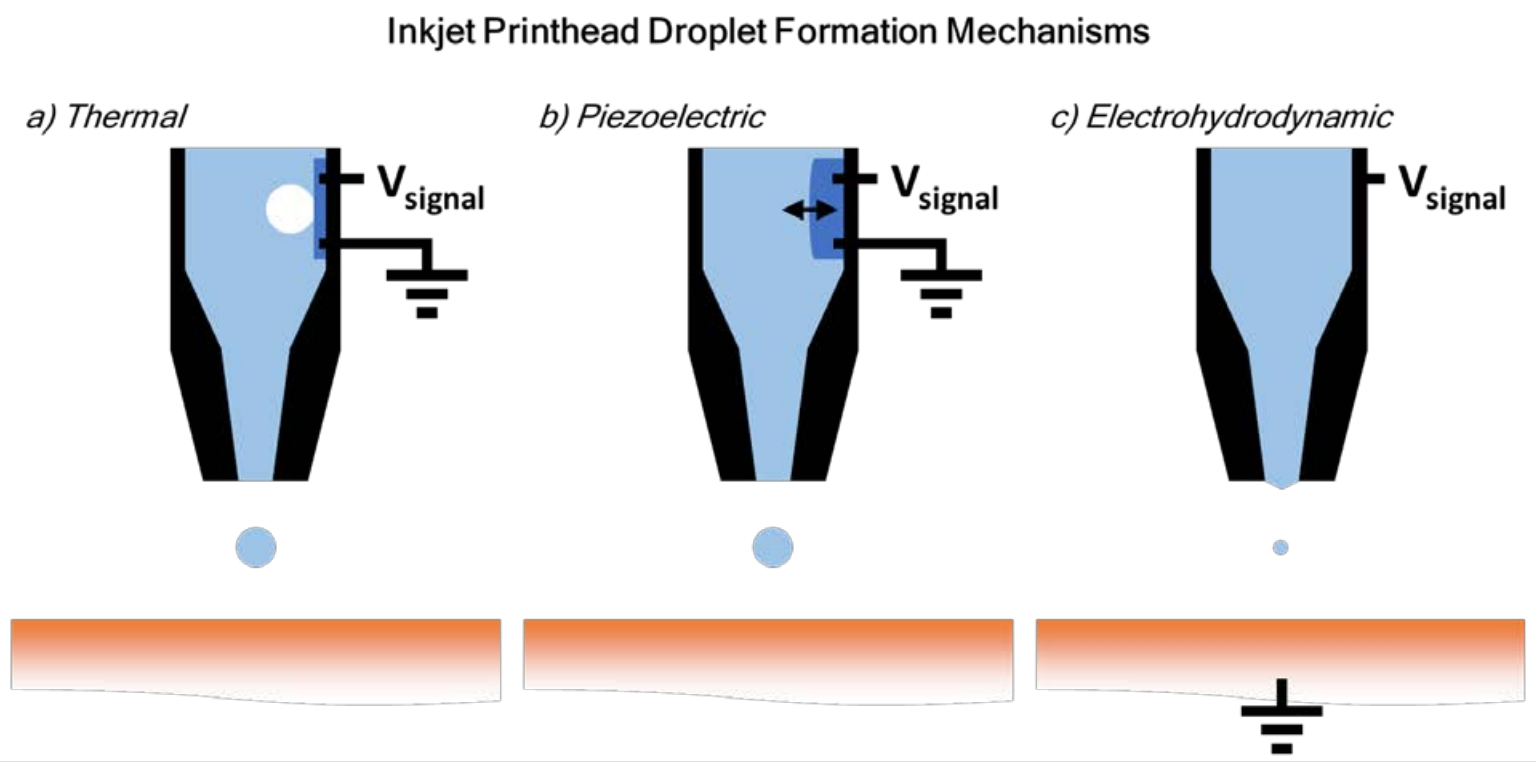
<ul>
<li><b><a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5iiJMv-jh7U">Thermal </a></b>
<ul>
<li> application of a voltage signal to a resistive film bordering the chamber
<li> resulting current ==> internal temperature increment ==> boiling
<li> bubble formation ==> ink droplet is forced out of the nozzle and onto the substrate
<li> voltage back to zero and the resist film cools
<li> chamber refills and process repeats
</ul>
<li><b><a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mJMOCmVPv8A">Piezoelectric </a></b>
<ul>
<li>application of a voltage signal to a piezoelectric film bordering the chamber
<li>inward deflection at a distance ~ applied voltage
<li>acoustic wave creation ==> ink droplet is forced out of the nozzle and onto the substrate
<li> voltage back to zero and the piezoelectric film relaxes ==> acoustic wave attenuates
<li>chamber refills and porcess repeats
</ul>
</ul>
Both types of DOD printing heads may be used to build free-standing objects, although modifications in both materials and methodology are required.
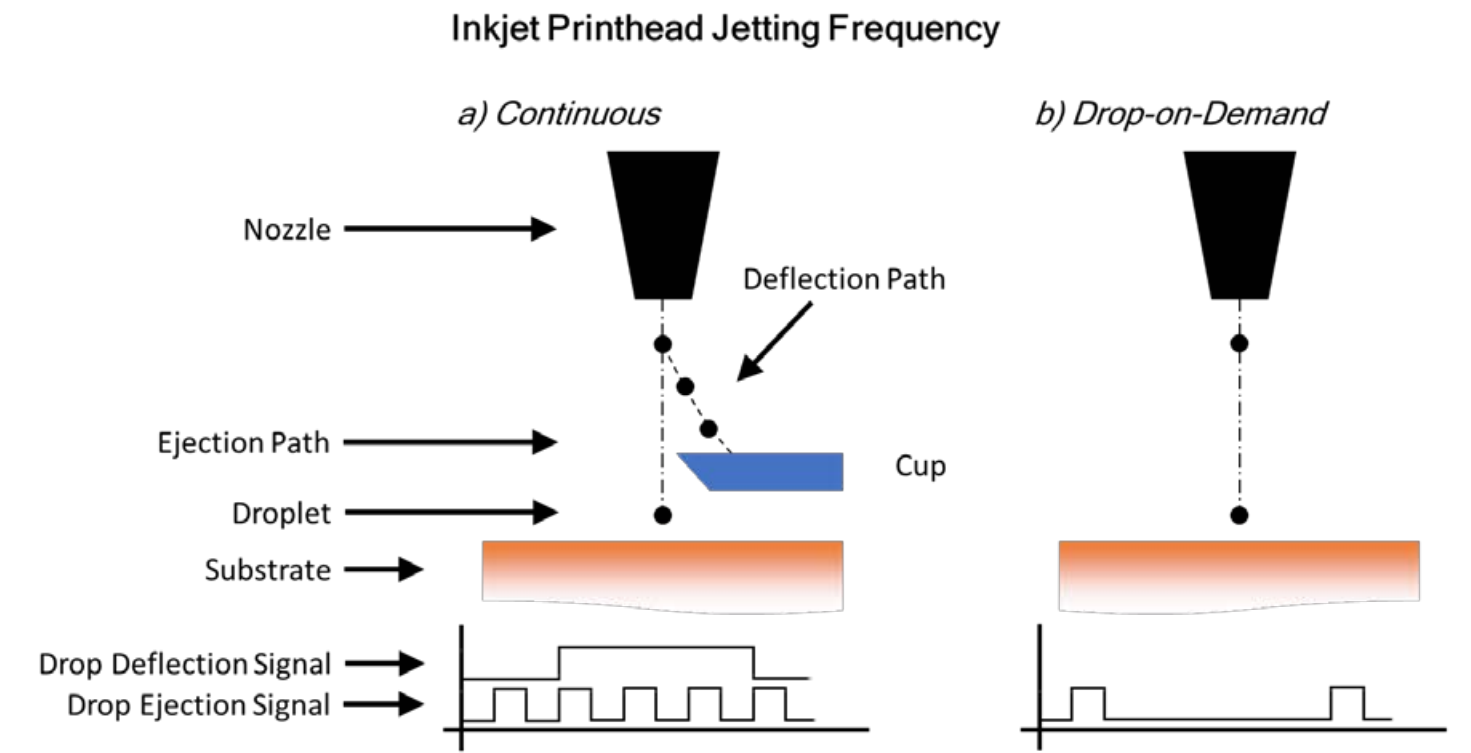
#### B. Jetting Frequency
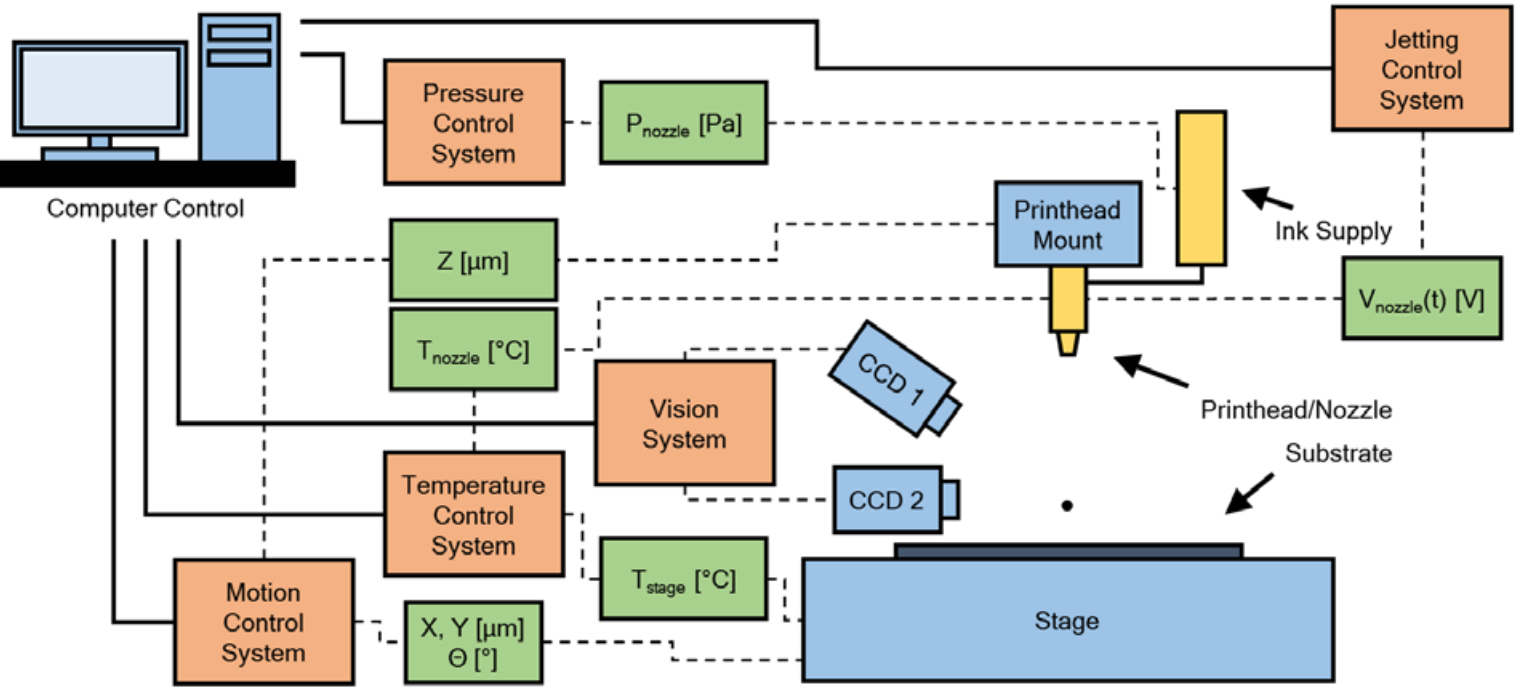
### Components of Inkjet Printer Systems
Block diagram of components of a fixed printhead inkjet printer. Blue blocks
represent physical hardware, orange blocks represent control and vision systems, and green
blocks represent the physical control system parameters.
Two early developed methods for applying inkjet printing for freeform fabrication are provided in patents from <b><a href="https://patents.google.com/patent/US5140937"> Brother Industries </a></b>and from <b><a href="https://patents.google.com/patent/US5260009"> Texas Instruments </a></b>.
The Brother patents describe an AM device,which uses an inkjet head to propel droplets of liquid thermoset resin (epoxy, melamine, or urea based) against a heated support. In a subsequent patent, a two-component thermosetting resin is described with the curing agent held within microcapsules.
In the Texas Instrument patents, the inkjet head is hot and the substrate is cold. The part is built from a wax, which is solid at ambient temperature and of sufficiently low viscosity at 70°C to form small droplets.
A second watersoluble material is jetted on top of the wax to fill the unprinted regions and support subsequent layers. While in the first case heat is used to cross-link and in the latter to induce flow, both AM methods can be considered forms of thermal inkjet printing.
3D inkjet printing with wax has been further developed (notably by <a = href="https://www.solidscape.com/products/3d-materials/Solidscape">Solidscape </a>) principally for wax and investment casting of metals.
### Parts
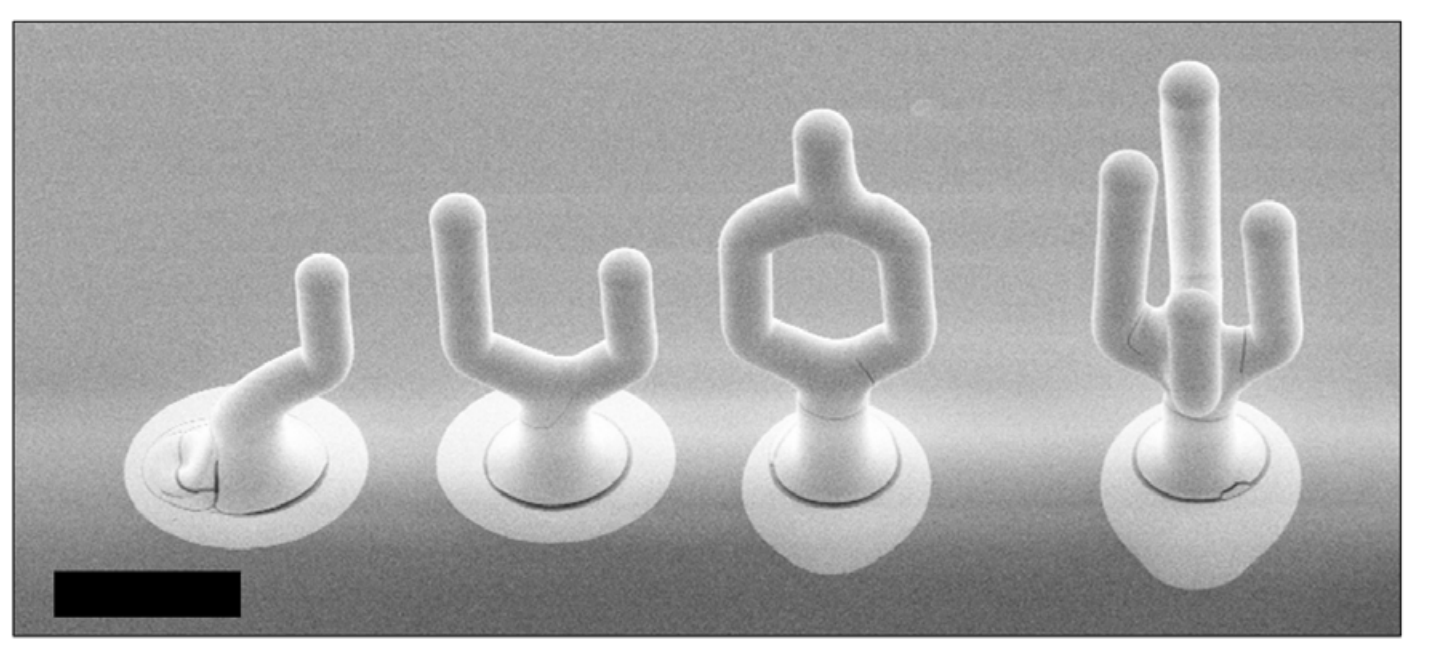
Scale Bar: 200 μm
<ul>
<li> <b>Solidscape</b>: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7jXrt8_54_I
</ul>
## Inkjet-based Lithography (The Polyjet Process)
Combining the benefits of lithographic methods (high feature resolution and good surface quality) with the advantages of material jetting (high build speed and large build volume), the two leading AM device producers (Stratasys and 3D Systems) have both developed <b>inkjet lithographic 3D-printers </b>.
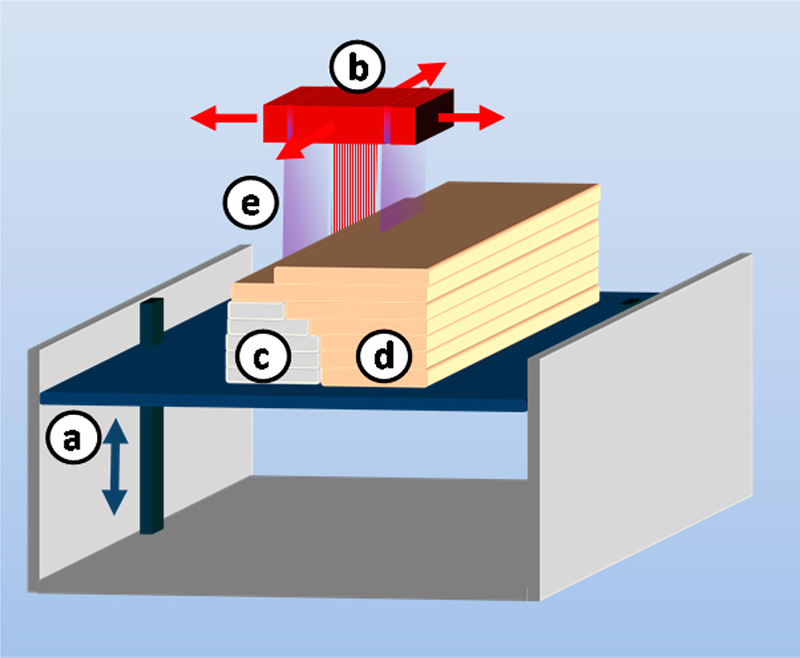
PolyJet process (from Stratasys) consisting of (a) vertically
movable building platform, (b) multinozzle inkjet head, (c) layers of
support material, (d) layers of building material, and (e) UV source
attached to inkjet head.
<a href ="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Cz7pKRcuTgs"> The Polyjet Process</a>
An inkjet head with several hundred nozzles is swept along the x-axis and in the process ejects small droplets of photopolymer. After deposition of one layer, a UV-lamp flash-cures the fresh layer and the process is repeated. In a typical setup, the inkjet head deposits two types of material: the building material and the support material. The support material is not part of the finished object but is required to support deposited build material in regions with voids or overhangs. In contrast to conventional stereolithography, where lightweight supports are only required in areas with severe overhangs, inkjet-based AM requires a completely dense support structure.
<b><a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vsYy8z_rOTg">The Evolution of Polyjet Materials</a></b>
## 3D Powder Binding Process (3DPB)
3DPPB comprised of (a) vertically movable build platform, (b) printed model embedded in supporting powder bed, (c) inkjet printing head for deposition of binder material, (d) support material feed stock, and (e) roller for powder distribution and leveling.

The key features of a 3DPB machine are a powder distribution unit, a vertically movable building platform, and the inkjet printing head enabling CAD-guided ink dispensing. In the first step, prior to layer solidification, a powder layer is deposited by moving the powder dispenser horizontally across the building platform. In the second step, the inkjet printing head dispenses a liquid, which bonds or fuses the particles together, thus forming a solid layer. In the third step, the building platform moves downward by one layer thickness to enable printing of the next layer. Residual powder particles remain on the building platform, serving as support during the print job, and upon completion they may be recovered and reused. The finished green body can be cleaned of residual adherent powder with pressurized air and then post processed by treatments such as sintering or resin infiltration, respectively.
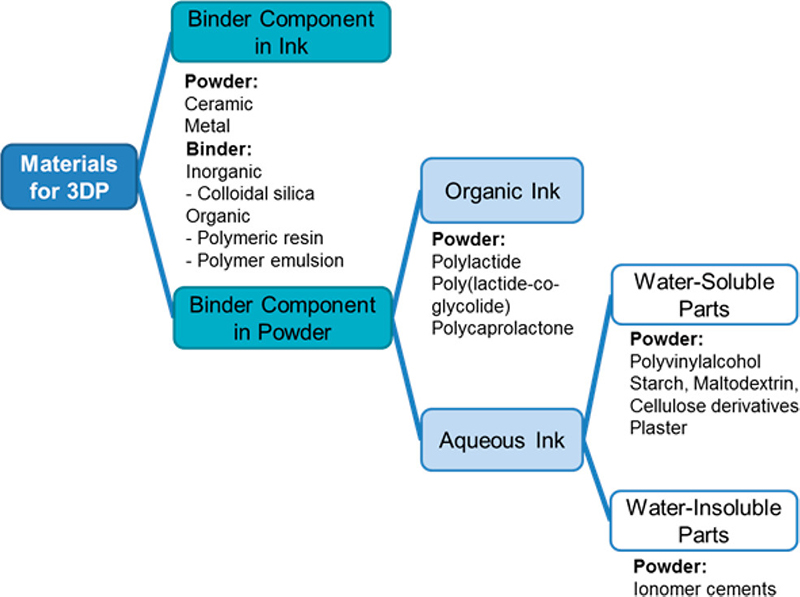
###Classification of powder/ink combinations used in 3DPB
<b><a href="https://www.desktopmetal.com/company/about/">Desktop Metal</a></b>
<b><a href = "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VXntl3ff5tc">HP Mulit-Jet Fusion Printers-1</a></b>
<b><a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DDeleRiIiQU">HP Multi-Jet Fusion-2</a></b>
<b><a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DDeleRiIiQU">ExOne Metal 3D Printers</a></b>
<b><a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TQgbMMw1GHo">Binder Jet M-Flex</a></b>