<br>
[MAS.865](../../) > [Additive](../index.html) > Selective Laser Sintering
## Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
###Underlying Mechanism
The principle design of selective laser sintering (SLS, 3D Systems) and laser sintering
(EOS) machines is very similar.
The sintering procedure:
<ul>
<li>powder deposition
<li>powder solidification
<li>Lowering of build platform by one layer thickness
<li>Repeat
</ul>

<b>Powder deposition</b>
<ul>
<li>blade (laser sintering) or roller (SLS)
<li>temperature-controlled process chamber - few degrees below the glass transition temperature of the powder
<ul>
<li>reduce processing time
<li>reduce the amount of thermally induced stresses during layered solidification
</ul>
<li>inert gas atmosphere
<li>loose powder particles remain on the build platform
<ul>
<li>complexity without implemention of support structures
<li>manufacturing of stacks of models
<li> looese poder can be reused
</ul>
</ul>
<b>Powder solidification</b>
<ul>
<li>laser source: 10.6 μm carbon dioxide
<li>laser radiation absorbance ==> local heating of powder particles
</ul>
### Historical development
<ul>
<li>1986: SLS development at University of Texas- Carl Deckard. Check the patent <a href='https://patents.google.com/patent/US4863538A/en'> <b>HERE!</b> </a>
<li>90s: SLS commercialization through DTM Corp.
<li>2001: <a href='https://www.3dsystems.com/3d-printers/plastic?gclid=EAIaIQobChMIqdj5_uPW2gIVA4xpCh2xVgmhEAAYASAAEgKvKPD_BwE#selective-laser-sintering-printers-sls'><b>3D Systems</b></a> buys DTM Corp.
<li> In parallel: <a href='https://www.eos.info/systems_solutions/metal/systems_equipment/eosint_m280'>EOS, Germany - Laser Sintering</a>
</ul>
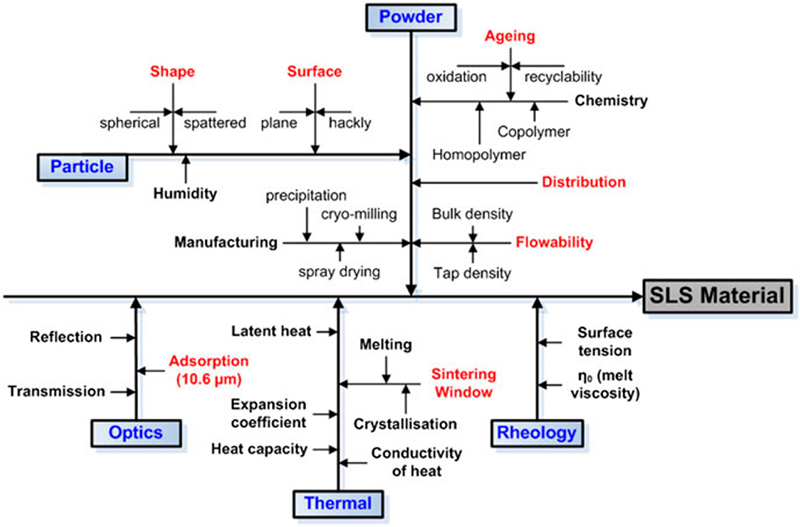
### Part Porperties, Pros & Cons
<ul>
<li>wide range of thermoplastics - durable enough for applications wityh mechanical loads

<li>resolution & surface roughness = f (particle size) | ~ 100 μm
<li>warpage or breakage due to relaxation of thermally induced stresses
<li>porosity level (amount of free volume) = f(material, particle powder distribution, process parameters)
<li>lightweight
</ul>
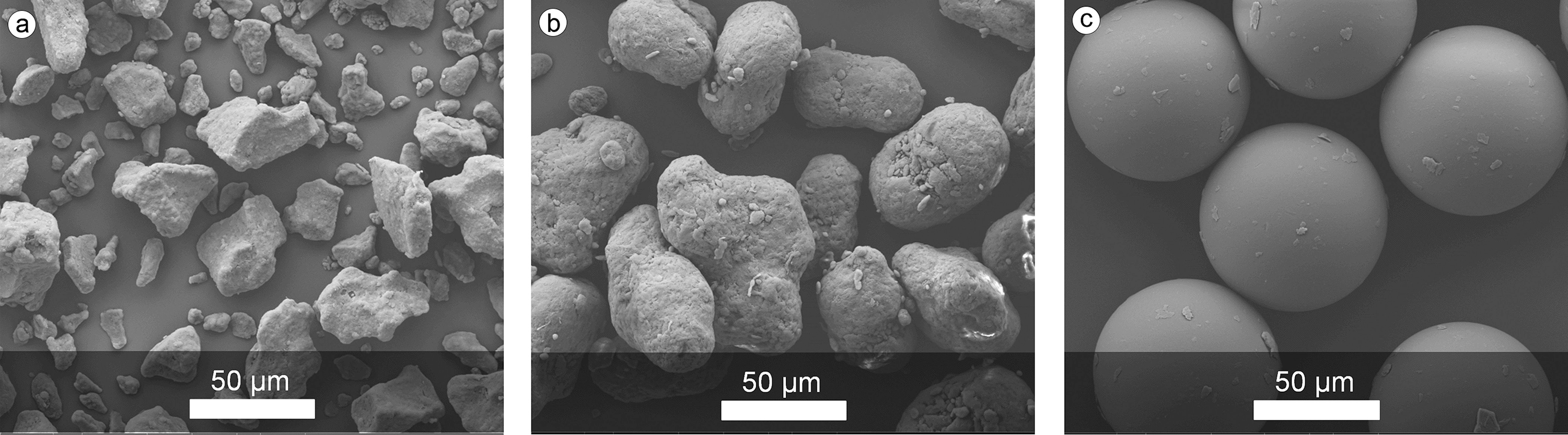
Morphology of commercial powders for polymer laser sintering. (a) Cryogenically ground, rough particles (PA-11 powder PA1101 from EOS GmbH); (b) potato-shaped particles precipitated from ethanol solution (PA-12 powder PA2200 from EOS GmbH); and (c) spherical particles produced by means of emulsion polymerization (PS powder PrimeCast 101 from EOS GmbH).

### Materials for SLS
Classification of materials for SLS additive manufacturing (a) according to inorganic or polymeric content; and (b) according to the so called pyramid of polymeric materials.

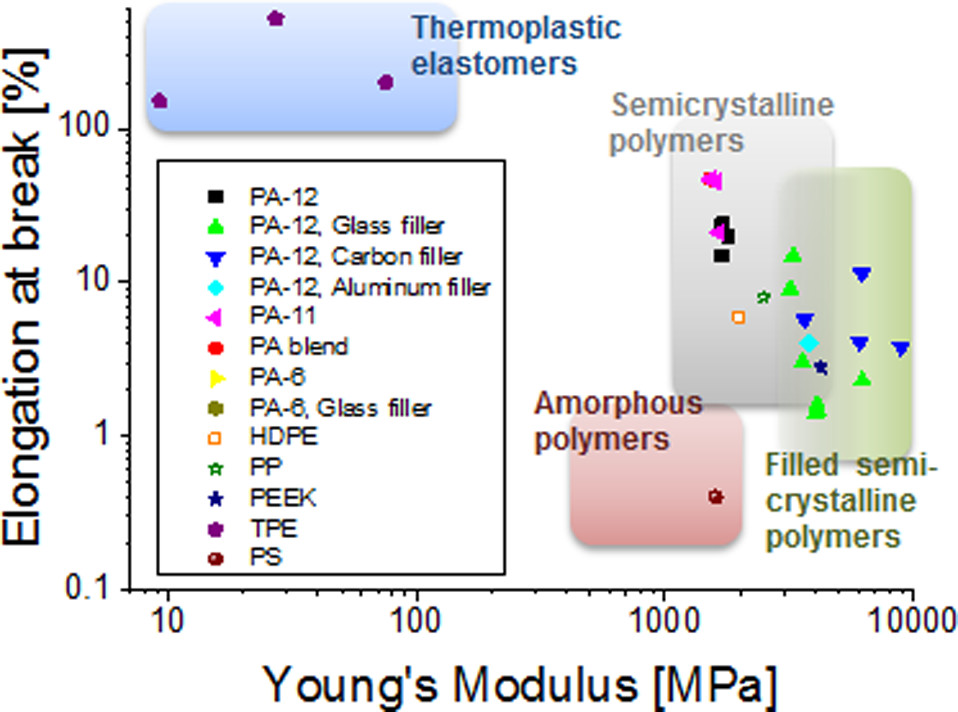
Stiffness/toughness-balance of commercial SLS materials. Mechanical properties (Young’s modulus and elongation at break) are based on technical information provided by the respective material suppliers.
### Desktop & DIY Systems
<ul>
<li> <a href = 'https://www.sinterit.com/'>Desktop SLS - Sinterit </a>
<li> <a href = 'https://sintratec.com/products/s1'> Desktop SLS - Sintratec </a>
<li> <a href = 'https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IrFYt3uUdrI'> Desktop SLS | Formlabs - Fuse 1 </a>
<li> <a href = 'https://formlabs.com/3d-printers/fuse-1/'> Desktop SLS | Fuse 1
<li> <a href = 'http://www.instructables.com/id/DIY-SLS-3D-Printer/'> DIY SLS - 1 </a>
<li> <a href = 'https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:33697'> DIY SLS - 2 </a>
<li> <a href = 'http://reprap.org/wiki/OpenSLS'> Open SLS - RepRap </a>
<li> <a href = 'http://pwdr.github.io/'> PWDR </a>
</ul>