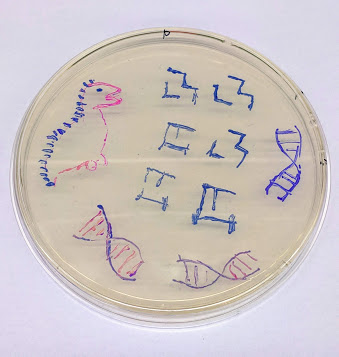
Next Generation Synthesis
Week 4
Next Gen Synthesis
Background of this Experiment (HTTGA)
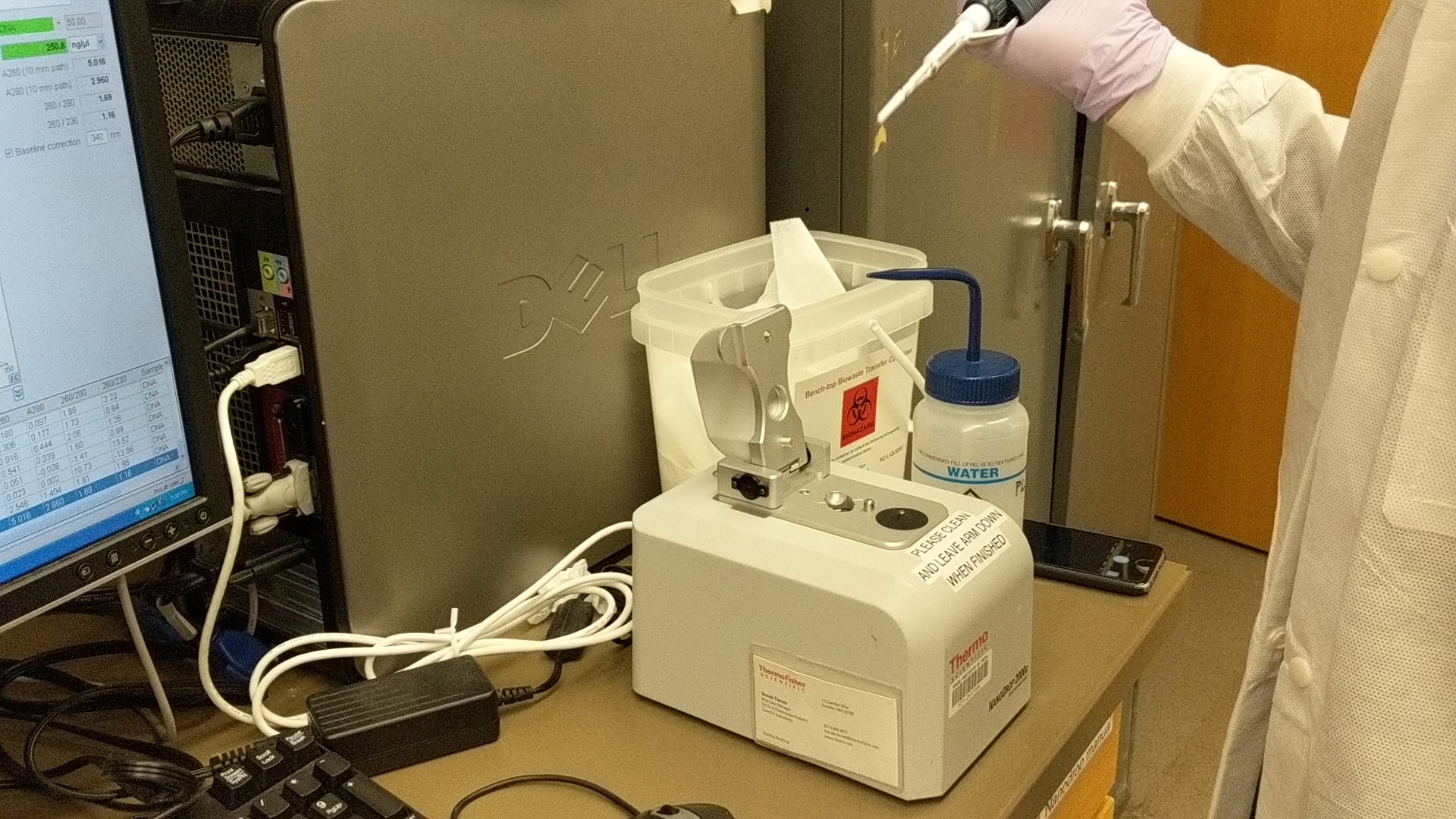
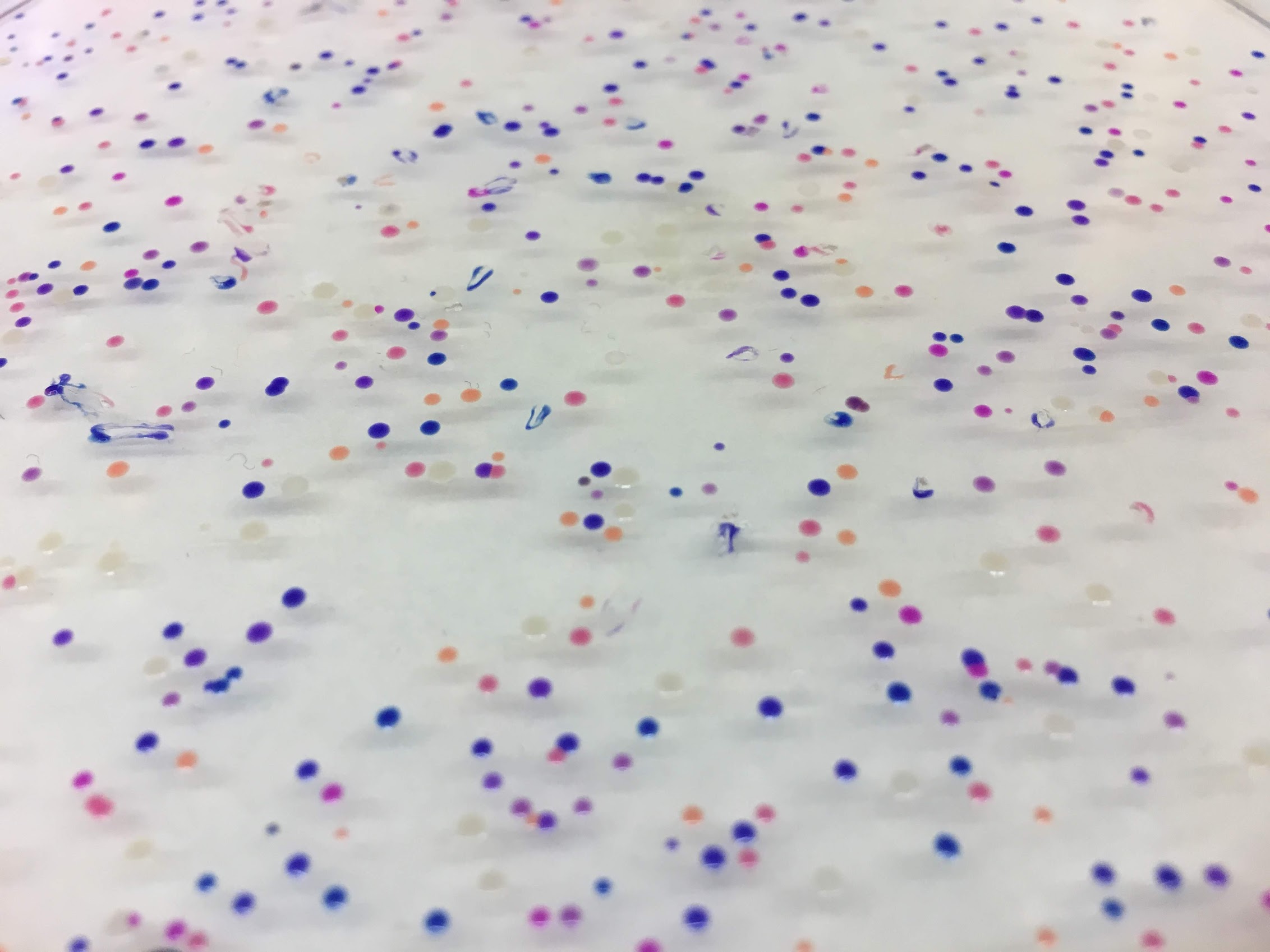
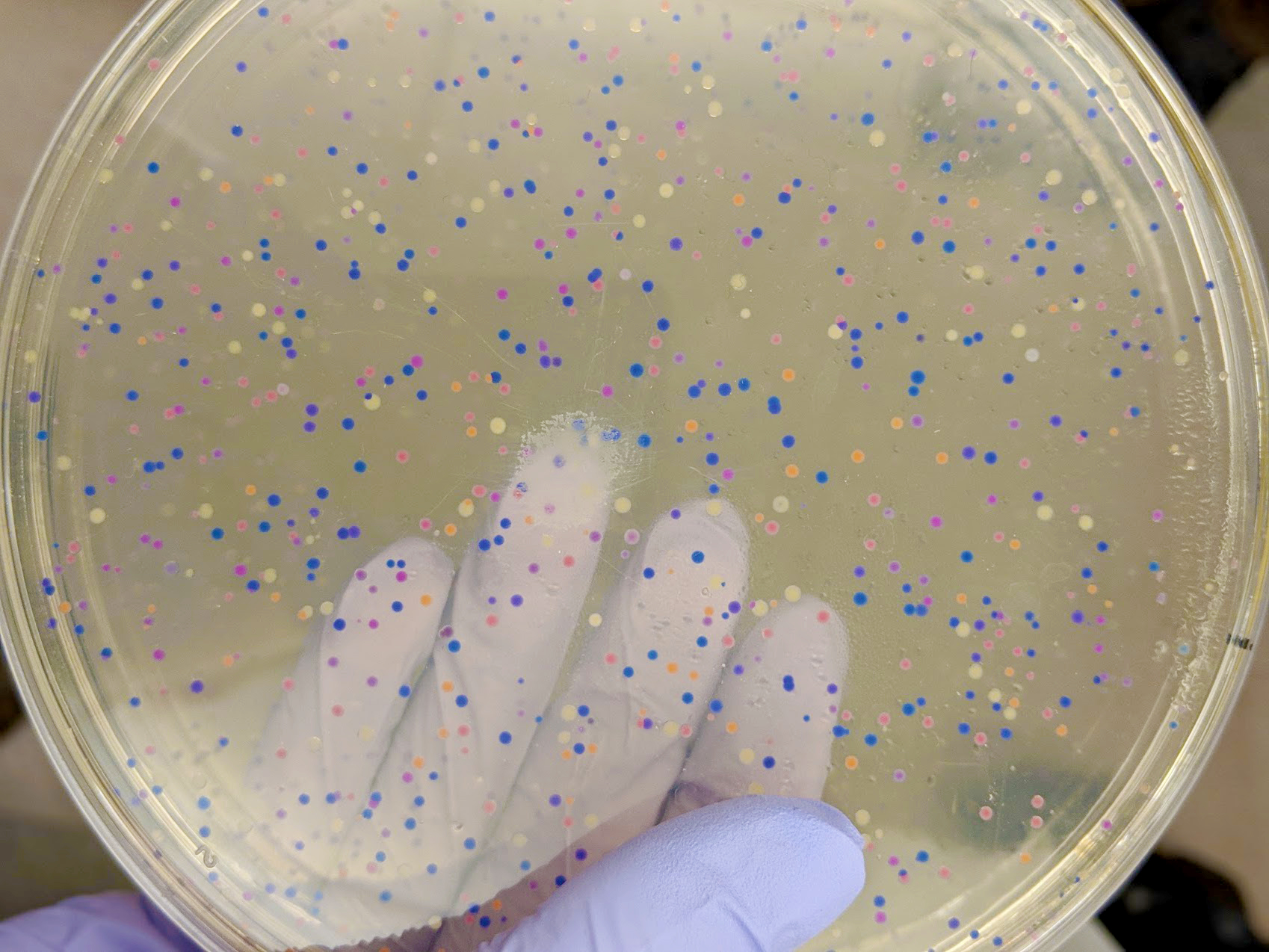
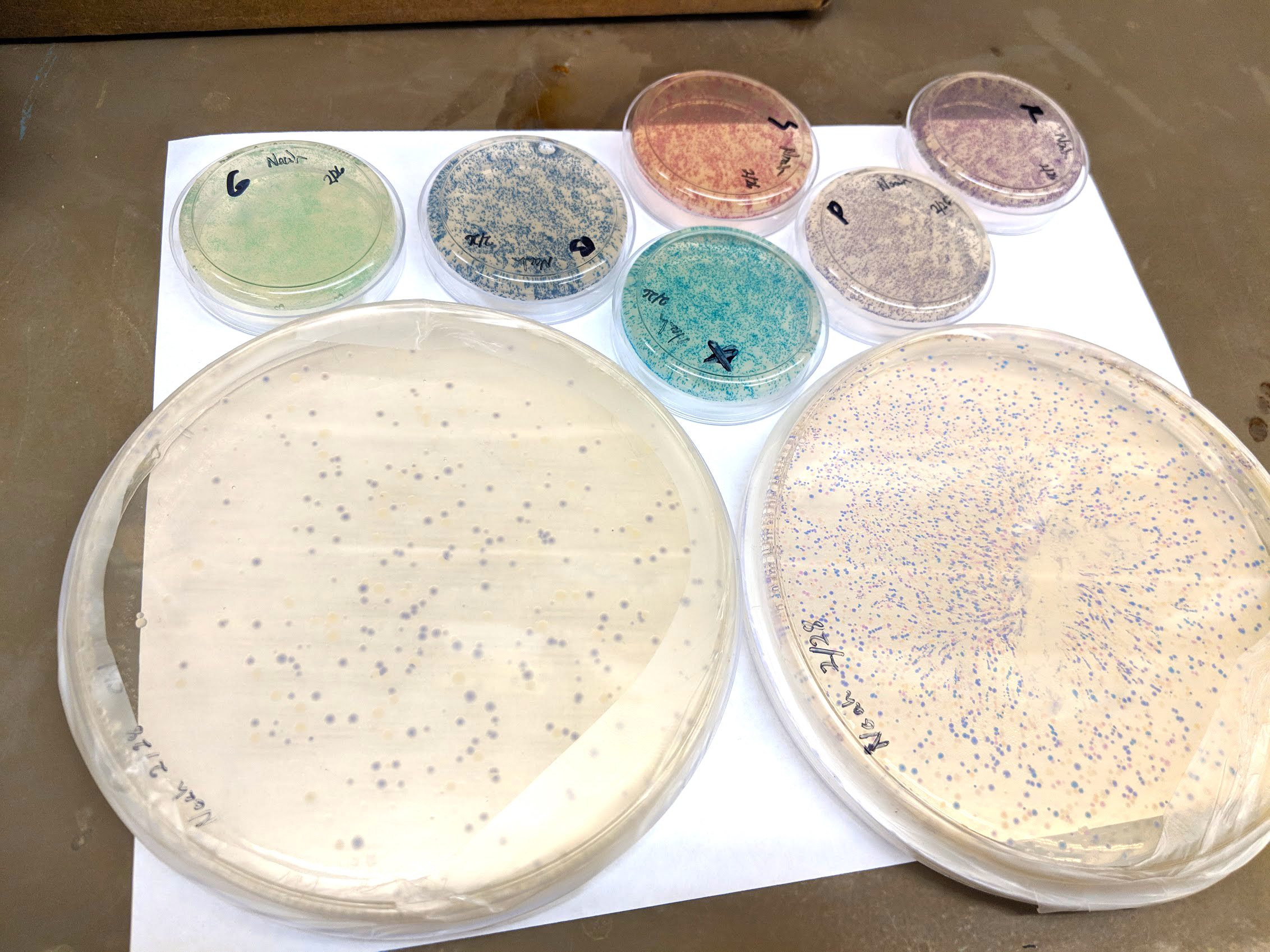
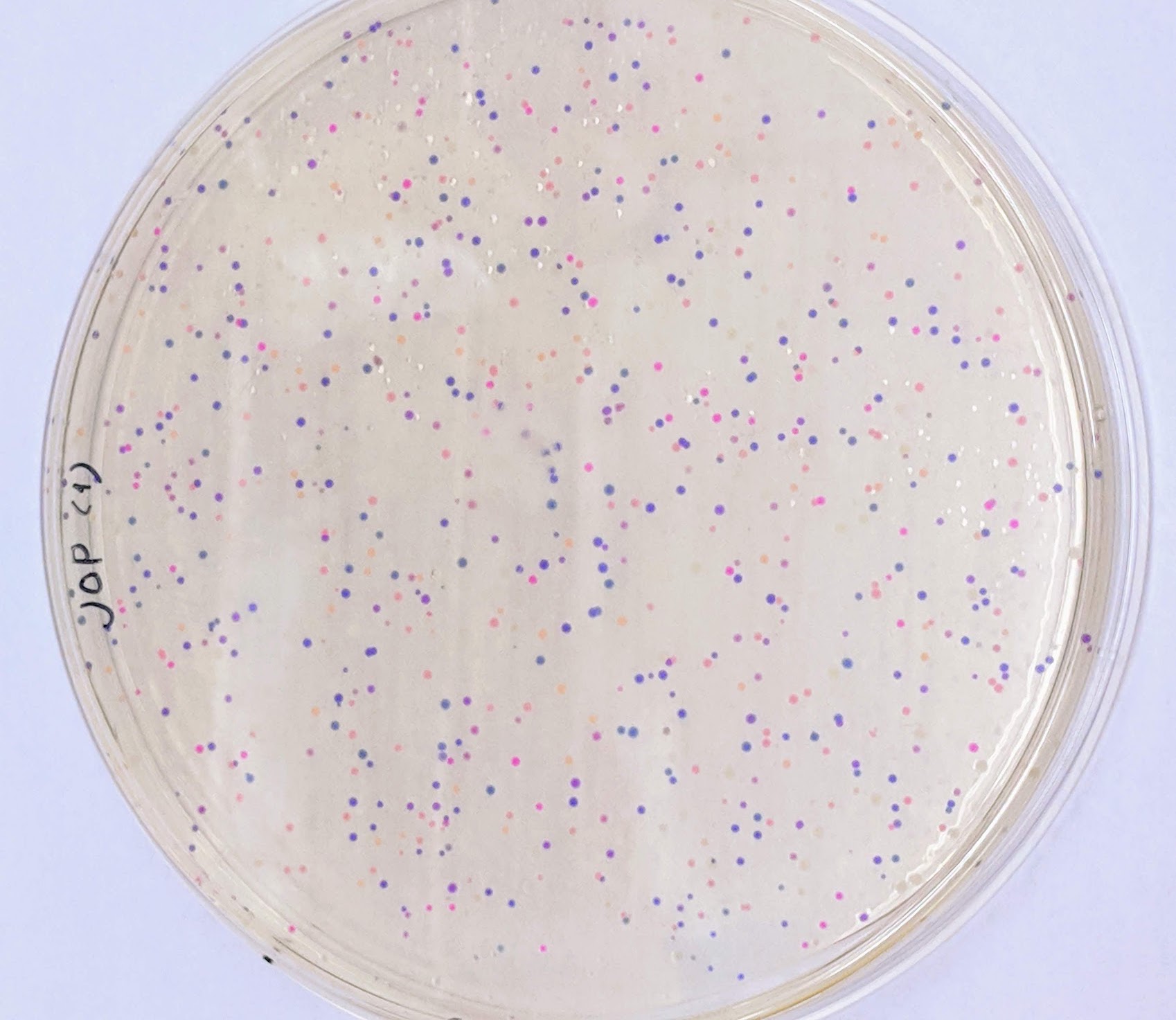
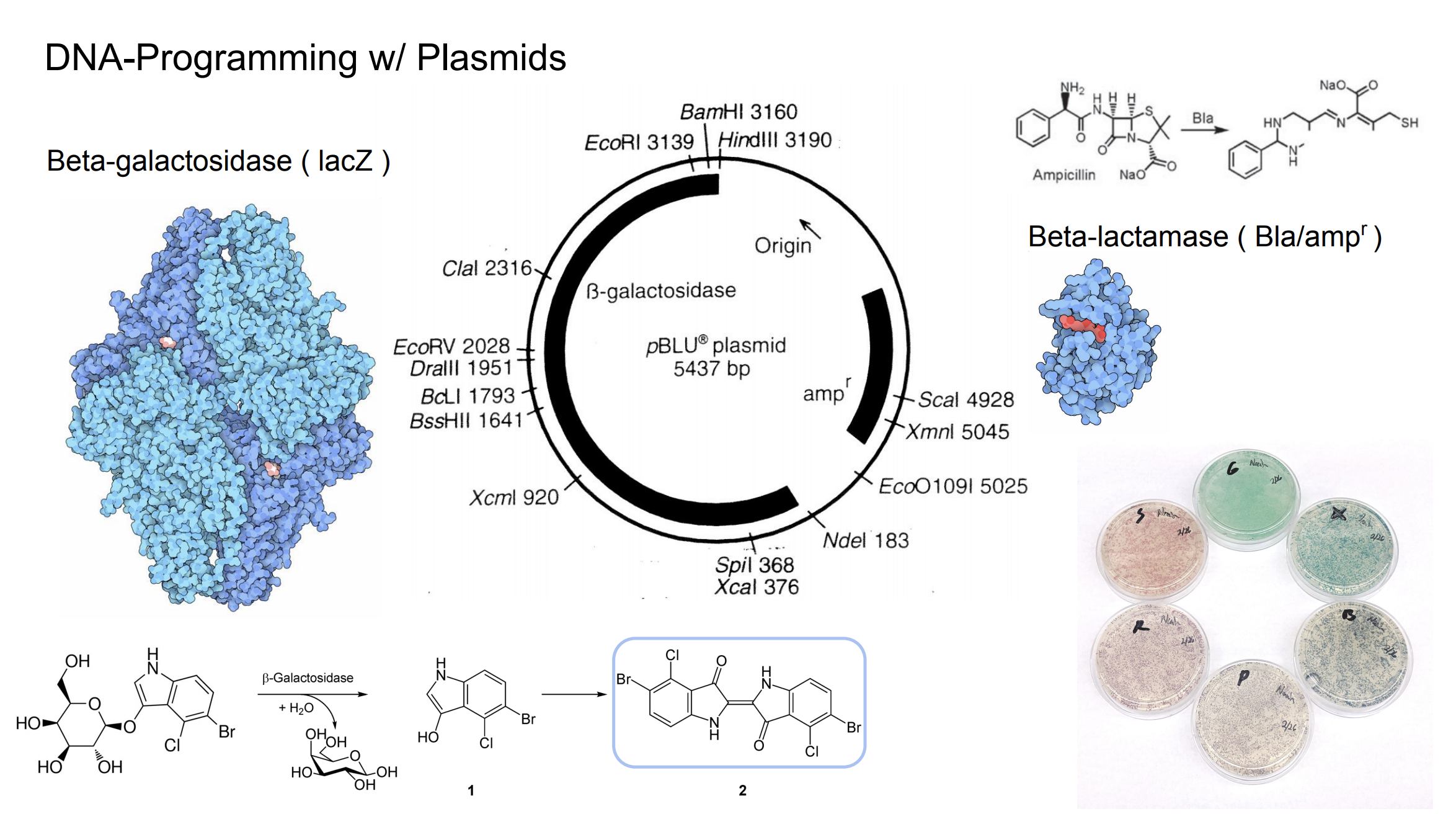
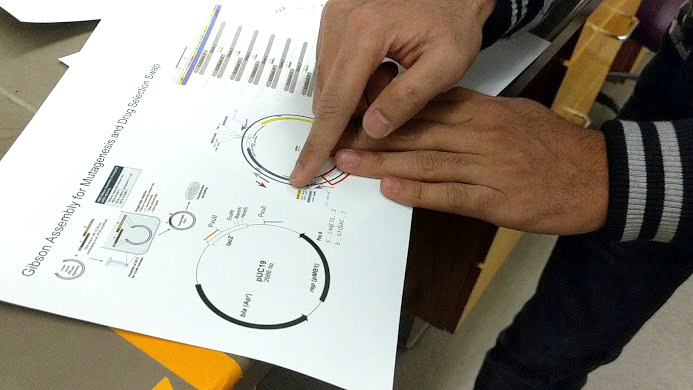
http://fab.cba.mit.edu/classes/S66.19/S66.19/assignments/nextgensynth.htmlWe will be changing the color-generating chromophore of the purple Acropora millepora chromoprotein (amilCP) to a variety of orange, pink, and blue mutants. These divergently-colored genetic variants of amilCP were described by Liljeruhm et al in 2018. Their strategy to identify where to mutate amilCP was inferred by sequence similarities to the chromophore region that allows for spectral engineering of the structurally-characterized and well-known green fluorescent protein (GFP), which is native to the jellyfish Aequorea victoria. First we will prepare for a Gibson assembly by using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to produce two sets of amplicons as inserts and a restriction digest of the common cloning plasmid pUC19 to produce a new backbone (i.e. origin of replication and drug resistance gene). As template, both reactions use the amilCP-encoding plasmid that was miniprepped from the Addgene mUAV sample (deposited by the Nakayama lab at the University of Edinburgh and related to their paper on Mobius Assembly via a Mobius Assembly Universal Acceptor Vector). One set of amplicons copy the region of the amilCP gene that precedes the chromophore, including the transcription promoter and translation ribosome-binding site (RBS). Another set amplicons copy the region that spans 24 basepairs before the chromophore to just beyond the gene's transcription terminators. The latter includes a diversified chromophore-coding segment dictated by mismatches in the PCR primers with respect to the mUAV DNA template. The amplicon sets both include one end that overlaps by 20-22 bases with distinct ends of the large backbone fragment from the pUC19 digest. Lastly, we will express our colorful variety of amilCP mutants in chemically competent E coli cell.
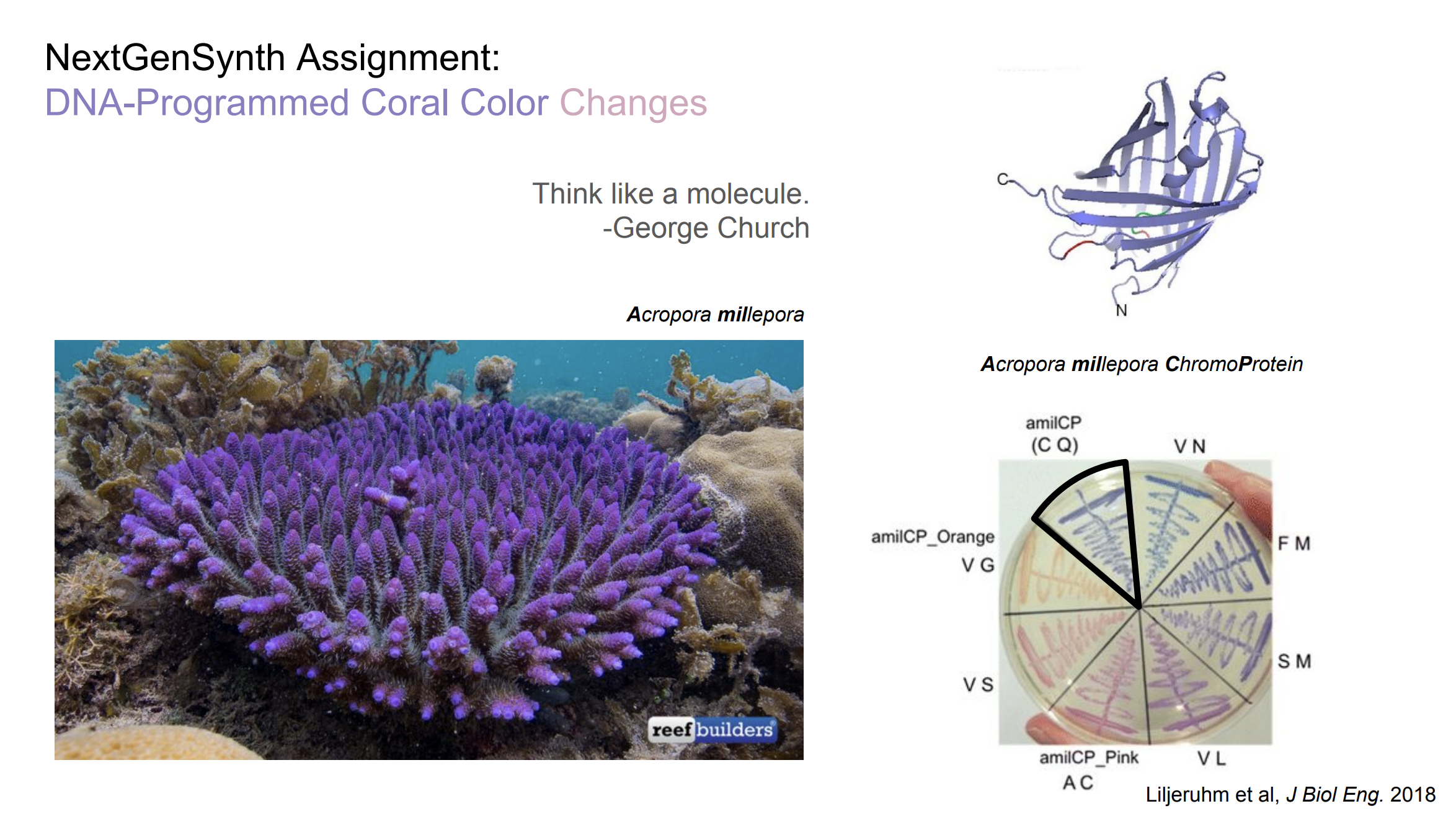
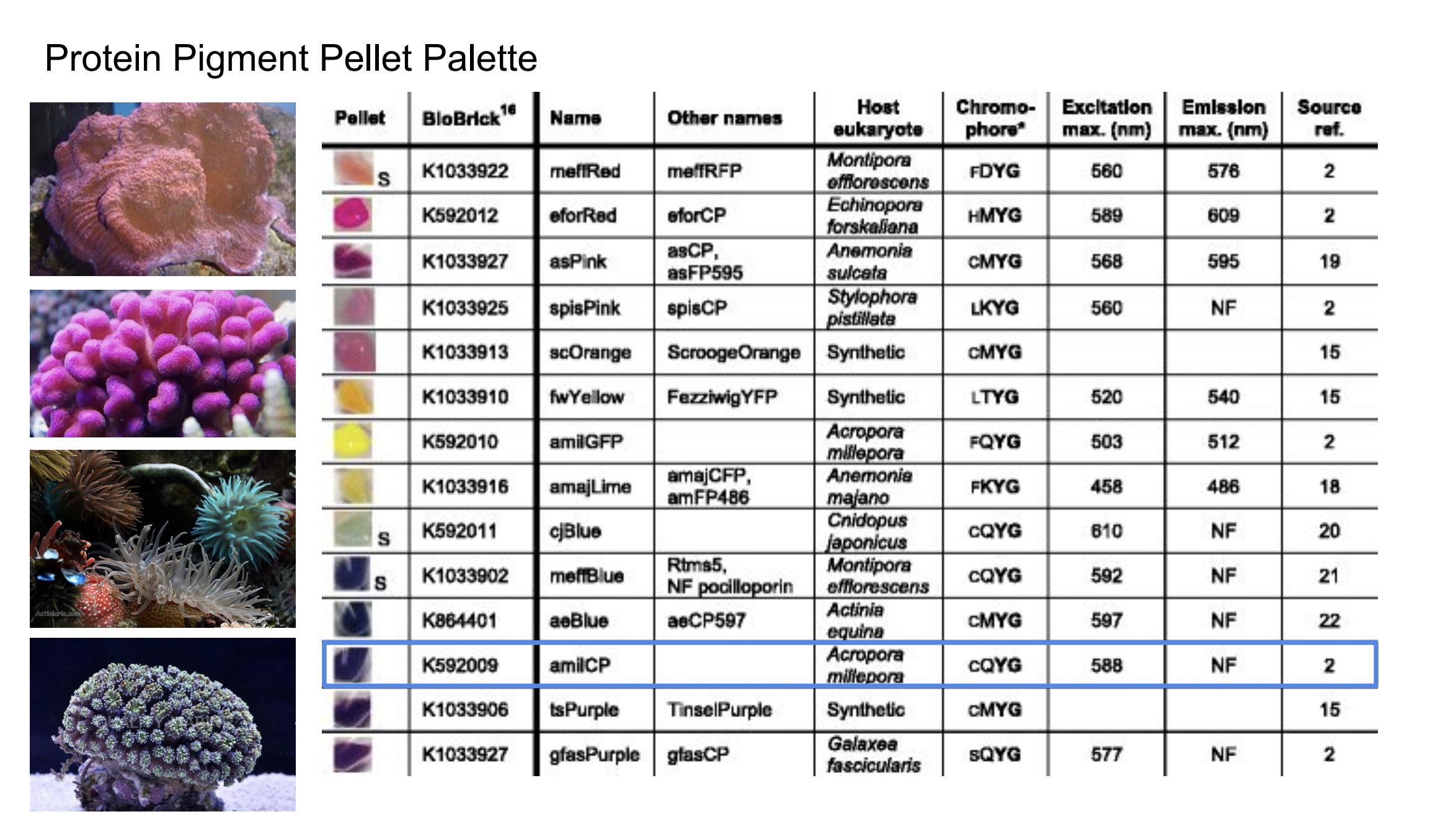
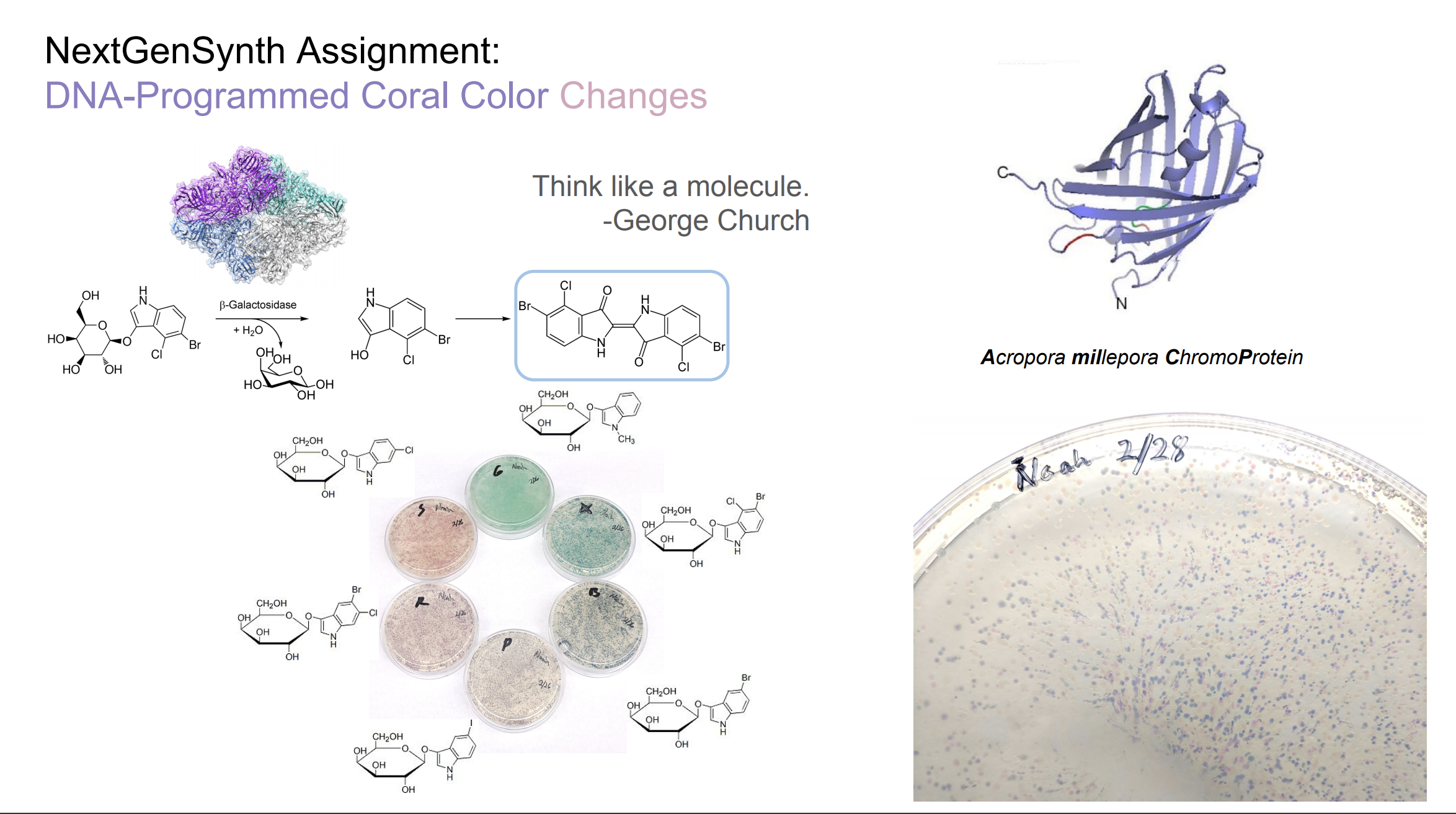
These uniquely shaded hereditary variations of amilCP were depicted by Liljeruhm et al in 2018. Their methodology to distinguish where to change amilCP was surmised by succession likenesses to the chromophore area that takes into consideration phantom building of the fundamentally portrayed and surely understood green fluorescent protein (GFP), which is local to the jellyfish Aequorea victoria.
First we will get ready for a Gibson get together by utilizing polymerase chain response (PCR) to deliver two arrangements of amplicons as supplements and a limitation overview of the normal cloning plasmid pUC19 to create another spine (for example root of replication and medication obstruction quality). As layout, the two responses utilize the amilCP-encoding plasmid that was miniprepped from the Addgene mUAV test (stored by the Nakayama lab at the University of Edinburgh and identified with their paper on Mobius Assembly by means of a Mobius Assembly Universal Acceptor Vector). One lot of amplicons duplicate the locale of the amilCP quality that goes before the chromophore, including the interpretation advertiser and interpretation ribosome-restricting site (RBS). Another set amplicons duplicate the locale that traverses 24 basepairs before the chromophore to simply past the quality's translation eliminators. The last incorporates a differentiated chromophore-coding fragment managed by jumbles in the PCR groundworks as for the mUAV DNA format. The amplicon sets both incorporate one end that covers by 20-22 bases with unmistakable finishes of the huge spine part from the pUC19 digest. In conclusion, we will express our beautiful assortment of amilCP freaks in synthetically equipped E coli cell.


In this experiment, we alter the shading producing chromophore of the purple Acropora millepora chromoprotein (amilCP) to an assortment of orange, pink, and blue freaks.