Basics of Networking
Why Networking
- modularity: make the break out boards and test it separately
- running the components in the different environment(e.g. high noise motor and low current component)
- serial bus
- limitaiton: flash each nodes separatley
- each node have transmit receive and transmit send. make packet and each node stripe up bytes in the packet of node.
- I2C
- scl(clock) tells when to read the data
- SDA
- SPI
- Main & Secondary
- clock line for synchronise and seocnd line for communication
- faster
- SD memory card
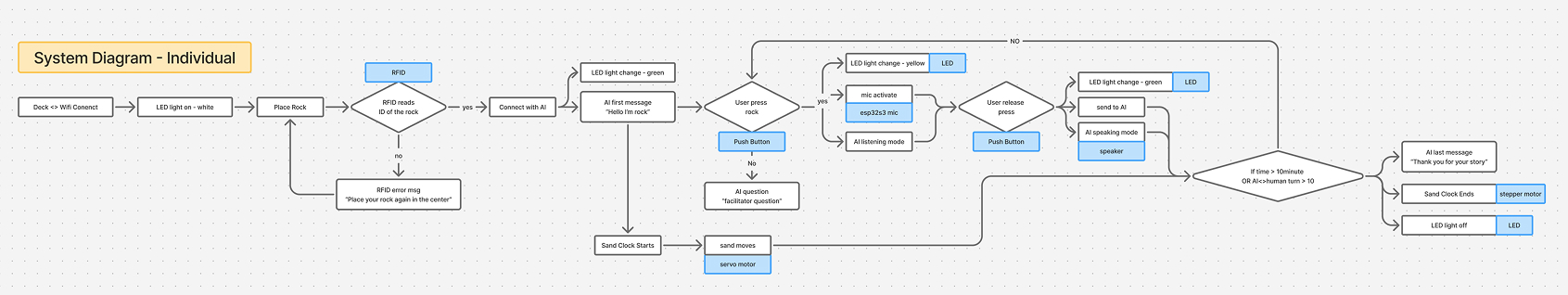
System Diagram
Wifi Networking
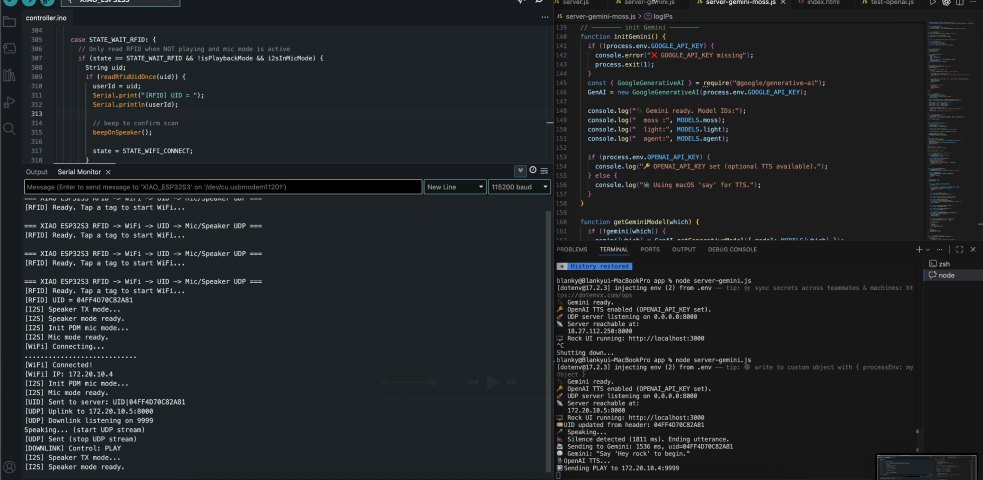
WiFi Connection with ESP32-S3
I used the XIAO ESP32-S3 board to establish WiFi connectivity for my interactive rock system. The implementation uses the standard WiFiClient library for ESP32.
WiFi Setup Process
- Configuration: WiFi credentials are stored in a separate
secret.hfile for security - Connection Method: Using
WiFi.begin(ssid, password)to connect to the network - Connection Monitoring: Implemented connection status checks with LED indicators and serial output
Network Challenges & Solutions
The ESP32-S3 had difficulty connecting to the lab's WiFi network. To resolve this issue, I switched to using a mobile hotspot as the access point, which provided more stable connectivity for the project.
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nWiFi connected");
Serial.println("IP address: " + WiFi.localIP().toString());RFID Tag Reading & Processing
RFID-RC522 Module Integration
I used the MFRC522 RFID reader connected via SPI to detect and read unique rock identifiers. Each rock is embedded with an RFID tag that triggers different AI personalities.
Hardware Setup
- SPI Connection: SS_PIN (D2), RST_PIN (D3)
- Library: MFRC522 by GithubCommunity
- Tag Type: MIFARE Classic 1KB cards
Tag Reading Process
- Detection: Continuously checks for new RFID cards using
mfrc522.PICC_IsNewCardPresent() - UID Extraction: Reads the unique identifier from the card
- Conversion: Converts UID bytes to a hexadecimal string format
- Mapping: Matches the UID to specific rock personalities (Wise Rock, Playful Rock, Sarcastic Rock)
String getRFIDTag() {
if (!mfrc522.PICC_IsNewCardPresent() || !mfrc522.PICC_ReadCardSerial()) {
return "";
}
String uid = "";
for (byte i = 0; i < mfrc522.uid.size; i++) {
uid += String(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i] < 0x10 ? "0" : "");
uid += String(mfrc522.uid.uidByte[i], HEX);
}
uid.toUpperCase();
return uid;
}Rock Personality Assignment
Each RFID tag triggers a different system prompt for the AI:
- Tag 1: Wise Rock - Philosophical and contemplative responses
- Tag 2: Playful Rock - Fun and energetic personality
- Tag 3: Sarcastic Rock - Witty and humorous interactions
AI API Integration
Gemini API Connection
I integrated Google's Gemini API to generate contextual responses based on the detected rock personality and user input.
API Implementation
- Endpoint:
https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-1.5-flash:generateContent - Method: HTTP POST requests with JSON payload
- Authentication: API key stored securely in
secret.h - Client: WiFiClientSecure for HTTPS connections
Request Structure
String payload = "{\"contents\":[{\"parts\":[{\"text\":\"" + prompt + "\"}]}]}";
HTTPClient https;
https.begin(client, geminiEndpoint + "?key=" + GEMINI_API_KEY);
https.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json");
int httpCode = https.POST(payload);Response Processing
The JSON response is parsed to extract the AI-generated text, which is then sent to the TTS service.
OpenAI Text-to-Speech Integration
I used OpenAI's TTS API to convert the AI responses into natural-sounding speech, giving each rock a voice.
TTS Configuration
- Model: tts-1 (faster inference)
- Voice: "alloy" voice for consistent personality
- Format: Audio streamed directly to DFPlayer Mini for playback
- Endpoint:
https://api.openai.com/v1/audio/speech
Audio Processing Pipeline
- Send text response to OpenAI TTS API
- Receive audio stream in real-time
- Buffer and play through DFPlayer Mini connected speaker
- Visual feedback via LED during speech
HTTPClient https;
https.begin(client, "https://api.openai.com/v1/audio/speech");
https.addHeader("Authorization", "Bearer " + String(OPENAI_API_KEY));
https.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json");
String ttsPayload = "{\"model\":\"tts-1\",\"input\":\"" + text + "\",\"voice\":\"alloy\"}";
int httpCode = https.POST(ttsPayload);Complete Workflow
The networking system follows this sequence:
- User places rock with RFID tag on reader
- ESP32 reads tag UID and determines personality
- User speaks question (captured via microphone)
- Question + personality prompt sent to Gemini API over WiFi
- AI response received and forwarded to OpenAI TTS
- Audio stream played back through speaker