Sustainability
- Four pillars: Human, Social, Economic, Environmental
- Sustainability and Sustainable development
Circular Economy
A model of resource production and consumption to go from linear wasteful economies to restorative and regenerative economies.
- Core principles: Reduce, reuse, recycle, recover
- Aims: sustainable development, economic prosperity, environmental quality and social equity
- Enablers: business models, consumer involvement, government, institutions
Can we cycle valuable metals, polymers, alloys, etc. so that they maintain their quality and continue to be useful beyond the shelf life of individual products?
Can goods of today become the resources of tomorrow?
- butterfly diagram
- Technical cycle
- Reuse (e.g. disassembly and reuse of parts)
- Physical transformation (e.g., reshaping plastics)
- Chemical transformation (e.g., depolymerization of plastics, pyrolysis, gasification)
- Biological cycle
- extraction
- decomposition
- regeneration
- Technical cycle
Circular Design methods
Circular design explanation (Video)
Circular design refers to a strategic approach aimed at developing products and services for the circular economy.
- Circular design methods (Ellen Macarthur Foundation)
- understand -> define -> make -> release
- Understand how to design for circular flows
- Define clearly the challenge or problem to solve
- Create or implement a working concept or prototype
- Release the project and ensure it is useful as long as possible
- understand -> define -> make -> release
| Understand | Define | Make | Release |
|---|---|---|---|
| circular flows: restorative and regenerative design | Identify circular opportunities | user-focused research research | product journey mapping with longevity in mind |
| regenerative thinking: local production networks | start small and then scale | circular brainstorming | create an aligned narrative with stakeholders |
| learning digital systems and processes | build collaborative teams | measure impact within the system | iterate design |
| inside-out (understand materials that go into products) | develop strategies to engage with stakeholders | Continuous learning: Embed feedback | |
| get inspired from nature | consider business models | understand and breakdown material choices | |
| create a brand promise | test concepts with rapid prototyping concept | ||
- Resource pressure Method: Uses six design parameters to design circular projects. Material required, product lifetime (frequency of replacement), material loss (in manufacturing), primary material content (demand for extracted resources), recyclability/reuse, cascadability (extending material utility)
- Circular design frameworks : 5 strategies - (1) circular supplies focused (prioritises biological cycles), (2) resource conservation focused (preventative, minimal resources), (3) cycle focused (design aimed at circulation of materials), (4) long life use focused (design aimed for reuse, repair) and (5) whole systems designs for value creation (innovative solutions combining all other strategies)
FabCity
The Fab City movement has set itself the goal of producing almost everything that is consumed in the city by 2054.
-
Fab City Full Stack, see also this article
- The Fab City Full Stack. Credit: Tomas Diez and Zoe Tzika, Fab City Foundation
- Layer 1 - Developing infrastructure and technologies for local production
- Layer 2 - Enabling new forms of learning
- Layer 3 - Incubating value-generating projects
- Layer 4 - Orchestrating efforts between local communities and initiatives
- Layer 5 - Prototyping place-based interventions
- Layer 6 - Applying bioregional strategies
- Layer 7 - Sharing knowledge with global networks
-
- Interfacer Platform (Video)
- digital product passports
- EU DPP commission initative
- Track and tracing
- Supply chain visibility
- Full lifecycle monitoring
- Better compliance
-
Challenges
- Supply chains
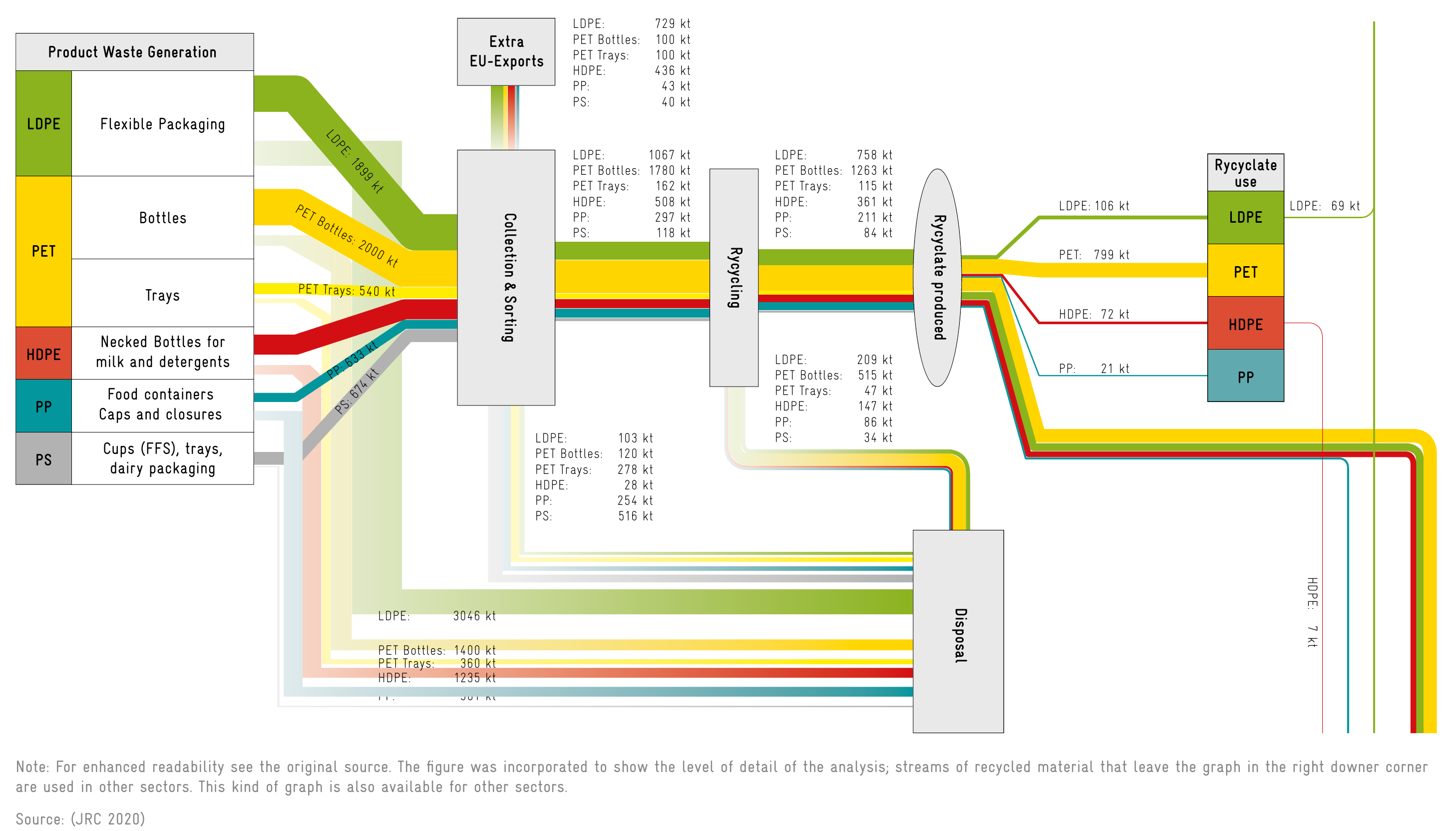
- Indicators
- Measuring flows
- Material flow analysis
Open Source Hardware
Documentation
-
Design for repair and replicability
-
Documenting
-
Assembly manuals
-
Gitbuilding (Open Flexure Microscope)
-
OSH-autodoc (inspired by Daniele Ingrassia's Fabulaser Mini Manual by Marc Kohlen and Liane Honda)
-
lego
-
-
Reusing parts
-
Read the docs
Repairability
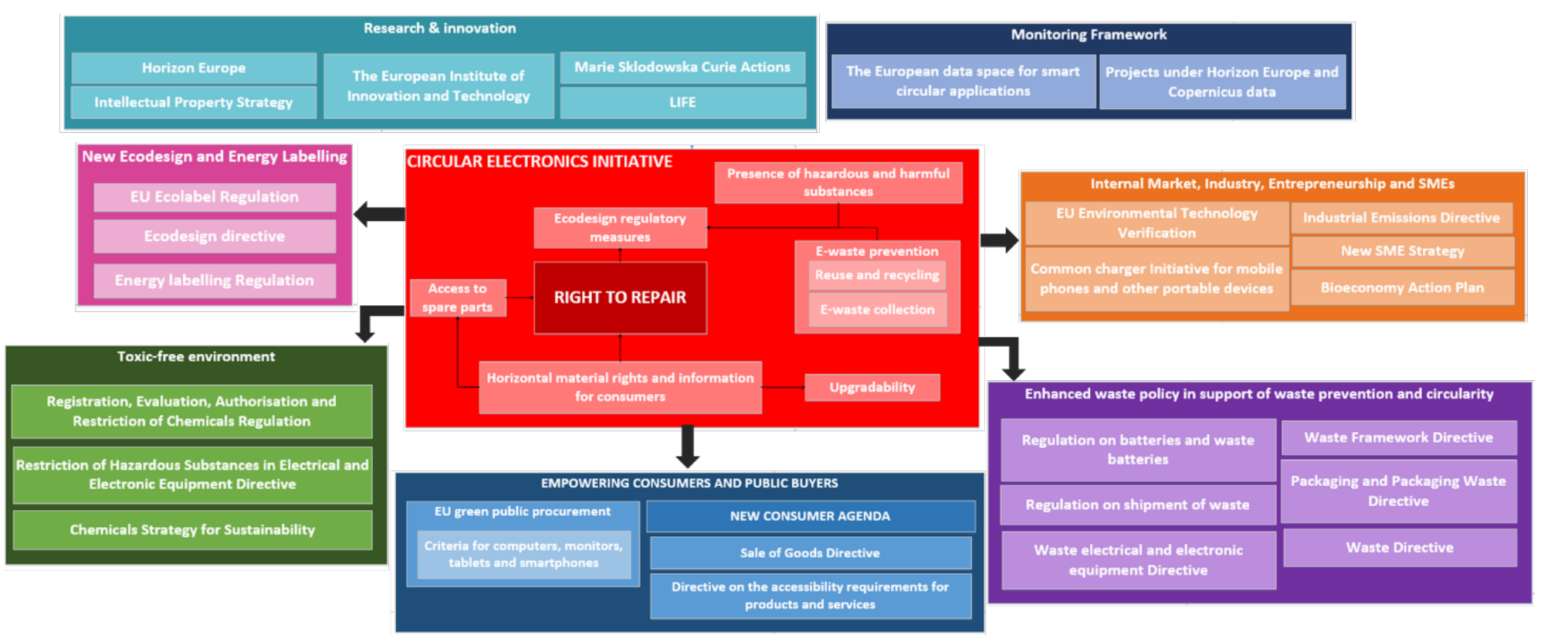
- Right to repair movement
Right to repair landscape in the EU (source: Towards an effective right to repair)
-
Environmental impact of electronic products (at diffent life cycle stages)
- mining and production of raw materials
- processing, assembly and transport
- use (e.g. lifespan, energy efficiency)
- end-of-life (collection, disposal, recycling)
-
Active Disassembly: disassembling products into their separate components
- Active disassembly using smart materials (ADSM)
- Use of smart materials in order to change shape or size and facilitate the release of parts.
- Shape memory alloys
- Shape memory polymers
- Active disassembly based on the shape memory effect of polymeric materials (video)
-
Design for disassembly DFDS (video)
- Fewer parts
- Pure material parts
- Removable batteries and circuits
- Modular design
- Joining methods:
- Standardised fasteners
- snap-click
- press-fit
Disposal methods
- Direct reuse (material reuse in existing form)
- Recovery (material purified to its original form for reuse)
- Recycle (material transformed into another substance)
- Fuel Blending (material substituted in place of virgin fuels)
- Treatment (Material is neutralised to allow for disposal)
- Incineration (Material is safely burned without energy recovery)
- Landfill (material is sent to an approved landfill)
Examples of sustainability of waste streams
| Waste | Disposal | Opportunity |
|---|---|---|
| Ammonium sulfate | Wastewater treatment (*) | fertilizer manufacturing |
| Metal plating waste | Landfill | Metal recovery |
| Calcium fluoride | Landfill (*) | Cement |
| Lithography solvents | Fuel blend (*) | Cyclohexanone recovery |
| Food Waste | Landfill | Soil conditioner |
Some Examples
SDG 6 Open call for water action
MNT reform: Modularity by design
Material sourcing
Plastic
Examples
- Material Database as open access
- machines, designs and marketplace for distributed plastic recycling and manufacturing
- modular design of headphones for higher repairability and modification
Resource Efficiency in Machine Tools
Modelling of Energy Profiles of Machines Tools

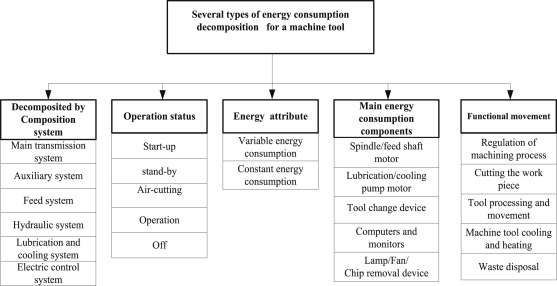
Automation architecture for data analysis of resource parameters from machines
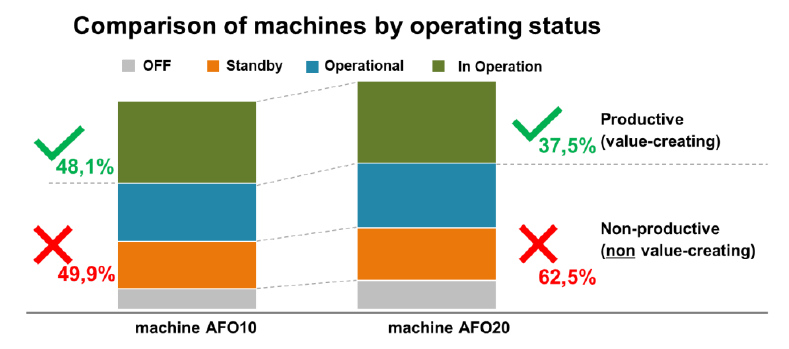
Example from Energy Tracking in Hamburg
![]()
![]()
![]()
Example from Industry
- Energy Monitoring and Energy Management in Industry on Machine Level
- ISO14966 - Environmental evaluation of machine tools
- Media Analysis for Machines, solution from SIEMENS
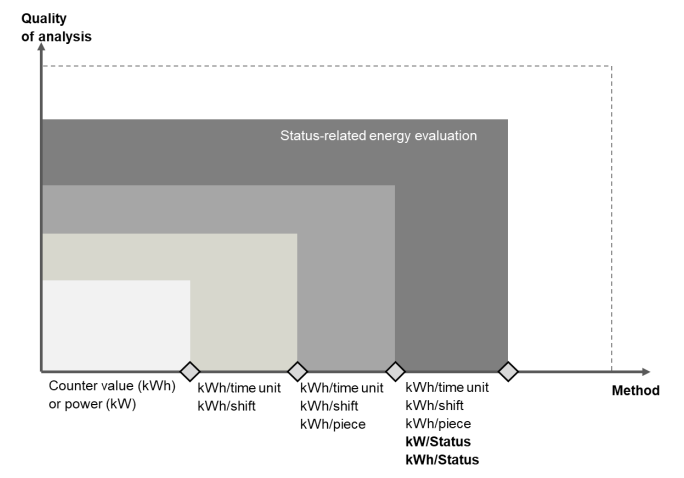
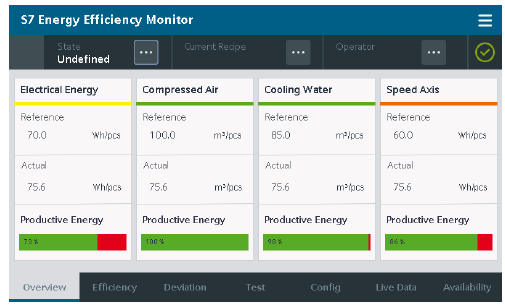
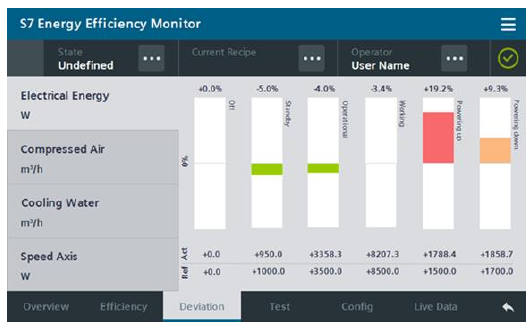
- Aim: develop machines that are responsible to the environment, economically viable, socially equitable and technologically adaptable