Week 08 ~ input devices
Capacitive sensing
For my final project I wanto to make actuated velcro-like surfaces and it would be great if they had feedback about
how far they have actuated/whether they have grabbed onto another surface.
Capacitive sensing sounds like it makes sense - I could add an extra conductive layer (copper tape) to the
material and measure the change in capacitance as the surface is folded or as another surface approaches. I also got reminded of this
research paper on integrating capacitive sensing into 3D printed metamaterials.
It looks like there are a range of analog approaches to capacitive sensing, although the simplest approach using a microcontroller seems to be an RC circuit
where you measure the time it takes for a circuit to respond to an input voltage, via the time constant t = RC. This can be done via two pins
(one for sending the pulse, the other for reading the response of the circuit).
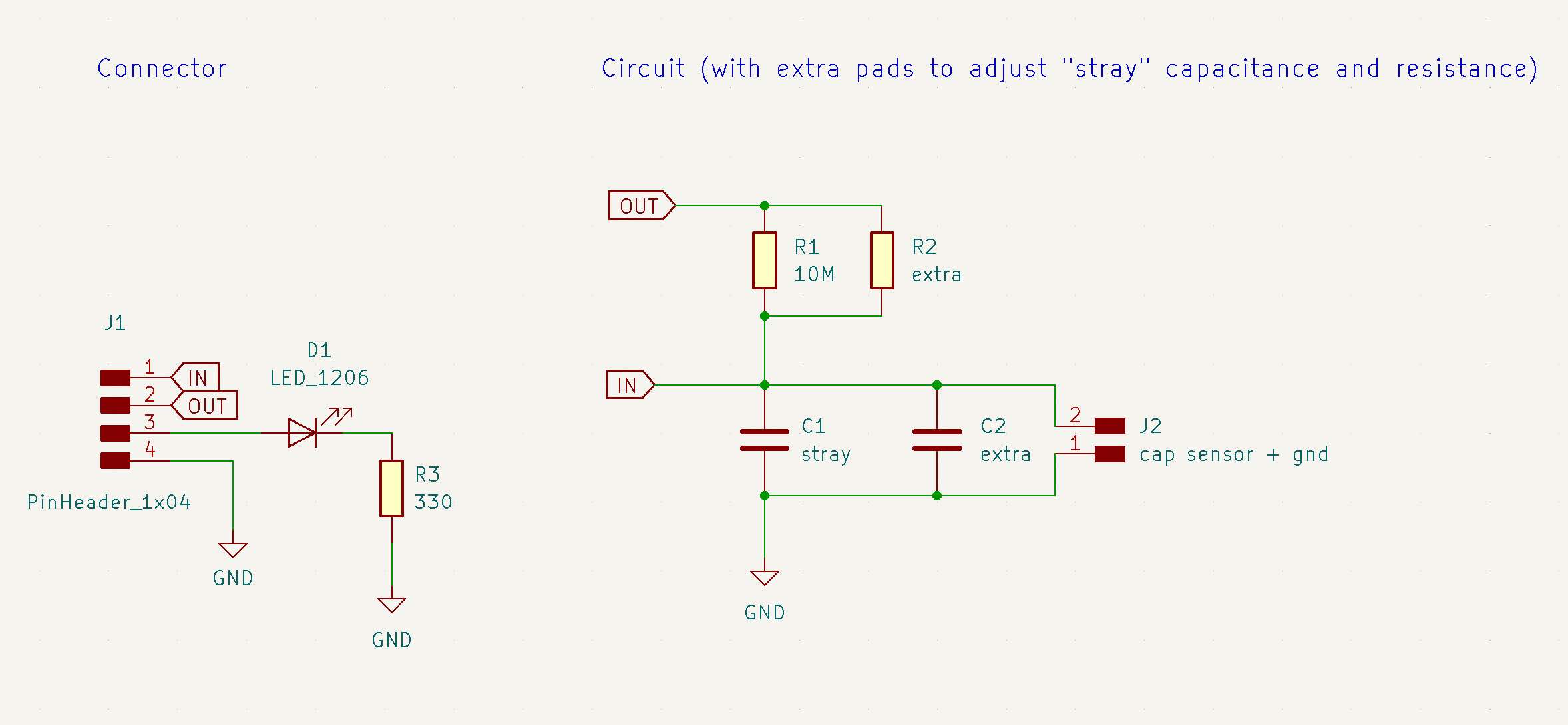 Schematic in KiCad - I added extra pads to adjust the R and C values of the circuit.
Milled board with soldered components; actual way I adjusted the resistance ...
Schematic in KiCad - I added extra pads to adjust the R and C values of the circuit.
Milled board with soldered components; actual way I adjusted the resistance ...
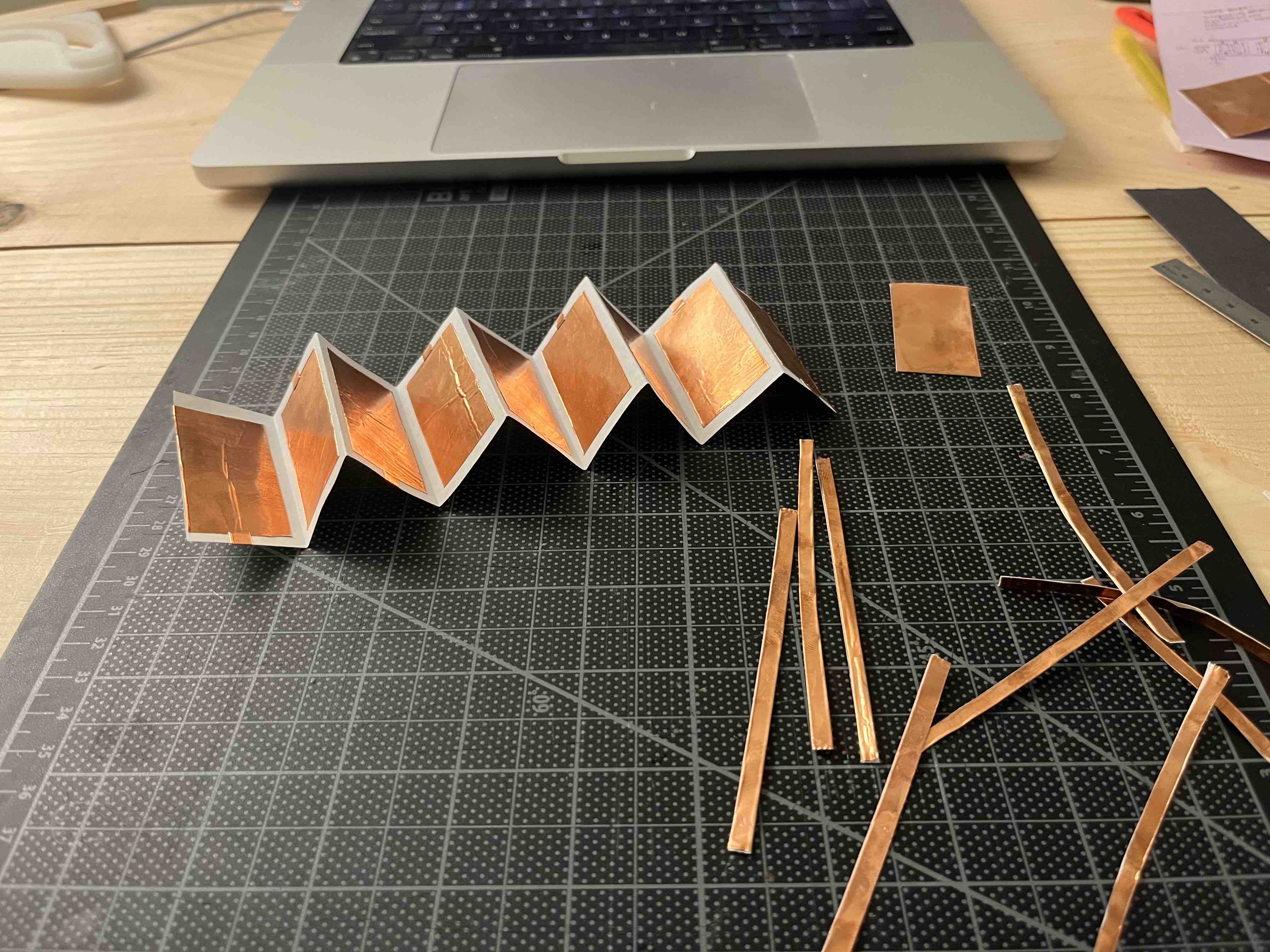 Making a capacitive sensor using copper tape: zig-zag faces will be connected in an alternating
fashion to form two halves of a capacitor (i.e. half the faces will be connected to the sensor pin, the other half to ground)
Making a capacitive sensor using copper tape: zig-zag faces will be connected in an alternating
fashion to form two halves of a capacitor (i.e. half the faces will be connected to the sensor pin, the other half to ground)
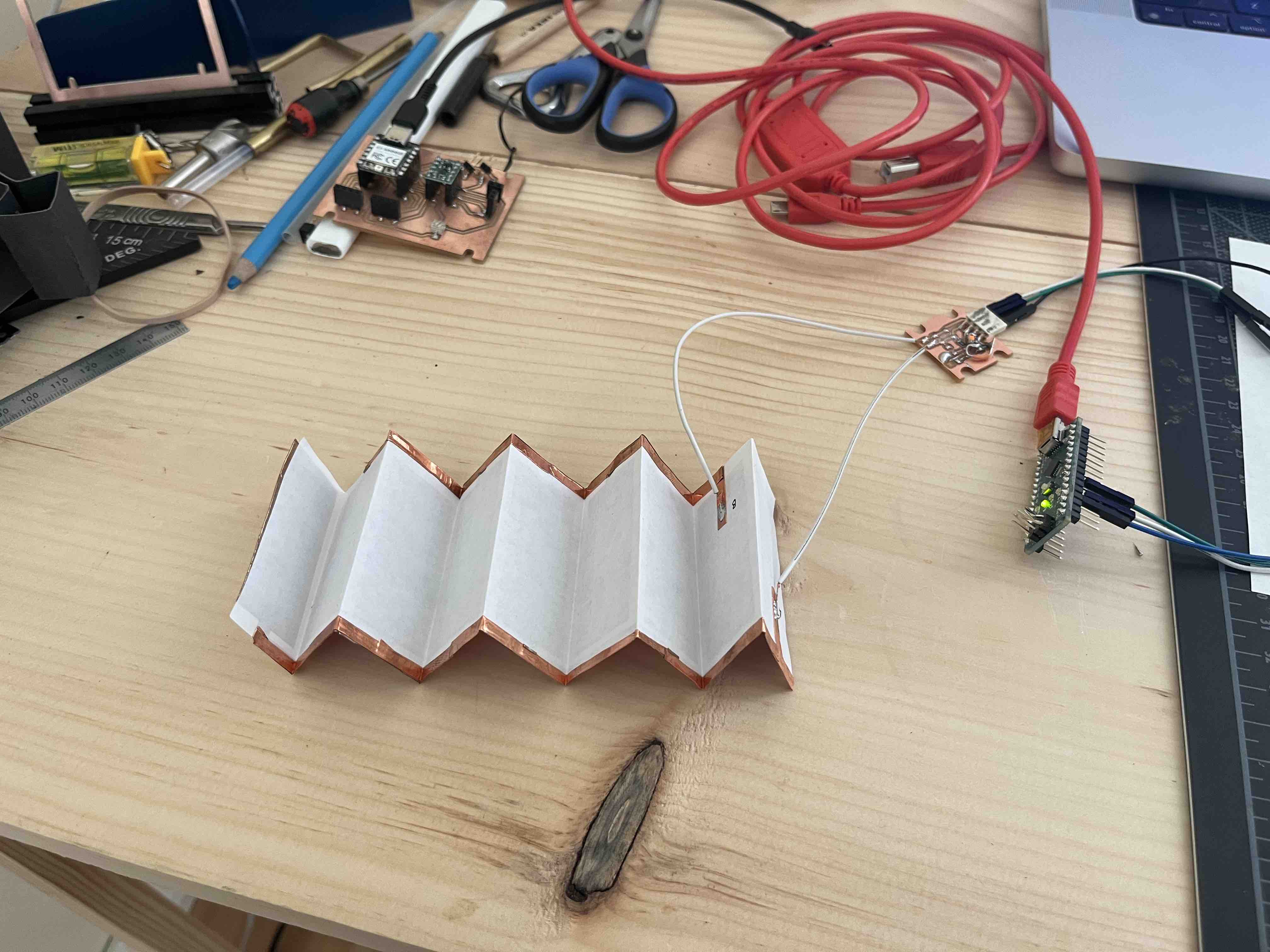 Reverse side of the sensor with connections to the milled circuit board.
Reverse side of the sensor with connections to the milled circuit board.
 Compressing the sensor should raise the capacitance, C ~ A / d (where d = distance between plates, A = area overlap), increasing the time it takes for the sensor pin to react to the signal pin, via the time constant t = RC).
Compressing the sensor should raise the capacitance, C ~ A / d (where d = distance between plates, A = area overlap), increasing the time it takes for the sensor pin to react to the signal pin, via the time constant t = RC).
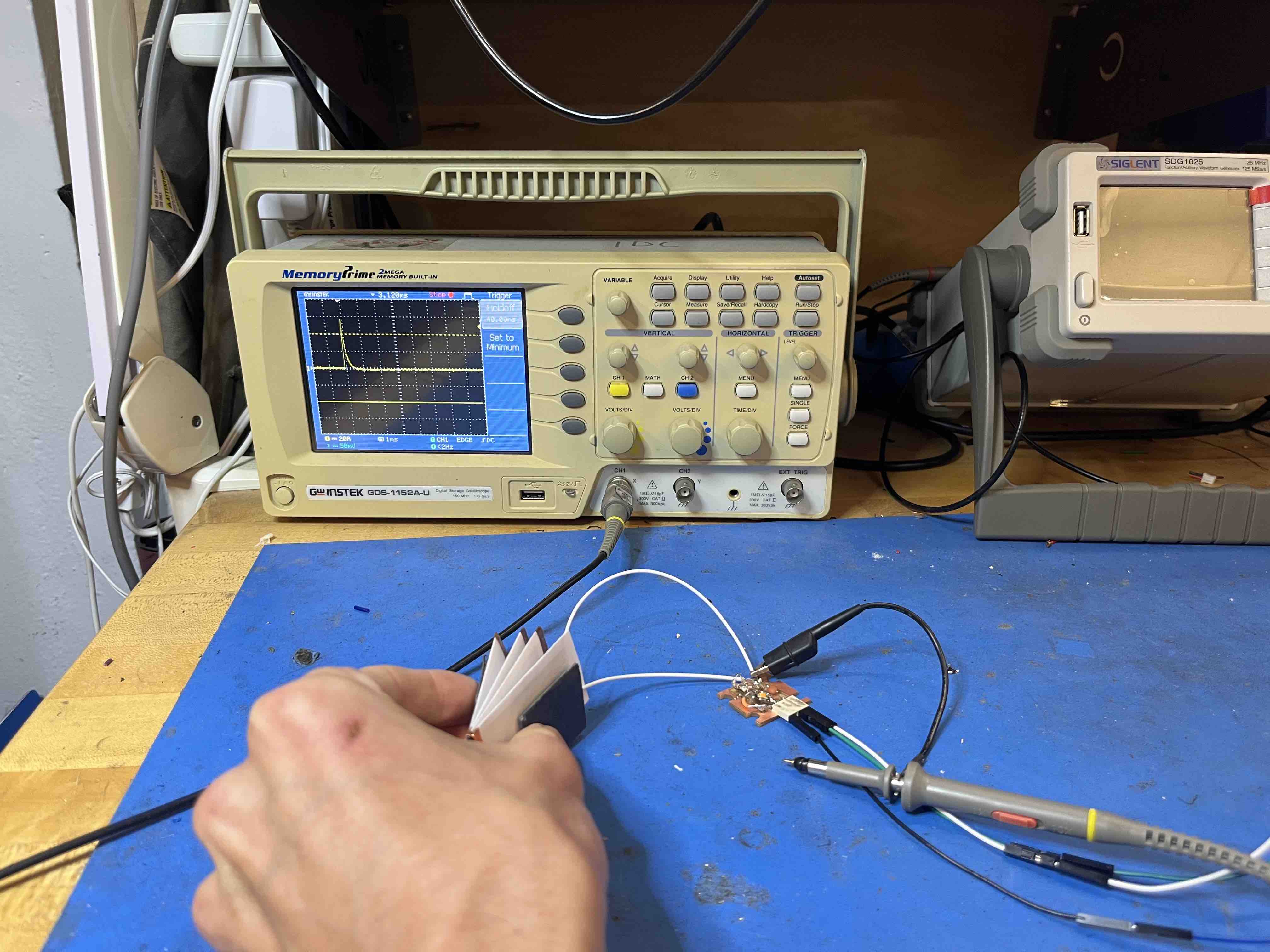 With an oscilloscope hooked up to the ground and sensor pin, using the 'trigger' function to capture the discharge through the sensor.
With an oscilloscope hooked up to the ground and sensor pin, using the 'trigger' function to capture the discharge through the sensor.
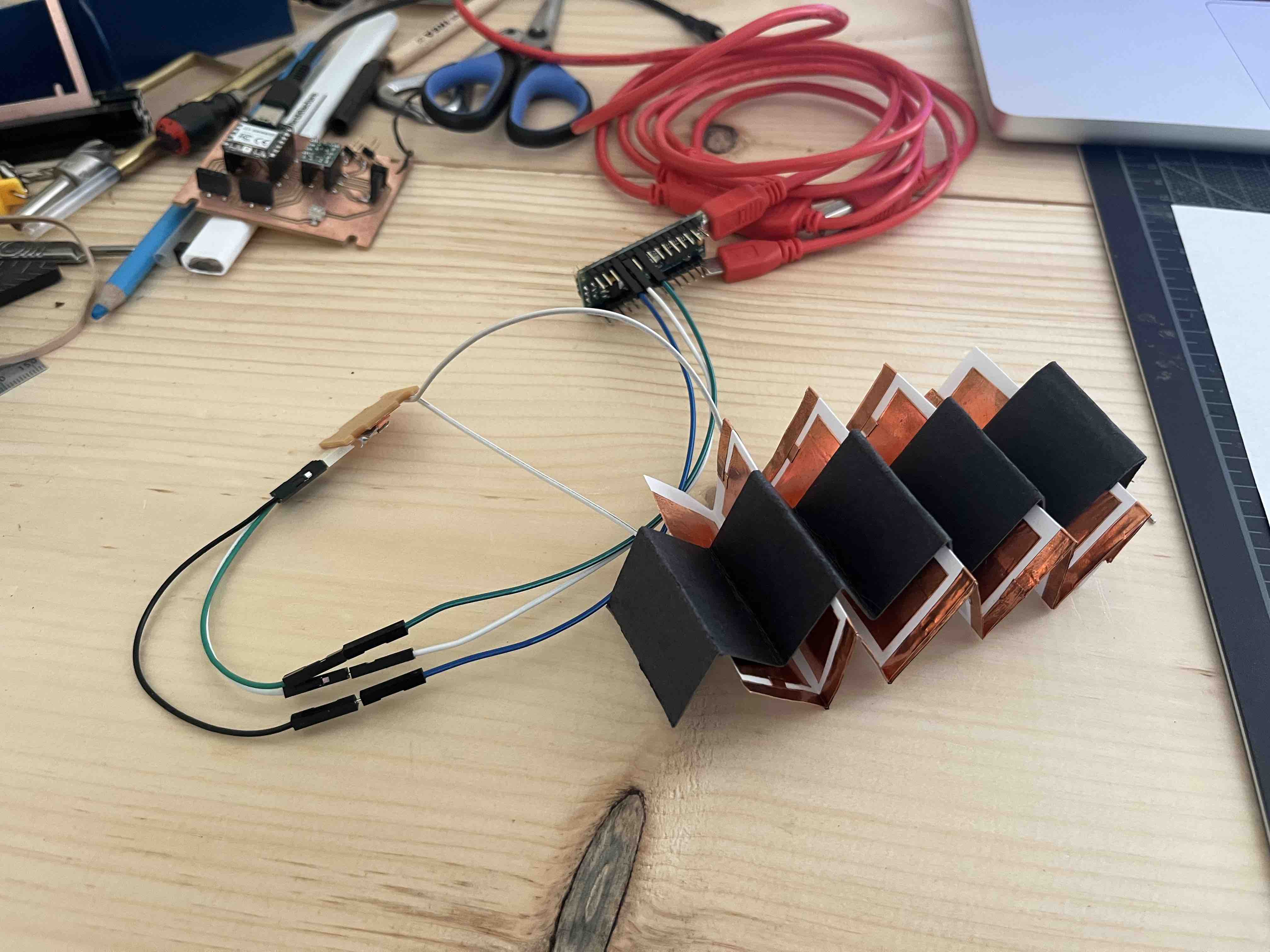
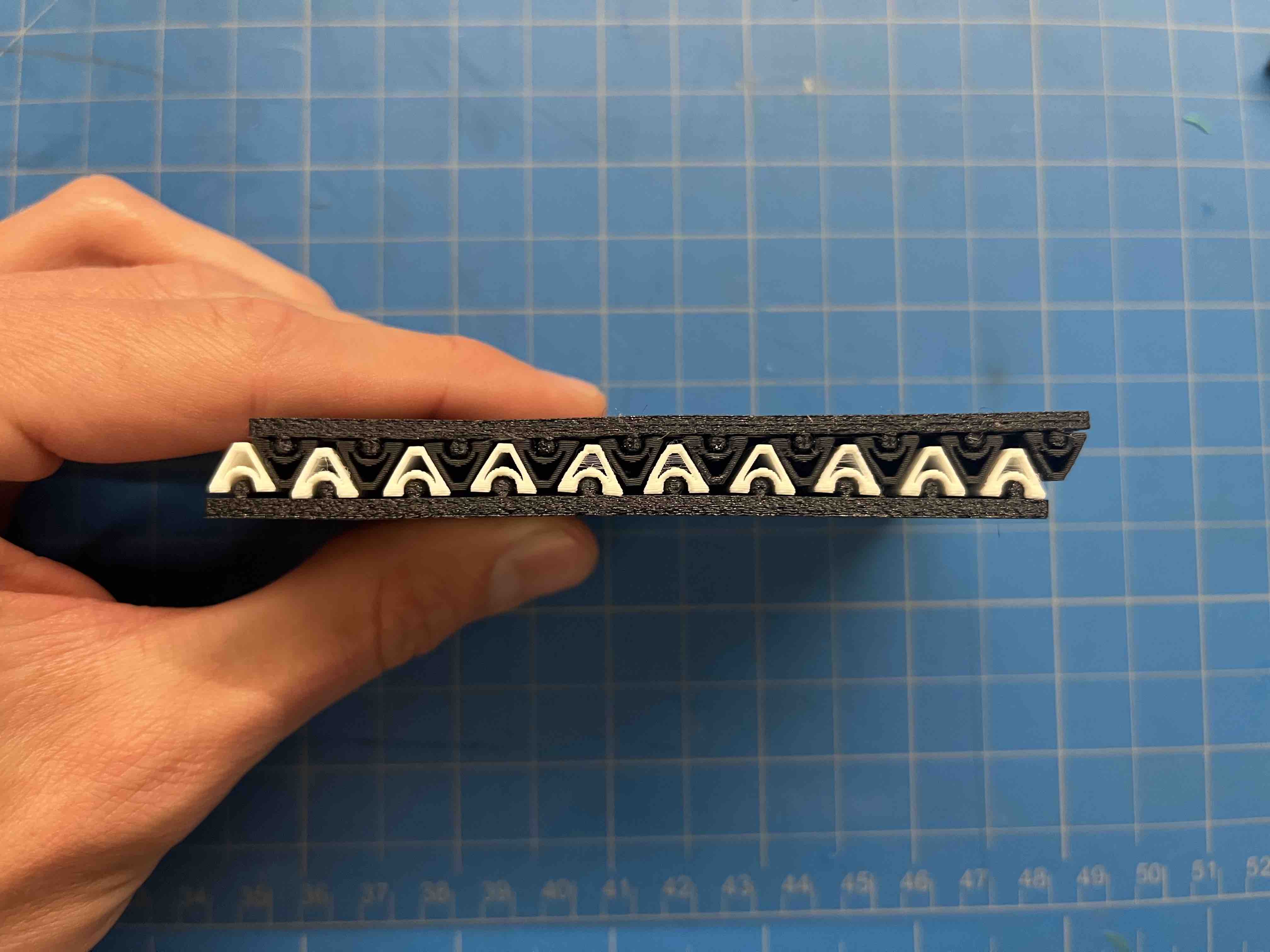 Zig-zag surfaces meshed together (with cavities to place copper foil?)
Zig-zag surfaces meshed together (with cavities to place copper foil?)
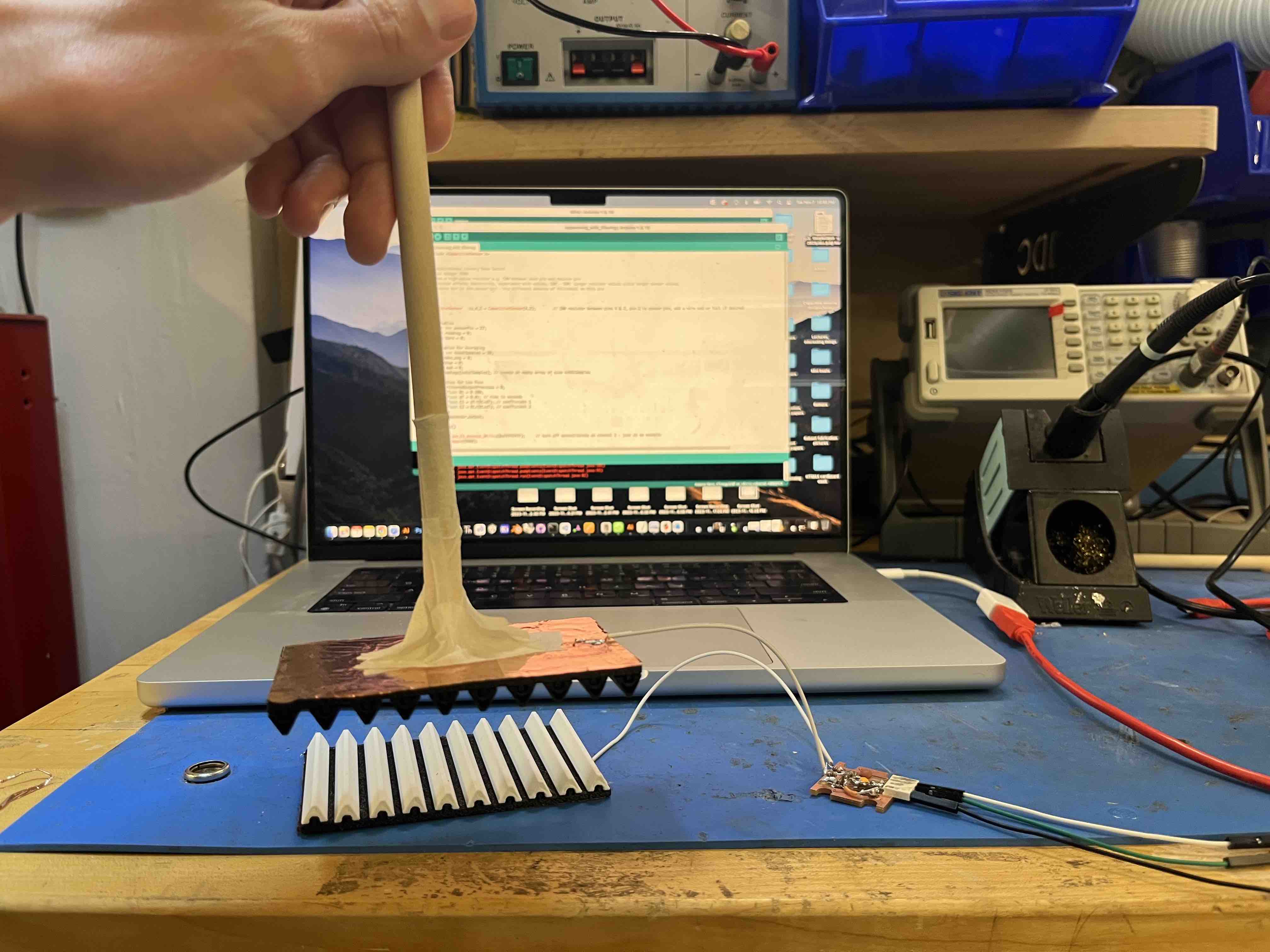 Two flexible surfaces with copper-foil backing - one connected to ground, the other to the sensor pin. Using a wooden stick to isolate the test from 'human capacitance'.
Test weith two surfaces (video).
Two flexible surfaces with copper-foil backing - one connected to ground, the other to the sensor pin. Using a wooden stick to isolate the test from 'human capacitance'.
Test weith two surfaces (video).
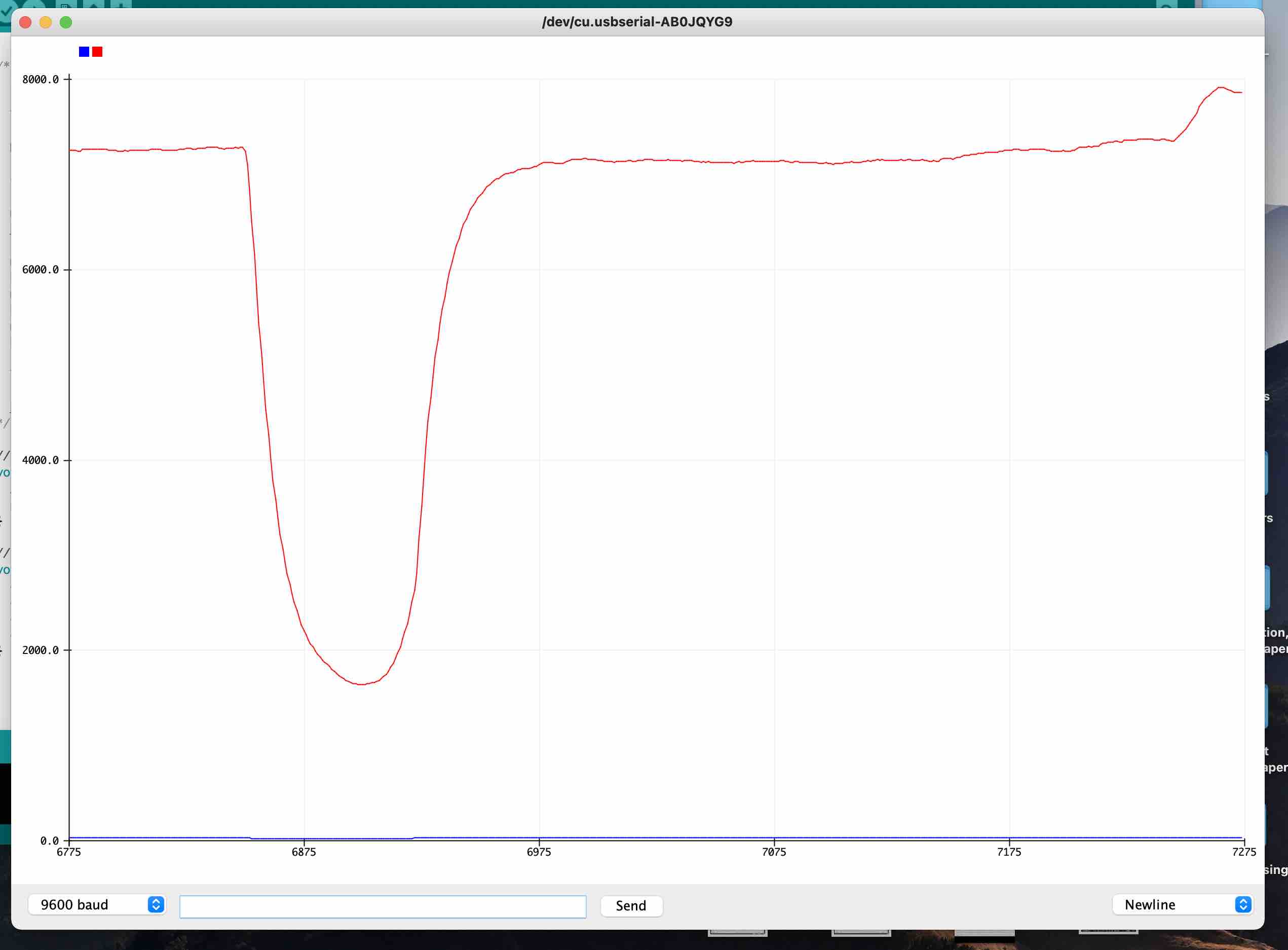 Serial plot of two plates test; integrating David's low-pass filter code.
The dip in the plot is when the two plates are touching: bringing the top plate back up, brought the value back up the original value (or close to!)
Serial plot of two plates test; integrating David's low-pass filter code.
The dip in the plot is when the two plates are touching: bringing the top plate back up, brought the value back up the original value (or close to!)
#include
CapacitiveSensor cs_4_2 = CapacitiveSensor(4,2); // 10M resistor between pins 4 & 2, pin 2 is sensor pin, add a wire and or foil if desired
// Variables
float reading = 0;
float tare = 0;
// Variables for Averaging
const int totalSamples = 10;
int index_avg = 0;
int value = 0;
float sum = 0;
int readings[totalSamples]; // create an empty array of size totalSamples
// Variables for Low Pass
float filteredOutputPrevious = 0;
const float RC = 0.100;
const float dT = 0.01; // time in seconds
const float C1 = dT/(RC+dT); // coefficient 1
const float C2 = RC/(RC+dT); // coefficient 2
float capsensor_output;
void setup()
{
cs_4_2.set_CS_AutocaL_Millis(0xFFFFFFFF); // turn off autocalibrate on channel 1 - just as an example
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop()
{
long start = millis();
long total1 = cs_4_2.capacitiveSensor(30);
Serial.print(millis() - start); // check on performance in milliseconds
Serial.print("\t"); // tab character for debug windown spacing
capsensor_output = total1;
// Serial.println(total1); // print sensor output 1
//delay(10); // arbitrary delay to limit data to serial port
//float filtered_reading = batchAverageRead() - tare; // Batch average reading
//float filtered_reading = movingAverageRead() - tare; // Moving average read
float filtered_reading = lowPassRead() - tare; // Low pass read
Serial.println(filtered_reading); // send our reading over USB to the computer
delay(dT*1000); // delay between reads in miliseconds (necessary for low pass)
}
// Batch Averaged sensor reading ----------------------------------------------------
float batchAverageRead(){
sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < totalSamples; i++){
sum = sum + capsensor_output; // sum totalSamples readings
delay(dT*1000); // wait for every reading! This is bad :(
}
return sum / totalSamples;
}
// Moving Average sensor reading ----------------------------------------------------
float movingAverageRead(){
sum = sum - readings[index_avg]; // Remove the oldest entry from the sum
value = capsensor_output; // Read the next sensor value
readings[index_avg] = value; // Add the newest reading to the window
sum = sum + value; // Add the newest reading to the sum
index_avg = (index_avg+1)%totalSamples; // Increment the index, and wrap to 0 if it exceeds the window size
return sum/(float(totalSamples)); // Divide the sum of the window by the window size for the result
}
// Low Pass Filter sensor reading -------------------------------------------------
float lowPassRead(){
float filteredOutput = capsensor_output*(C1) + filteredOutputPrevious*(C2); // All we need to do here is to measure once and do some fast multiplication with our coefficients! This is great :)
filteredOutputPrevious = filteredOutput; // And store our output for next time
return filteredOutput;
}