How to Make (Almost) Anything. Advice and epic failures of weekly fabrication challenges.
Make: To bring into existence by shaping, modifying, or putting together material; construct, change from one form or function to another, cause to exist or happen; bring about; create.
touch, soft, retraction, felt, feathers, muscles, boards, shrinking, step response, electrodes, array?, small scale model, transparent, current impulse, sensing?, hand, proximity, alive electronics, installation, flower!, output only...
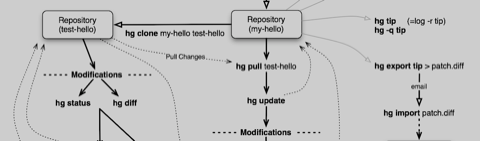
Mercurial tricks..."cd" to your Archive folder, "pull" all changes, ask for "status" to know what you changed, "merge" branches if needed, don't forget to commit message, "add" changes and also commit them, then "push" :)
PRESS FIT(n) - (Engineering / General Engineering) Engineering a type of fit joint for mating parts, usually tighter than a sliding fit, it is used when the parts do not have to move relative to each other. They can also admit some flexibility.
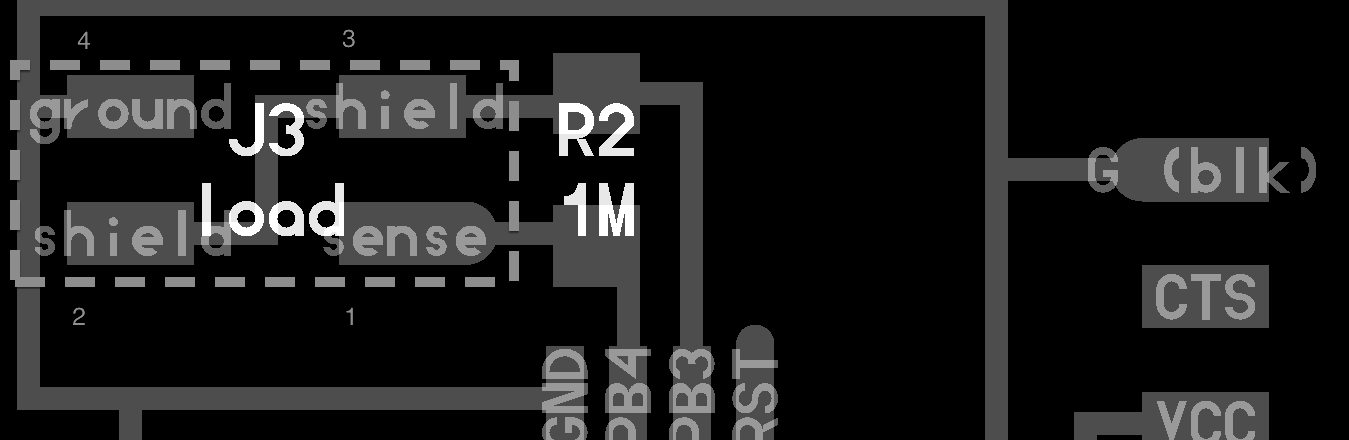
An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Basic electronic components may be packaged discretely, or integrated inside of packages.
Additive manufacturing or 3D printing is a process of making three dimensional solid objects from a digital model; it is achieved using additive processes, where an object is created by laying down successive layers of material.
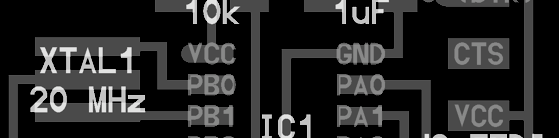
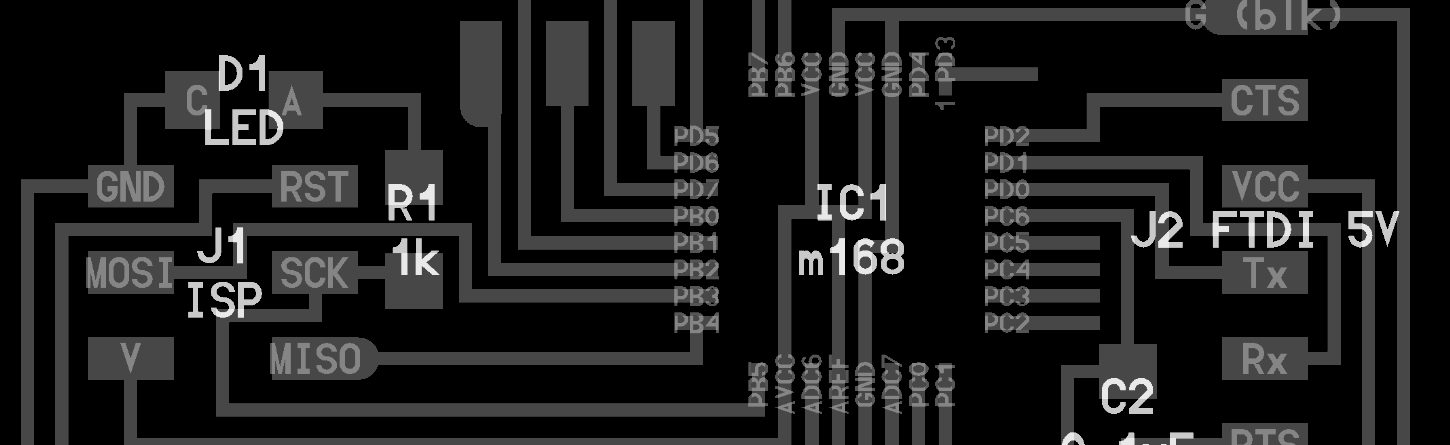
EDA or ECAD is a category of software for designing electronic systems such as printed circuit boards and integrated circuits. The tools work together in a design flow used to design and analyze entire semiconductor chips.
Casting is a manufacturing process by which a liquid material is poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process.

Embedded programming is the term for the computer programming that lives in and operates the great many computer-controlled devices that surround us. Embedded computers (microcontrollers) add intelligence to countless devices and systems.
Machining is a process in which a piece of raw material is cut into a final shape by a controlled material-removal process. The many processes that have this common theme, controlled material removal, are known as subtractive manufacturing.
An input device is any peripheral used to provide data and control signals to an information processing system such as a computer or other information appliance. Input and output devices make up the hardware interface between a computer and a scanner.
Composite materials are engineered or naturally occurring materials made from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties which remain separate and distinct within the finished structure.

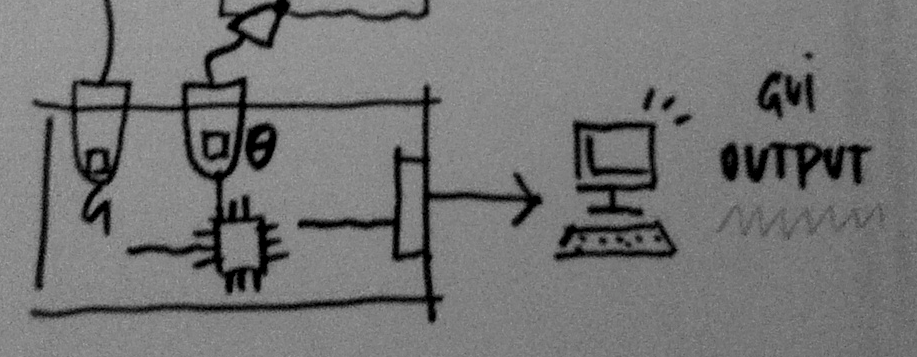
An output device is any piece of computer hardware equipment used to communicate the results of data processing carried out by an information processing system which converts the electronically generated information into human-readable form.

User interface design or user interface engineering is the design of computers, appliances, machines, mobile communication devices, software applications, and websites with the focus on the user's experience and interaction.