Vocabulary:
Transformation efficiency: Efficency of cells taking in extracellular DNA, calculated by dividing the number of successful transformants by the amount of DNA used during a transformation procedure (electropration, heatshock, etc.).
5' to 3' exonuclease activity: "chew back", something
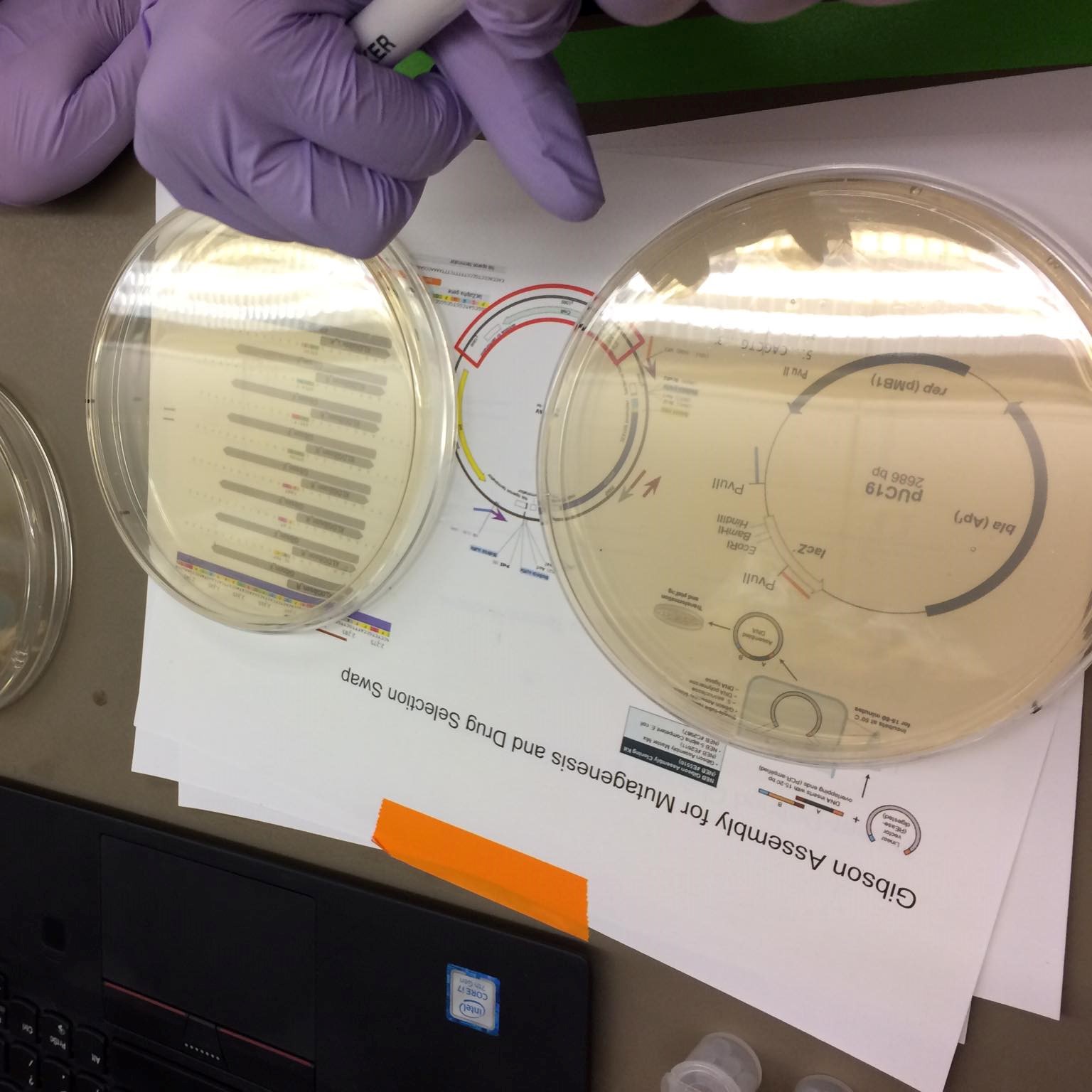
Gibbson assembly: A process used to join overlapping gene fragments into a single molecule. See video above. "First a 5' to 3' exonuclease activity creats single stranged 3' overhangs. The complementary sequences then anneal and DNA polymerase extends the 3' ends and fills in the gaps and DNA ligase seals the "nick". This results in fully-sealed, double stranded DNA."
Oligo, oligonucleotides: a polynucleotide whose molecules contain a relatively small number of nucleotides.
Melting temperature: Temperature at which a primer will attach to the template.
Exonuclease: an enzyme which removes successive nucleotides from the end of a polynucleotide molecule.
Ligase: Enzyme that combines DNA fragments together
Primer: A small strand of RNA or DNA
Pathway: A metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell.
Flux balance analysis: something
Chromophore: The part of a molecule that gives it color
Vector & Backbone: "The vector itself is generally a DNA sequence that consists of an insert (transgene) and a larger sequence that serves as the "backbone" of the vector. The purpose of a vector which transfers genetic information to another cell is typically to isolate, multiply, or express the insert in the target cell."
Tube terminology: