![[Profile Image Placeholder]](profile.jpg)
Week 11
Networking & Communications
Week Highlights
Key captures from the group and individual assignments with links to their sections.
Table of Contents
Course Content
Training & Documentation
Assignments & Projects
Networking & Communications
This week focuses on connecting devices through wired and wireless networks. We'll explore communication protocols, network addressing, and how to build networked systems with local input and output devices.
This Week's Goals
- Network Protocols
Learn about ESP-NOW, Wi-Fi, I²C, SPI, UART, and other communication protocols - Network Addressing
Understand MAC addresses, IP addresses, and bus addressing schemes - Networked Systems
Design, build, and connect wired or wireless nodes with local I/O devices
Assignments
- Group Assignment
Send a message between two projects - Individual Assignment
Design, build, and connect wired or wireless node(s) with network or bus addresses and local input &/or output device(s)
Tools & Materials
- ESP32-S3 Microcontroller Boards
- Wi-Fi Access Point
- OLED Displays (SSD1306)
- Camera Modules
- Touch Sensors
Training Documentation
Training materials and documentation for networking and communications protocols.
Recitation Notes: How to Integrate (Almost) Any System
View original notes on Slack • Recitation link
Announcements
- LoRa radios available tomorrow morning
- Plugin for KiCad FabLib (visit GitLab)
- Visit fablab.aalto.fi
System Disintegration: How Systems Fail
Understanding failure modes is critical for robust system design. See the class system integration page for detailed failure mode documentation and links.
Design: PCs vs Macs (Box vs Designed Products)
The contrast between functional boxes (PCs) and designed products (Macs) illustrates the importance of user experience design. This connects to "How to Design (Almost) Anything" and "How to Make (Almost) Anything Usable" classes.
Dr. Jan Borchers's Session: Usability
hci.rwth-aachen.de/fabusability — Computer science, design, and psychology intersect in usability research. Usability focuses on designing systems that work great for people, whether in projects, startups, or products like FabFame.
Golden Rules of Usability
- Simplicity — Keep it simple, avoid feature creep. Consider user (price tag and feature list), task (reduce complexity to fit the task), and context.
- Visibility and Feedback — Immediately see current state, available features, and how to access them.
- Gestalt Laws — How we perceive units/groups through distance/proximity, shapes, and similarity.
- Natural Mapping — Physical arrangement matches physical movement (e.g., up/down buttons, sliders, rotational dials). Additive dimensions (power, heat, light, water level, volume). Haptic feedback enables operation without looking (e.g., car safety: physical buttons vs touch screen).
- User's Language — Use terminology familiar to users.
- Avoid Modes — Prevent mode confusion.
- Principle of Least Surprise — Systems should behave as users expect.
- Dialogue, Not Monologue — Interactive, responsive systems.
- Tolerate Errors — Provide constructive feedback and error recovery.
- Visual Design — Use nice color schemes (e.g., color.adobe.com).
Process Tips
- Design is iterative and agile
- Observe and ask first, then start solving
- Design: Search the solution space
- Prototype: Implementations for feedback
- Analyze: Observe and ask for constructive interaction
- Analyze: Retrospective testing
- Iterate to expand and focus solution
Literature: The Design of Everyday Things (intro to human computer interaction). See hci.rwth-aachen.de/fabusability for more resources.
Packaging
Route wiring appropriately and mount circuit boards in a box—don't just throw them in! See examples from Gianfranco Paluto on Fab Academy. Consider mechanism alignment and surface finish.
Testing
Prevent defects (QA) and detect defects (QC). Methods include shake and drop tests, power cycling, environmental testing, and random inputs.
Failure Modes
Details and links available on the class system integration page:
- Mechanical — Static vs dynamic failure (e.g., Tacoma Narrows Bridge)
- Wiring — Ground mecca necessary where all grounds meet. Can't just daisy chain power and ground; otherwise devices get different grounds.
- Components — Component-level failures
- Power — Robust against wrong connections
- Software — Buffer overflow is a serious vulnerability. Security through obscurity is insufficient.
- Scaling — O(?) complexity, phase transitions in complexity
- Manufacturing — Production-related failures
- Collaboration — Team and communication failures
Fail Fast!!! — Feed-forward vs feedback development. Murphy's Law (rocket test engineer): "Anything that can go wrong, will go wrong." This means you have to anticipate how it'll fail and prevent it.
Repair
- Drop/Shake — Test robustness
- Modularity — Debug module at a time
- Widlarize — Bob Widlar's approach: smash it with a hammer (as a broken system) to understand failure modes
Lifecycle
- Right to Repair — Design for repairability
- Disassembly — Consider how systems come apart
- End-of-Life — Plan for system retirement and recycling
Assignment: System Integration for Final Project
Design and document the system integration for your final project:
- What are the modules? (Hardware and software)
- CAD for how everything comes together
- Architecture for modularity: how all hardware comes together
- Architecture: how all software comes together
Good example: Fab Academy 2016 system integration assignment
Networking Protocols Overview
Networking and communications enable devices to exchange data through wired and wireless connections. Understanding different protocols helps select the right communication method for each application.
Wired Communication
- UART/USART — Asynchronous serial communication (RS-232, RS-422, RS-485)
- I²C/TWI — Two-wire interface with SCL/SDA, requires pull-up resistors
- SPI — Serial Peripheral Interface with MISO/MOSI/CS/SCK lines
- USB — Universal Serial Bus for device communication
- Ethernet — Wired network communication
Wireless Communication
- ESP-NOW — Low-power peer-to-peer communication for ESP32 devices
- Wi-Fi — 802.11 wireless networking (2.4 GHz, 5.8 GHz)
- Bluetooth/BLE — Short-range wireless communication
- LoRa — Long-range, low-power wireless communication
- RF — Radio frequency communication (433 MHz, 868 MHz, 915 MHz, 2.4 GHz)
Network Addressing
Devices on networks require unique addresses for identification and communication:
- MAC Address — Media Access Control address, unique hardware identifier (e.g., D8:3B:DA:75:05:AC)
- IP Address — Internet Protocol address for network routing (e.g., 192.168.1.100)
- Bus Address — Device address on shared communication buses (I²C, SPI)
Useful Documentation
Essential resources for networking and communications protocols.
Class Page
Networking and Communications - MIT Academy
Comprehensive resource covering wired protocols (UART, I²C, SPI, USB, Ethernet), wireless protocols (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LoRa, RF), network addressing, OSI layers, modulation techniques, channel sharing methods, error detection/correction, and Internet protocols. Includes detailed tutorials, code examples, and implementation guides for various communication protocols.
Key Topics
- Wired Communication: UART, I²C, SPI, USB, Ethernet, CAN, LIN, MODBUS
- Wireless Communication: ESP-NOW, Wi-Fi (802.11), Bluetooth/BLE, LoRa, RF (433/868/915 MHz, 2.4/5.8 GHz)
- Network Protocols: IPv4/IPv6, TCP/UDP, HTTP, DNS, DHCP, NAT
- Modulation: PCM, PPM, OOK, FSK, BPSK, QAM, OFDM, FHSS, DSSS, UWB
- Channel Sharing: TDMA, FDMA, CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA, CDMA, MIMO
Individual Assignment: Networking & Communications
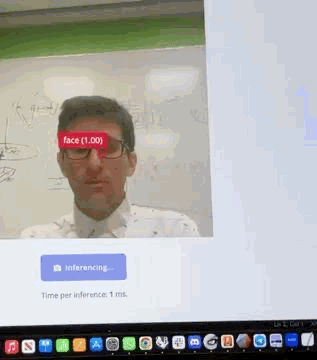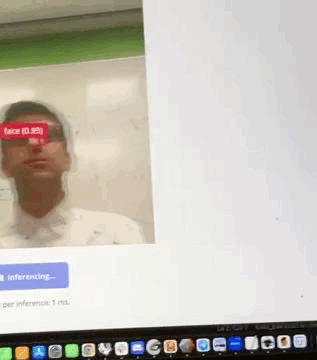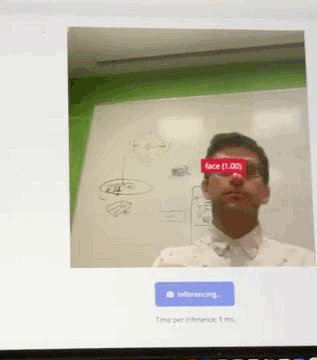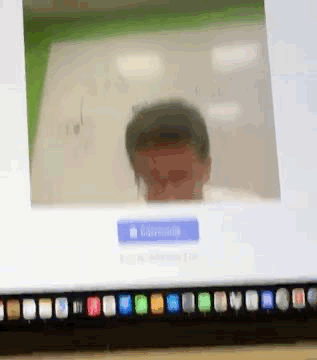
Design, build, and connect wired or wireless node(s) with network or bus addresses and local input &/or output device(s). This assignment demonstrates two networked systems: an ESP-NOW multiplayer game and a Wi-Fi camera streaming system with edge AI processing.
Related Documentation
- Week 2: Embedded Programming & Nintendo Training — ESP-NOW multiplayer game development
- Week 2: Design Files — CircleSquareShapeSongSwingalong Arduino code
- Week 10: Camera & Edge AI — Wi-Fi camera streaming system
- Week 10: Design Files - Camera — Camera stream code and system implementation
Networked System 1: CircleSquareShapeSongSwingalong (ESP-NOW)
A collaborative multiplayer game featuring geometric shape interactions, synchronized gameplay between two ESP32-S3 devices using ESP-NOW wireless communication. The system uses MAC address-based player identification and real-time state synchronization for coordinated gameplay. See Week 2 documentation and design files for complete details.
Design & Build
The system consists of two XIAO ESP32-S3 development boards, each with an SSD1306 OLED display (128x64) and capacitive touch sensors. The boards communicate wirelessly using ESP-NOW protocol, enabling low-latency peer-to-peer communication without requiring a Wi-Fi access point.
Network Type & Protocol
Network Type: Wireless peer-to-peer (ESP-NOW)
Protocol: ESP-NOW (Espressif's proprietary low-power wireless communication protocol)
Addressing Scheme: MAC address-based device identification
Input & Output Devices
- Input Devices: Capacitive touch sensors (6 touch pads per device) for player controls (left, right, jump)
- Output Devices: SSD1306 OLED display (128x64, I²C address 0x3C) for game rendering and player state visualization
Shape Song Swing Along educational content integration and gameplay
Circle and square shape interaction gameplay mechanics
Connections
Each ESP32-S3 board connects to an OLED display via I²C (SDA pin 5, SCL pin 6) and reads touch sensor inputs from GPIO pins. The ESP-NOW communication is handled entirely through the ESP32-S3's built-in Wi-Fi radio, requiring no external hardware connections.
See Network Address Tables for complete device addressing information including MAC addresses for both player devices.
Download Design Files
- TwoSquares_XiaoESP32S3_Touch_ReadySplash_MACFix.ino — Complete Arduino sketch for ESP-NOW multiplayer game
- get_mac_address.ino — Utility to read MAC addresses from ESP32-S3 devices
Networked System 2: Camera Livestream & Edge AI (Wi-Fi)
A Wi-Fi-enabled camera system using ESP32-S3's built-in camera and HTTP server capabilities to stream JPEG frames over Wi-Fi using MJPEG (Motion JPEG) protocol. The system also includes edge AI face detection using a FOMO (Faster Objects, More Objects) model from Edge Impulse for real-time person tracking. See Week 10 documentation and design files for complete details.
Design & Build
The system uses a XIAO ESP32-S3 Sense development board with an integrated camera module. The camera captures frames at QQVGA (160x120) or QVGA resolution, processes them through an Edge AI inference pipeline, and streams the results over Wi-Fi via HTTP multipart response. The system can also display camera output and inference results on an OLED display connected via I²C.
Network Type & Protocol
Network Type: Wireless local area network (Wi-Fi)
Protocol: HTTP over Wi-Fi (802.11), MJPEG streaming
Addressing Scheme: IP address (DHCP-assigned) and MAC address (hardware identifier)
Input & Output Devices
- Input Devices: Camera module (integrated on XIAO ESP32-S3 Sense) for image capture, button for capture trigger
- Output Devices: OLED display (SSD1306, 128x64, I²C address 0x3C) for displaying camera frames and inference results, Wi-Fi HTTP server for remote streaming
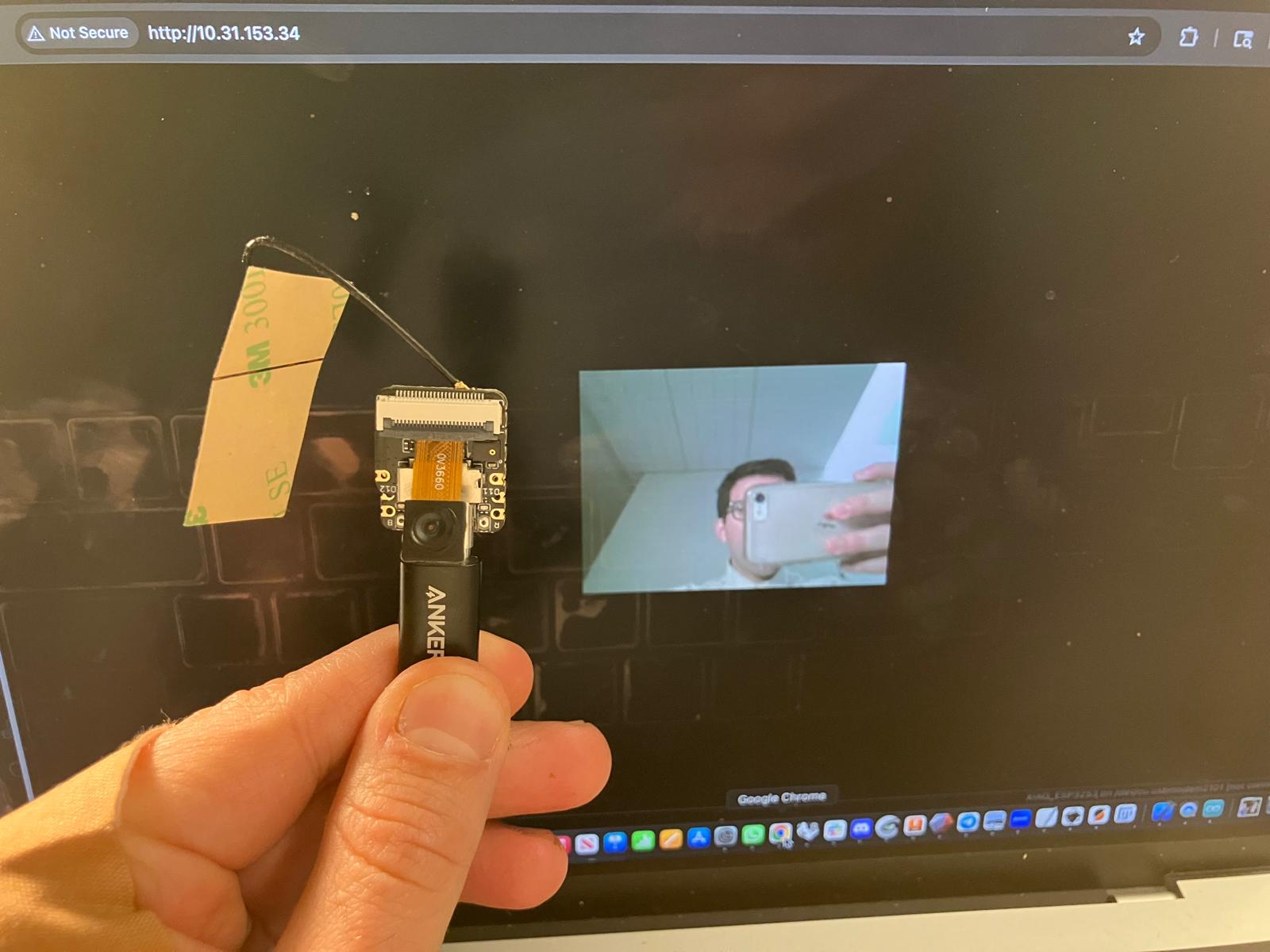
Connections
The camera module is integrated directly on the XIAO ESP32-S3 Sense board, connected via parallel data bus (Y2-Y9), control signals (XCLK, PCLK, VSYNC, HREF), and I²C interface (SIOD, SIOC). The OLED display connects via I²C (SDA pin 5, SCL pin 6) with pull-up resistors. Wi-Fi connection is established through the ESP32-S3's built-in Wi-Fi radio.
See Network Address Tables for complete device addressing information including MAC and IP addresses for the camera system.
Connecting to MIT Wi-Fi Network
To connect the ESP32-S3 camera system to the MIT Wi-Fi network, you need to generate a device-specific password. The MIT network uses WPA2-PSK authentication for devices that are not 802.1X compatible.
- Navigate to https://wifi.mit.edu/ in your web browser.
- Click on "Using a device not 802.1X compatible? Click here" link.
- Login with Touchstone using your Kerberos credentials.
- The system will generate a QR code and password for the "MIT" network. You can have the password emailed to yourself or copy it directly.
- Use the generated password in your Arduino code:
const char* ssid = "MIT";
const char* password = "insert generated password from steps above";
Download Design Files
- camera_stream.zip — Complete camera stream project (includes .ino and .h files)
- camera_stream.ino — Main Arduino sketch for camera livestreaming
- camera_pins.h — GPIO pin definitions for XIAO ESP32-S3 camera module
- ei-face-detection--fomo-arduino-1.0.90.zip — Edge Impulse Arduino library for FOMO-based face detection
Networked System 3: Long Range Radio Board Design, Fabrication, and Connection to Meshtastic
A custom PCB design integrating the XIAO ESP32-S3 with the Wio-SX1262 LoRa radio module for Meshtastic communication, connected to a MAX30102 pulse oximeter sensor. The system enables long-range wireless communication using LoRa (Long Range) radio technology and the Meshtastic mesh networking protocol for decentralized device-to-device messaging.
Invisible String
This project draws inspiration from the Invisible String book series by Patrice Karst, which explores the concept of invisible connections that link us to the people we love, even when we're far apart. The book series and workbook include activities for making an invisible string chain of hearts, symbolizing these connections. This long-range radio system embodies that concept by creating invisible wireless links between devices across distances, enabling communication and data sharing through the Meshtastic mesh network.
Design & Build
I designed a custom PCB that integrates the XIAO ESP32-S3 & Wio-SX1262 Kit for Meshtastic & LoRa (see usage documentation) with a MAX30102 Heart Rate Sensor Module for pulse oximetry. The design process followed the same PCB design workflow established in Week 4, using Fusion 360 Electronics for schematic capture and PCB layout.
The MAX30102 sensor integrates red and infrared LEDs, a photodetector, and low-noise electronics for heart rate and blood oxygen (SpO2) measurement. Reference schematics were sourced from the Amazon product page and the Analog Devices MAX30102 datasheet.
Component Selection and Library Management
Component selection required careful library management in Fusion 360 Electronics. I started by identifying the correct through-hole header variants needed for the XIAO ESP32-S3 and Wio-SX1262 modules, ensuring proper pin spacing and mechanical compatibility.

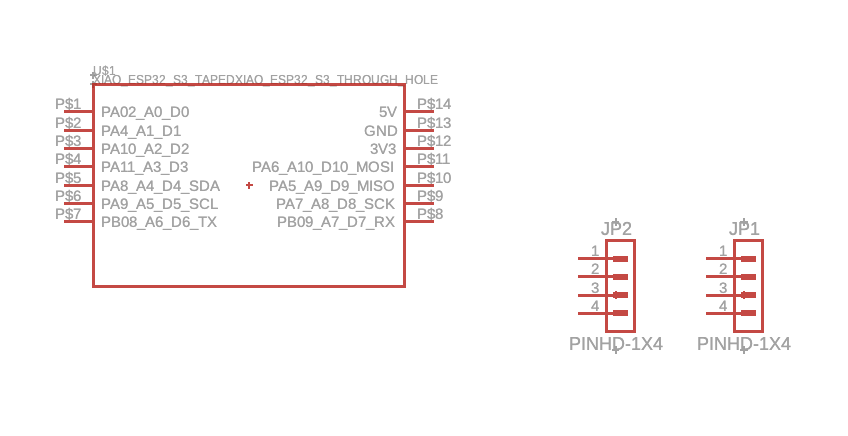
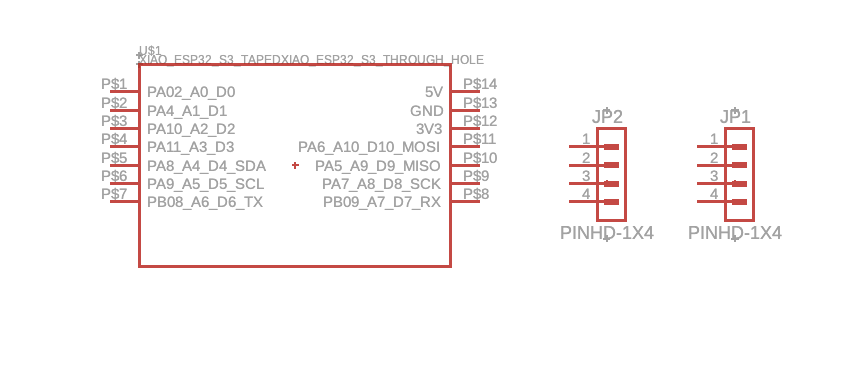
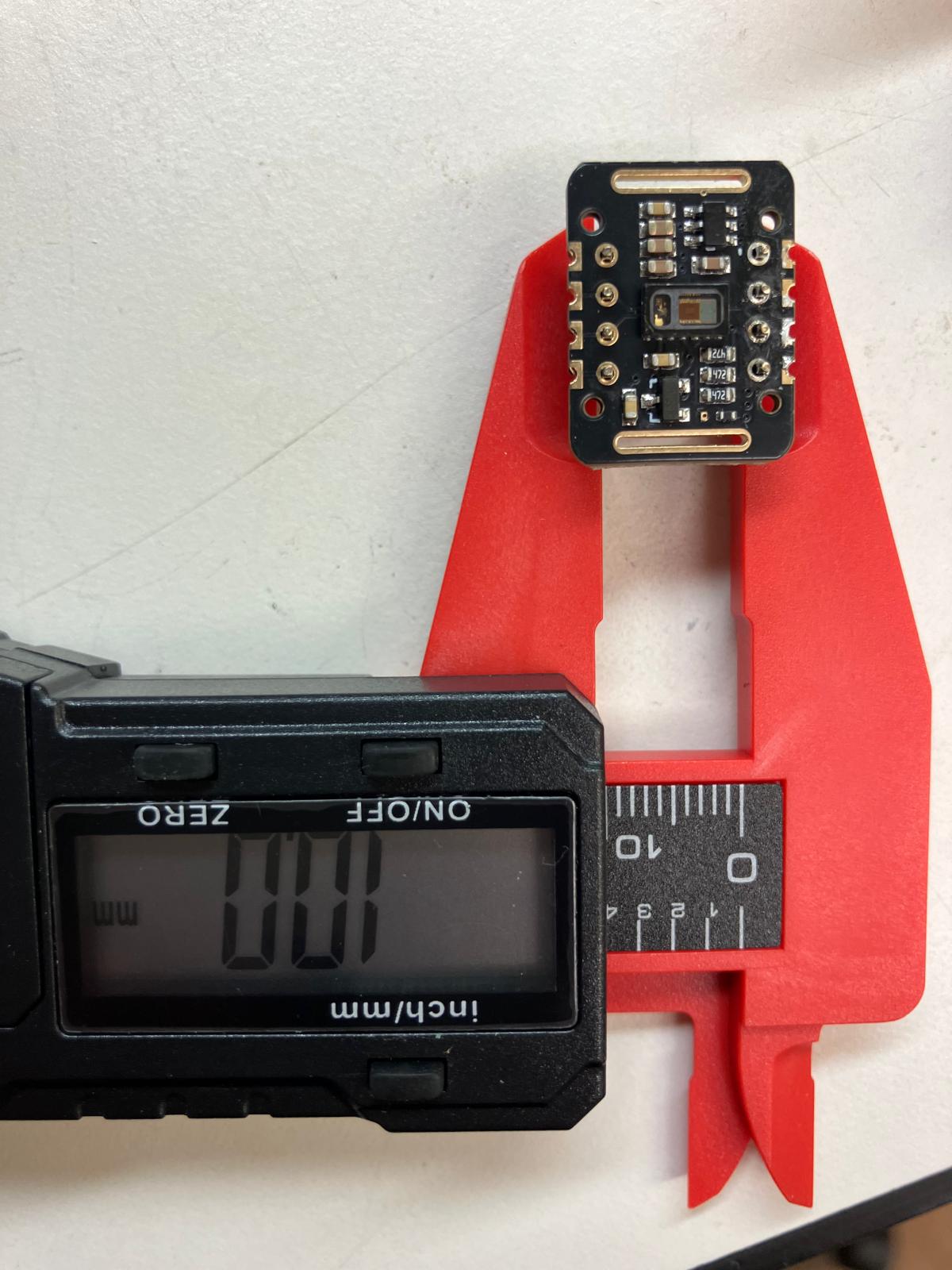
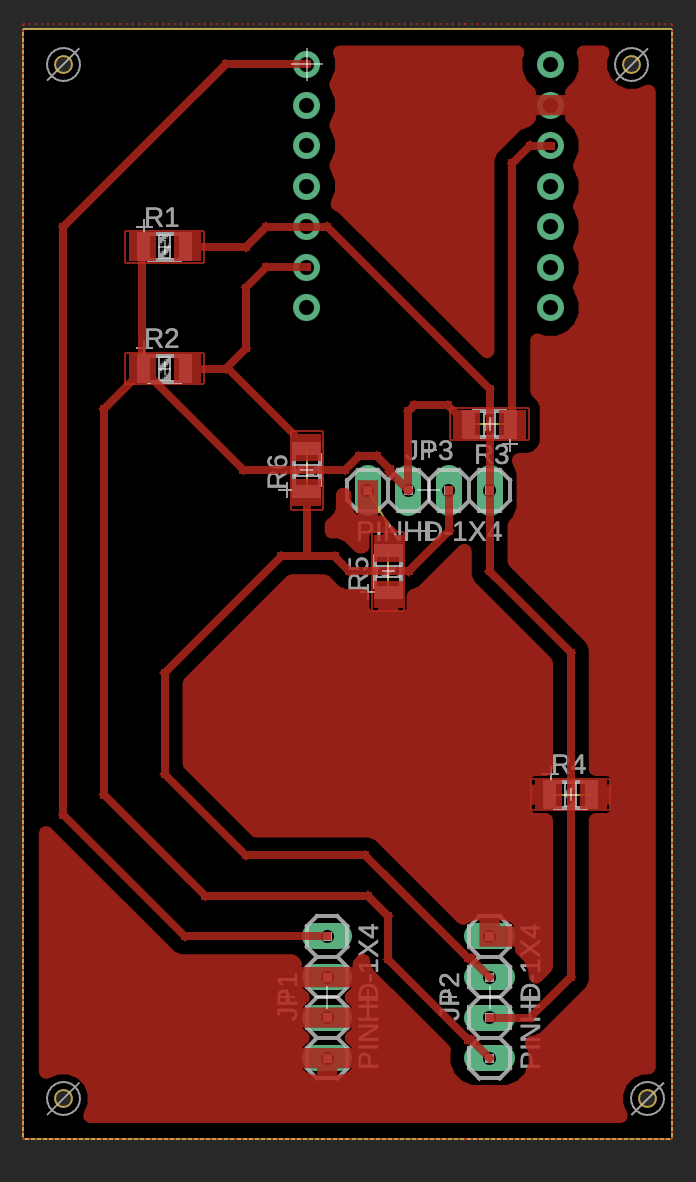
PCB Layout and Distance Measurement
Accurate spacing between components was critical for proper module alignment. I used physical measurements from breadboard prototypes and Fusion 360's measurement tools to ensure correct header placement and pin spacing.

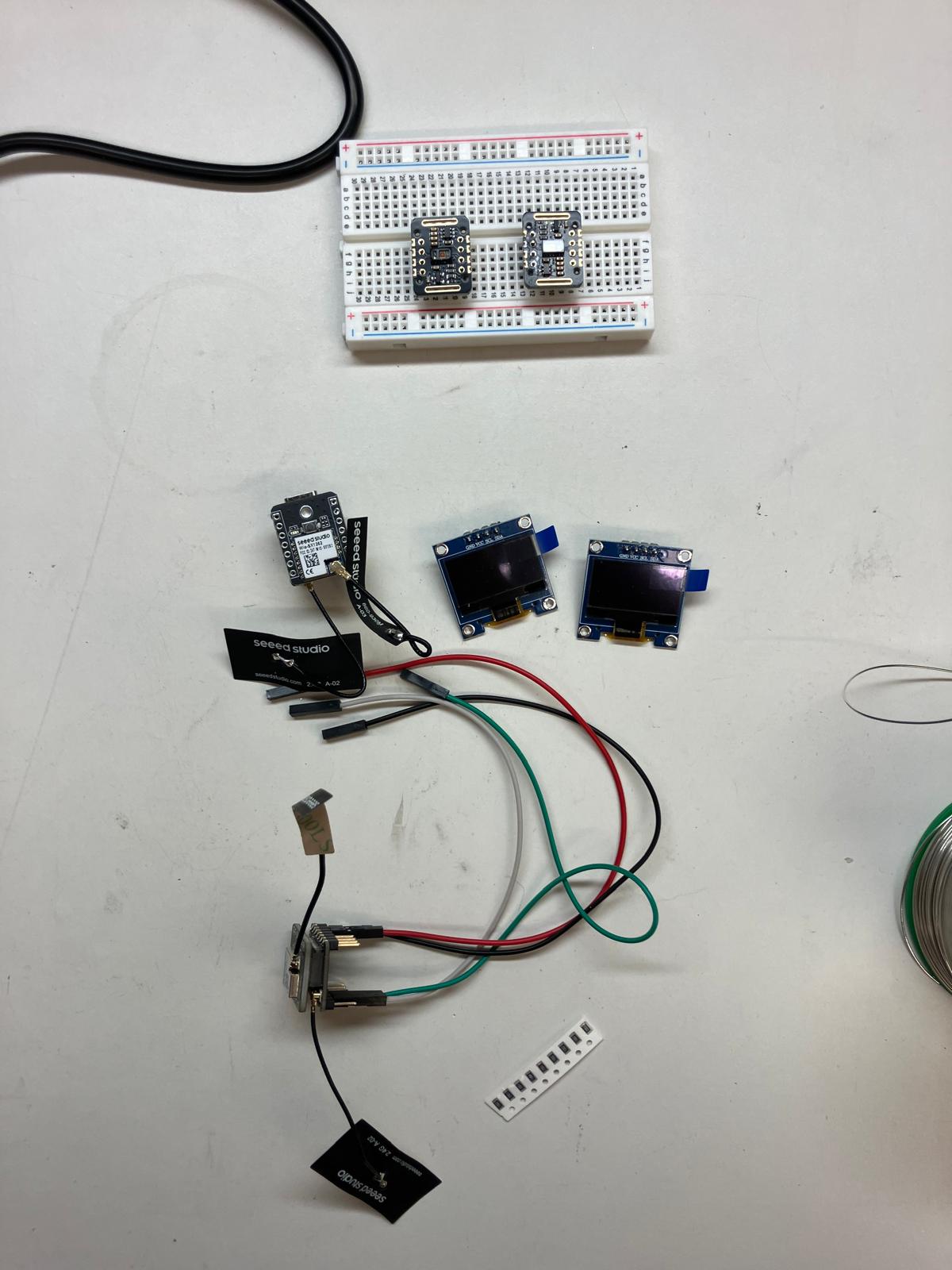
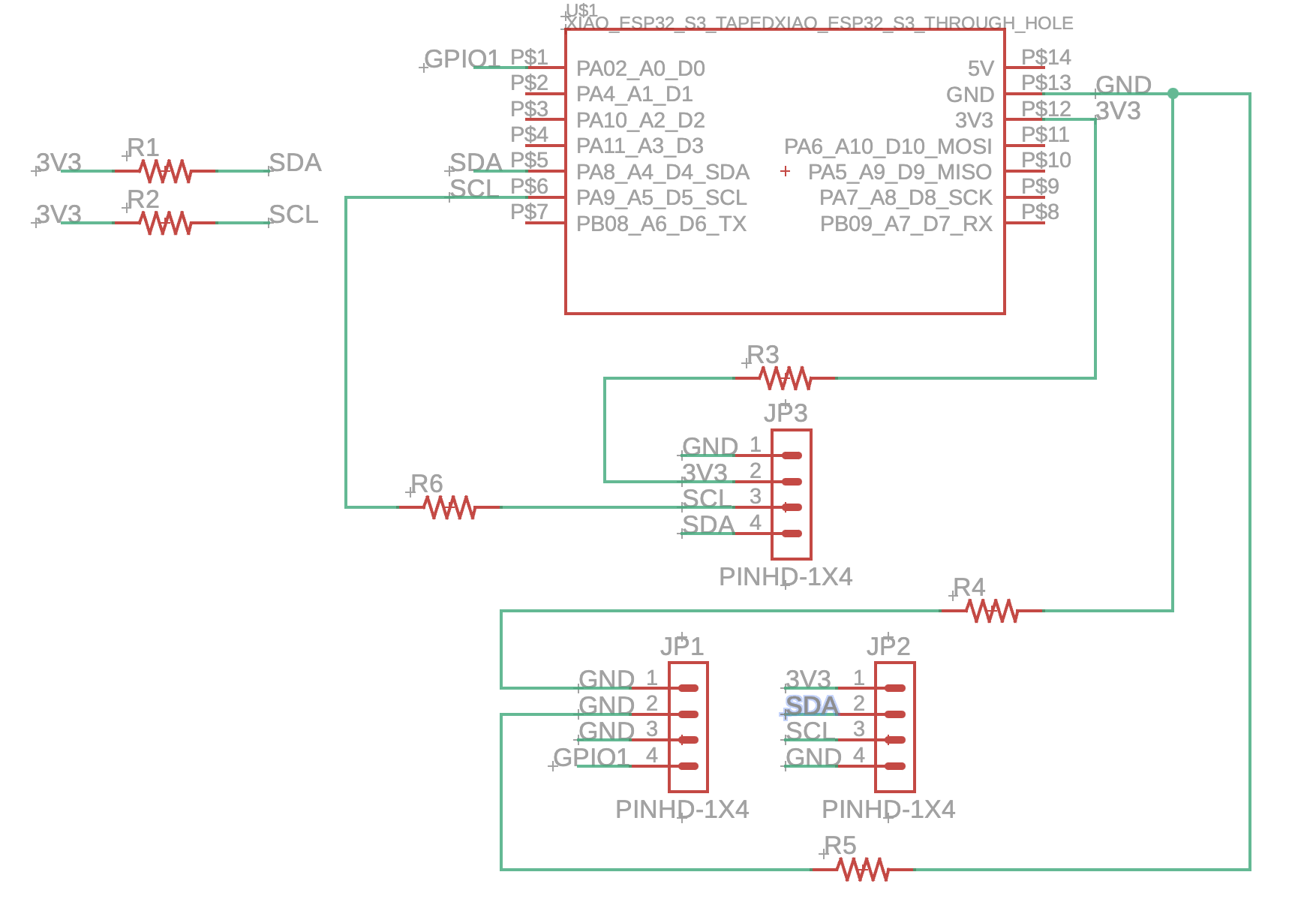
Schematic Design and Component Connections
The schematic integrates the MAX30102 sensor with pull-up resistors for I²C communication, connects power and ground planes, and routes all necessary signals between the ESP32-S3, Wio-SX1262, and sensor modules.
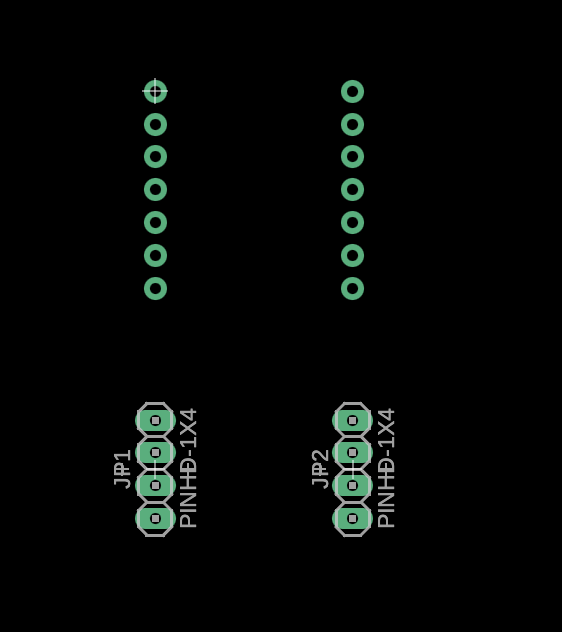
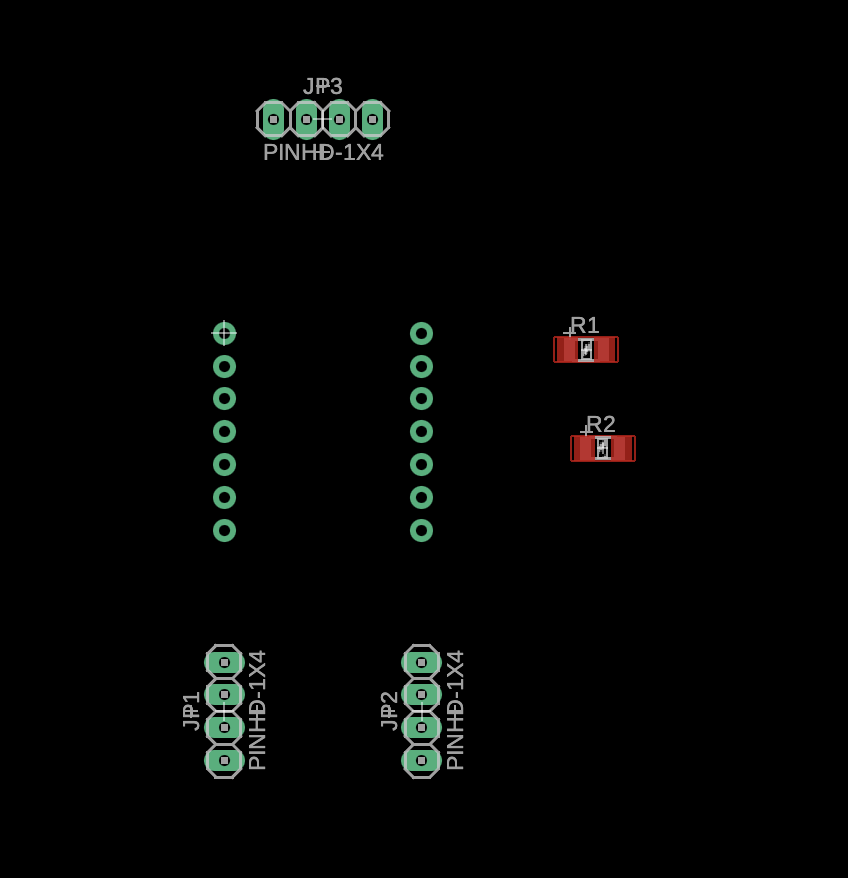
Routing and Design Rule Check
PCB routing required careful attention to signal integrity, especially for I²C lines and power distribution. I iterated from initial routing to clean, labeled connections, then performed design rule checks to ensure manufacturability.
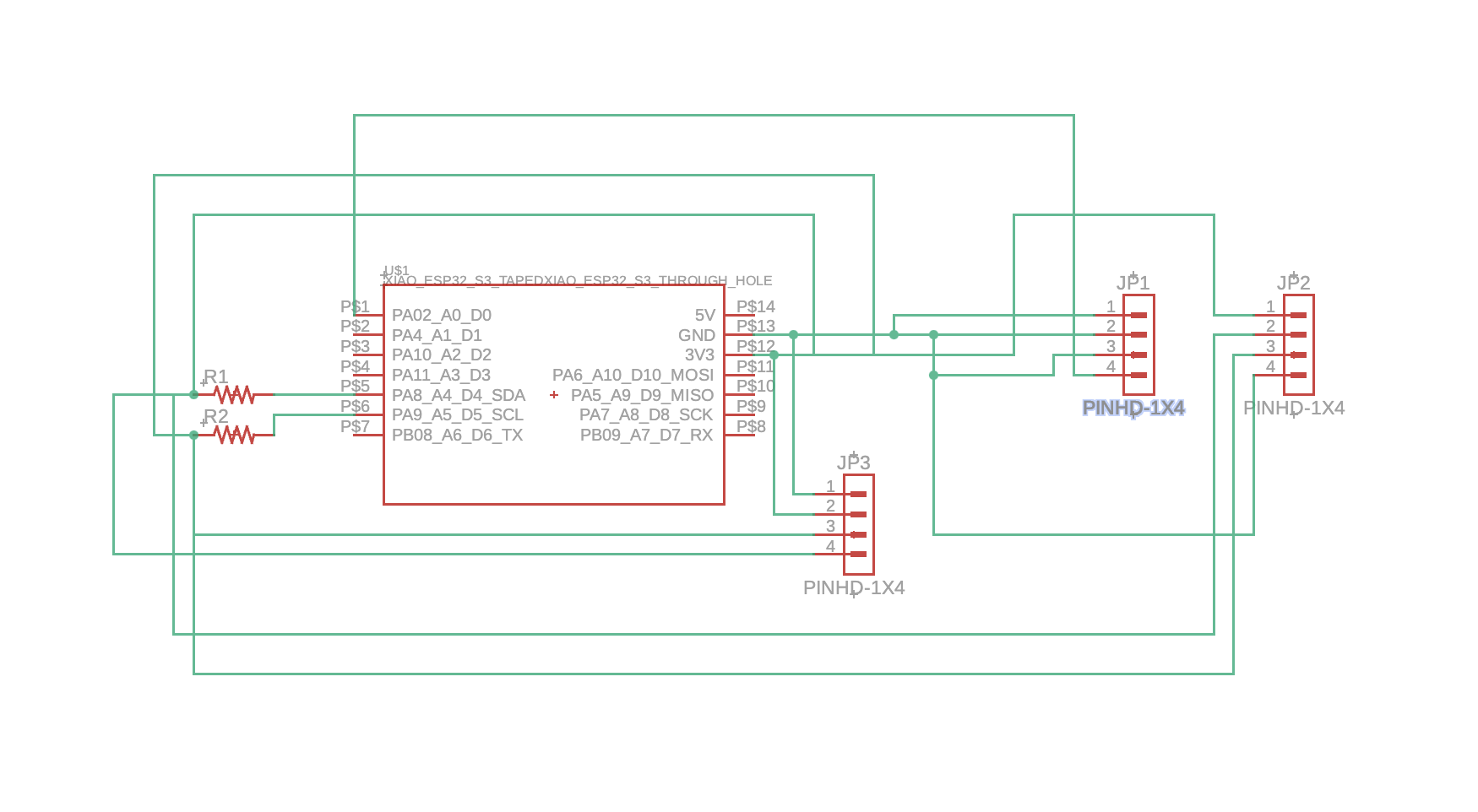
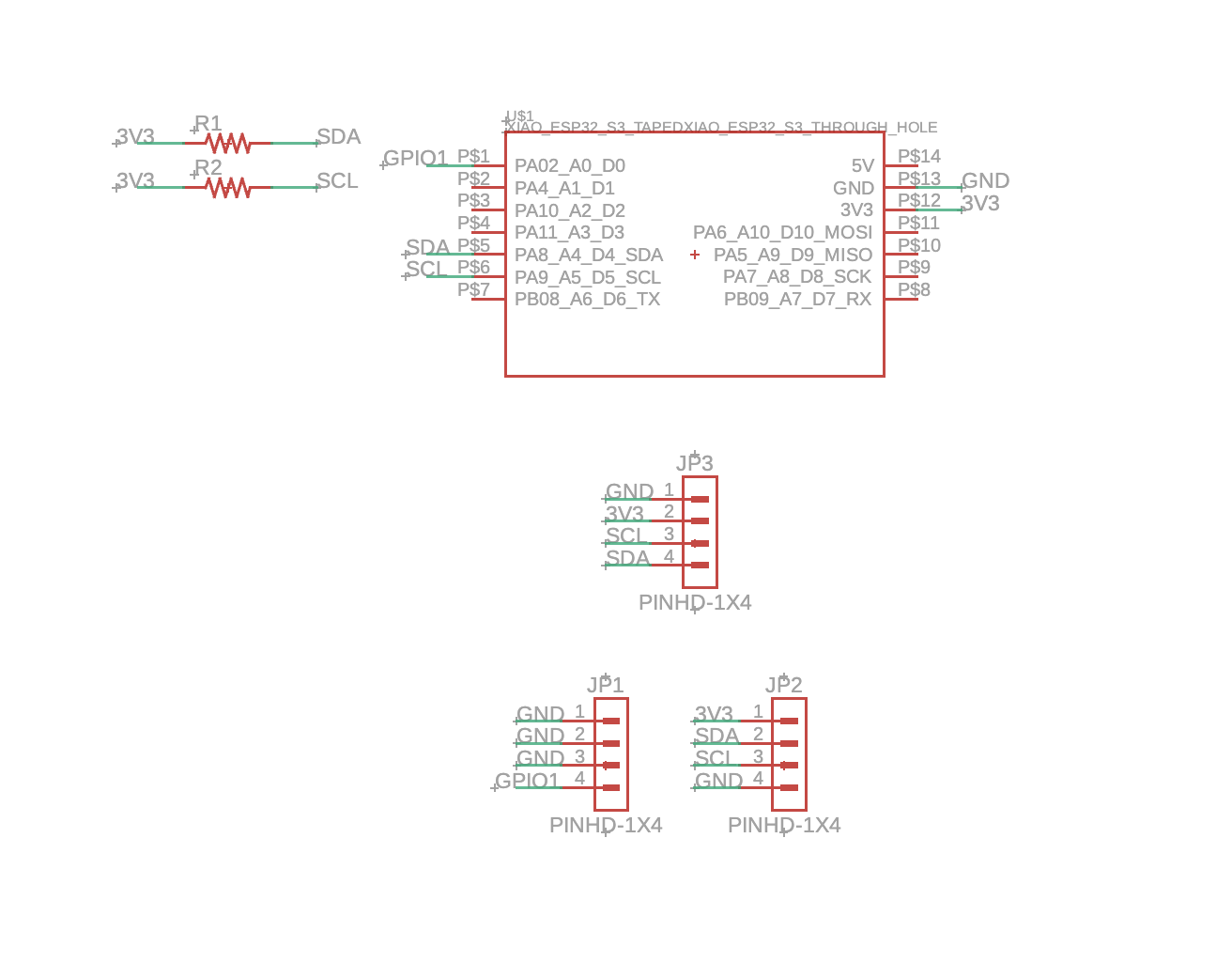
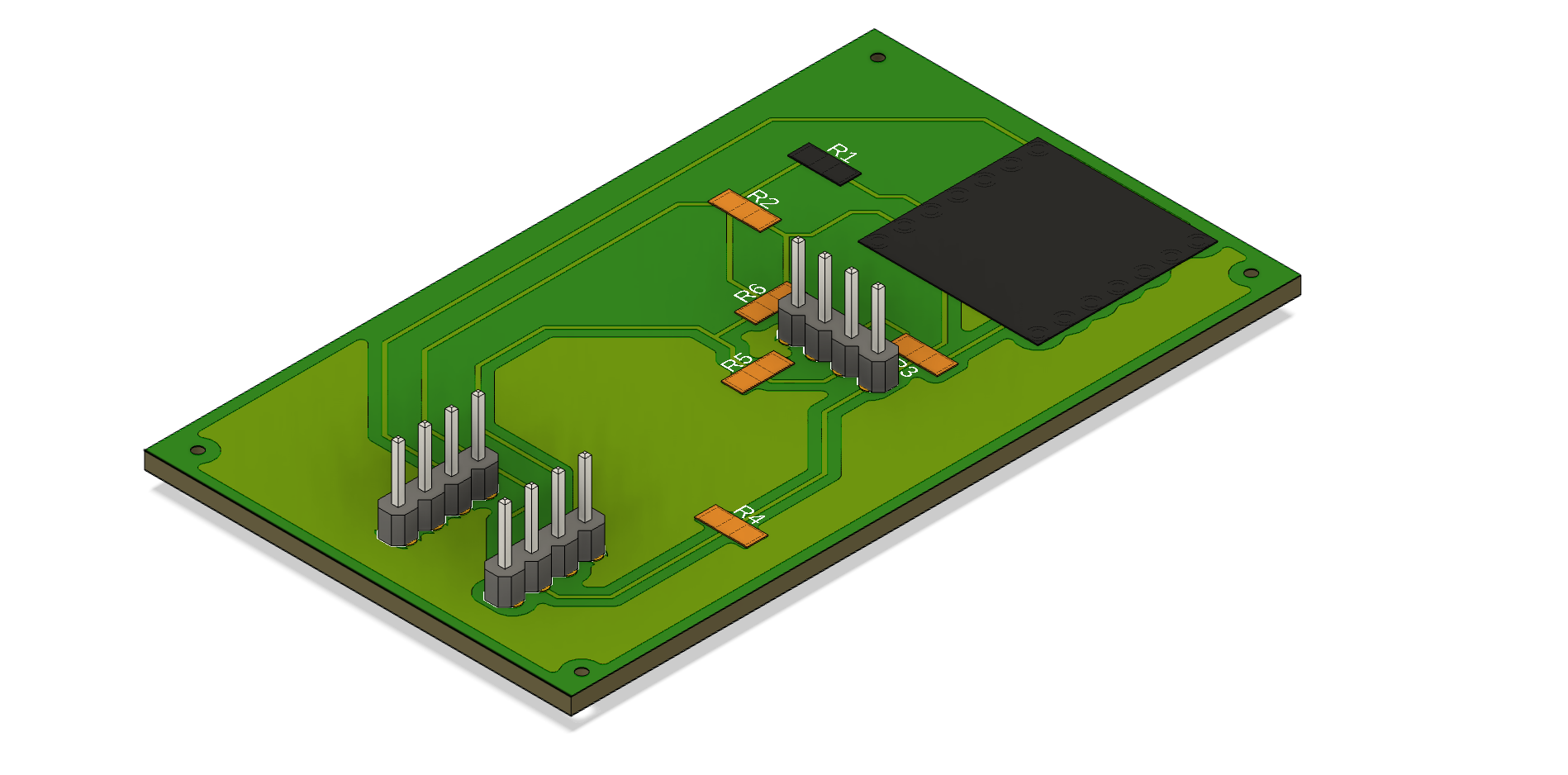
Final Design Files
The final design includes a complete schematic, PCB layout, and 3D CAD rendering showing the assembled board with all modules and components.
PCB Milling and Fabrication
The board was milled using the Othermill (Bantam Tools) in room 38-501, following the electronics production protocol established in Week 5. The milling process required careful tool selection, proper depth settings, and multiple passes for traces and isolation.
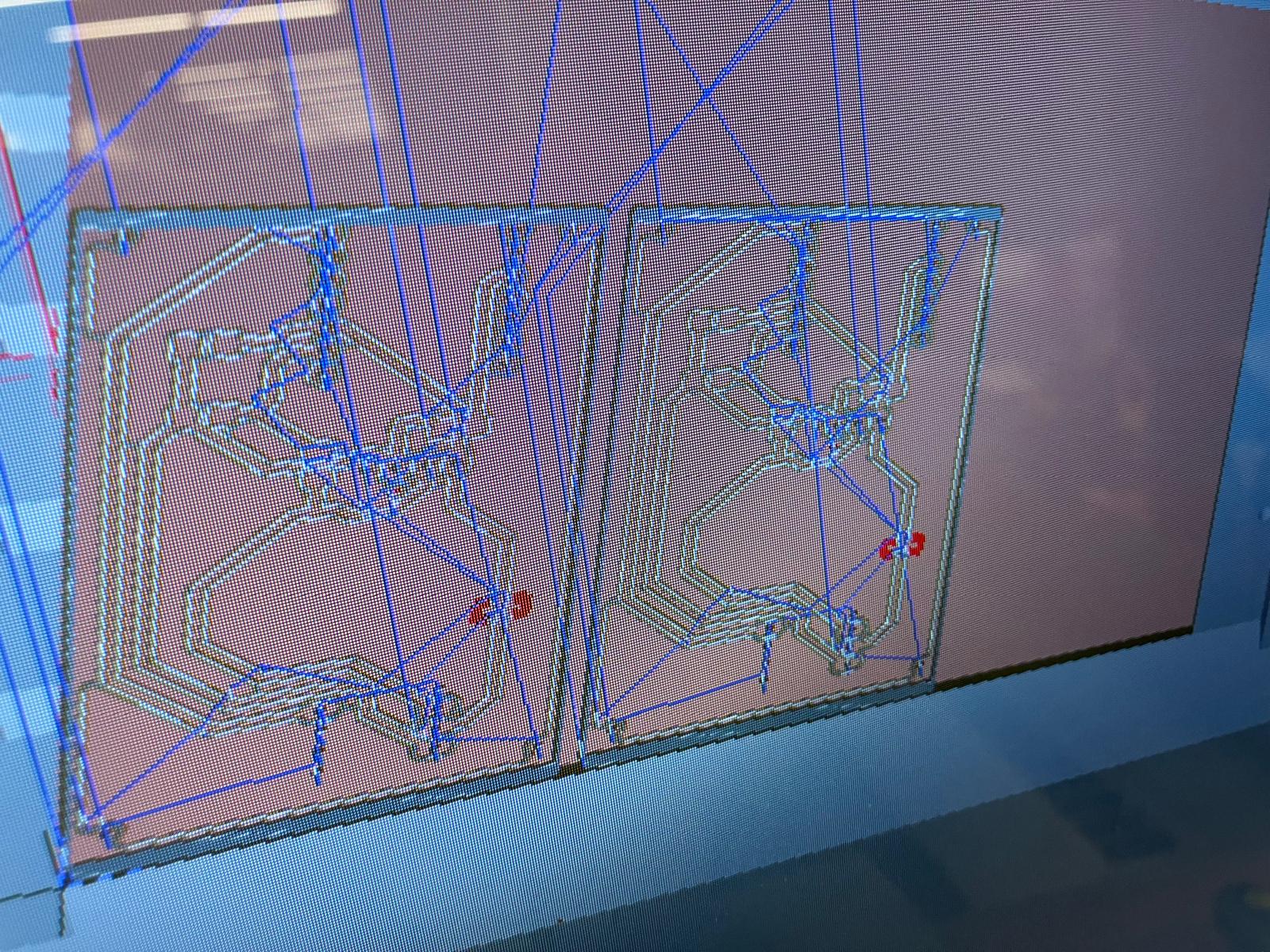
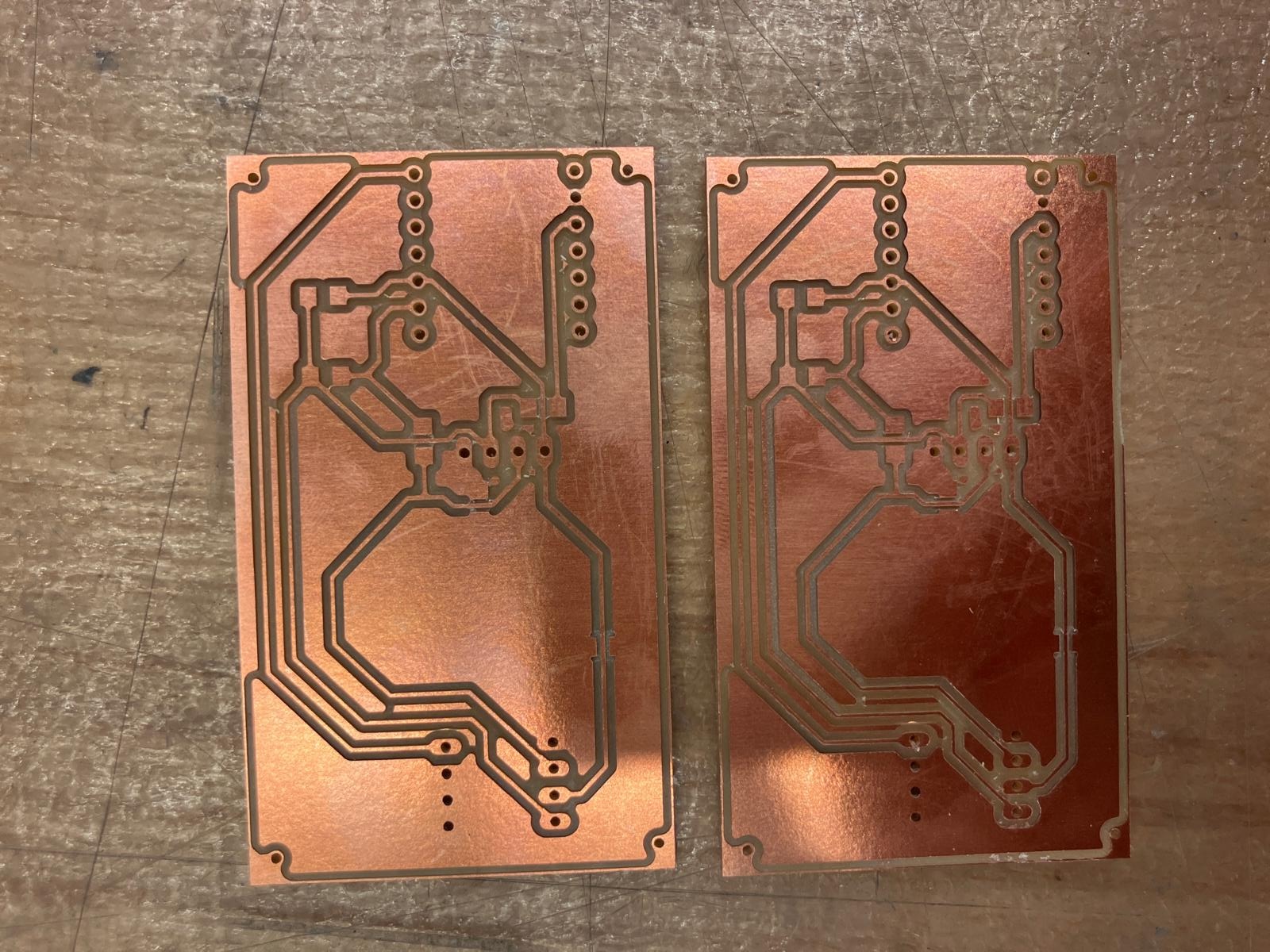
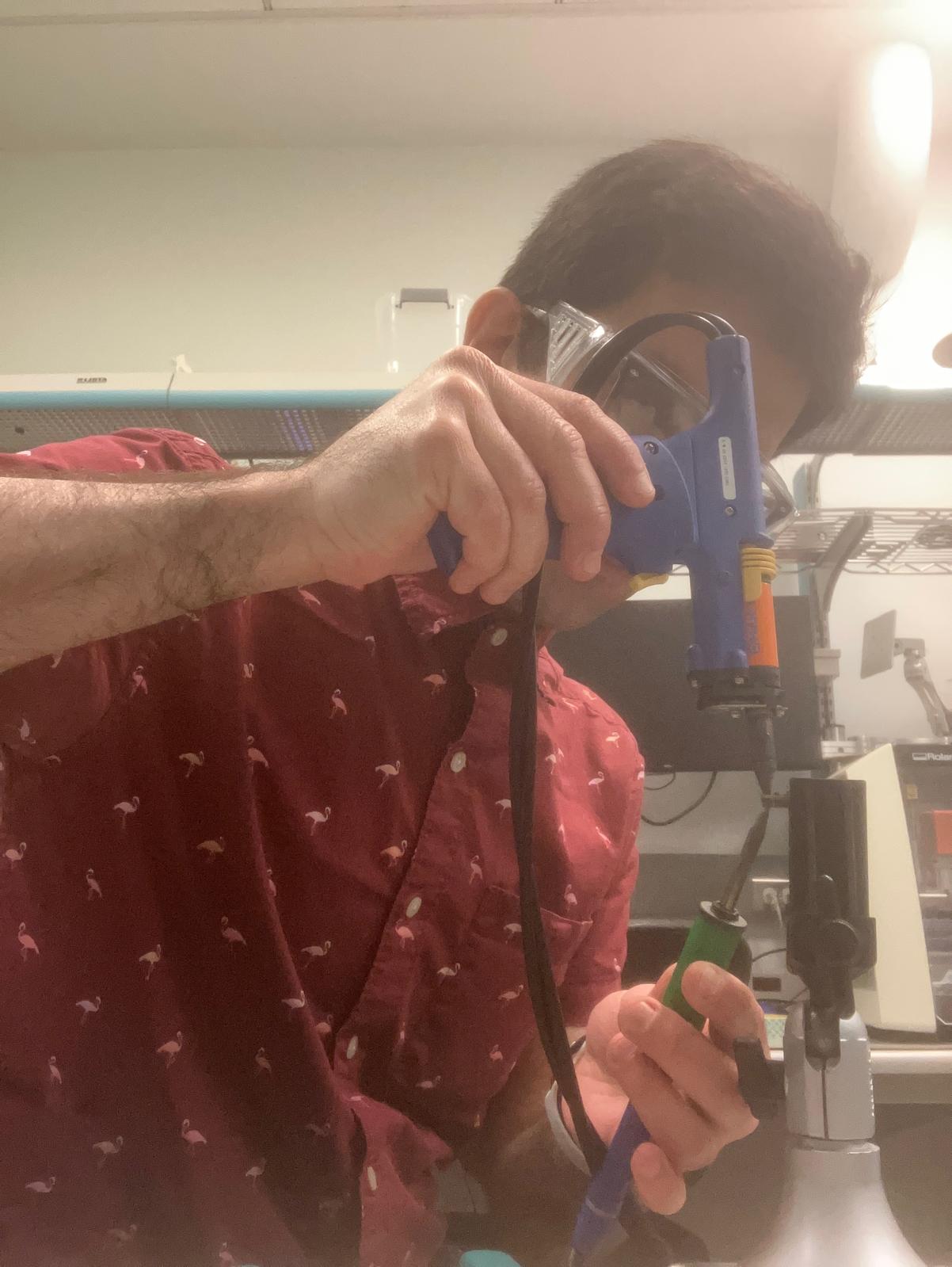
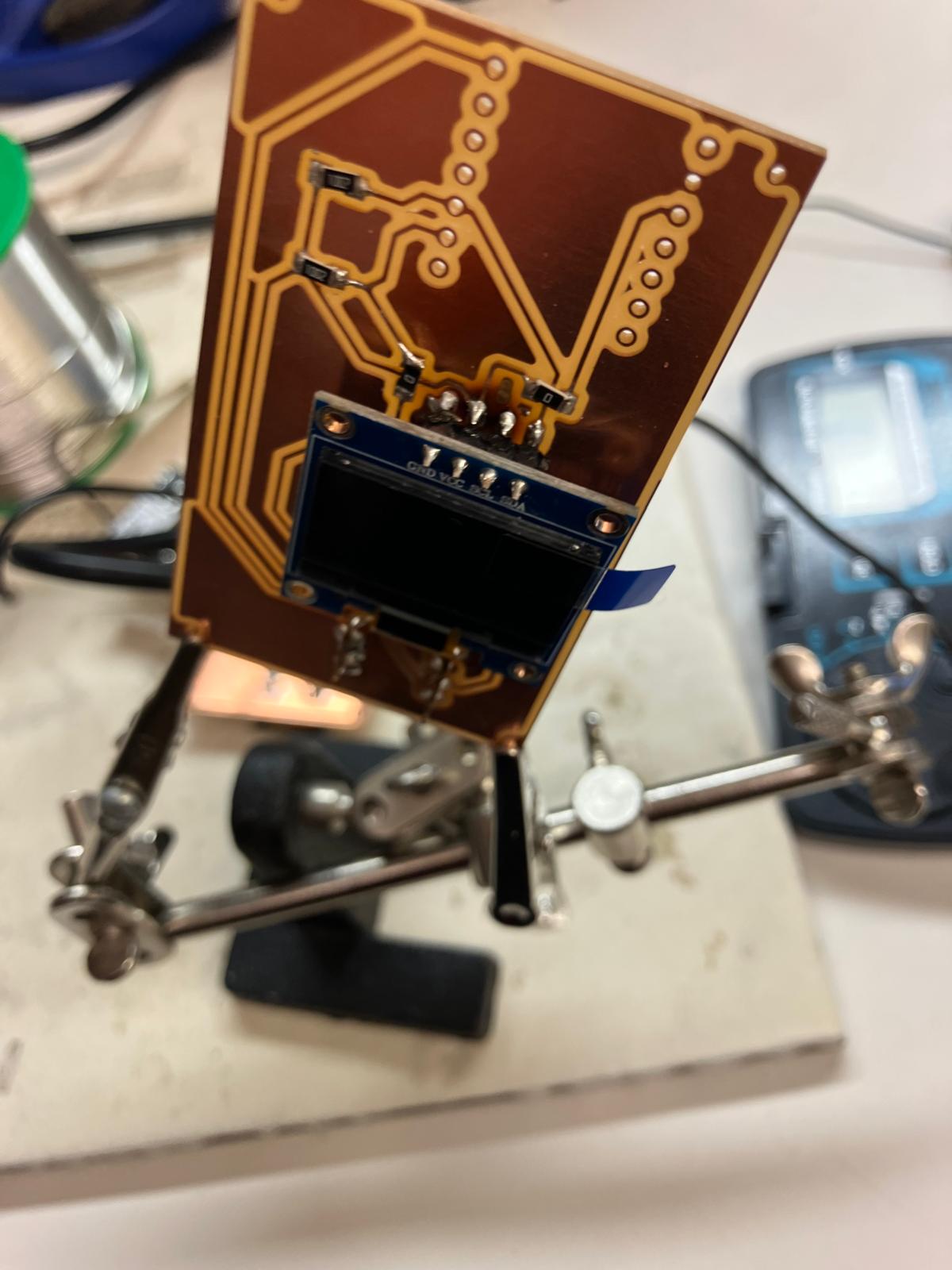
Soldering and Assembly
Through-hole component soldering required advanced techniques using a board stand, positioning the board vertically or horizontally depending on component location. This approach improved access to pads and ensured consistent solder joints.

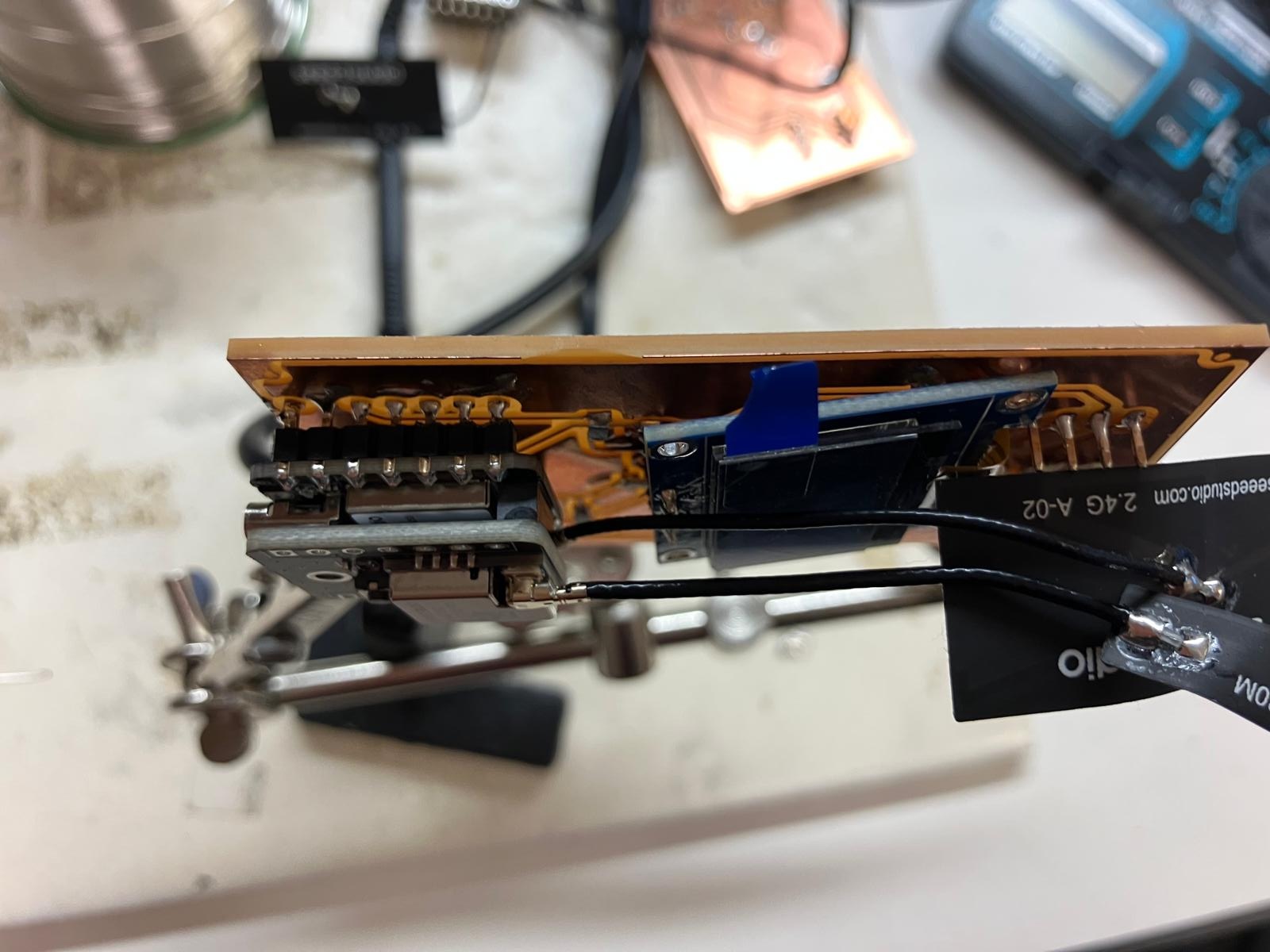
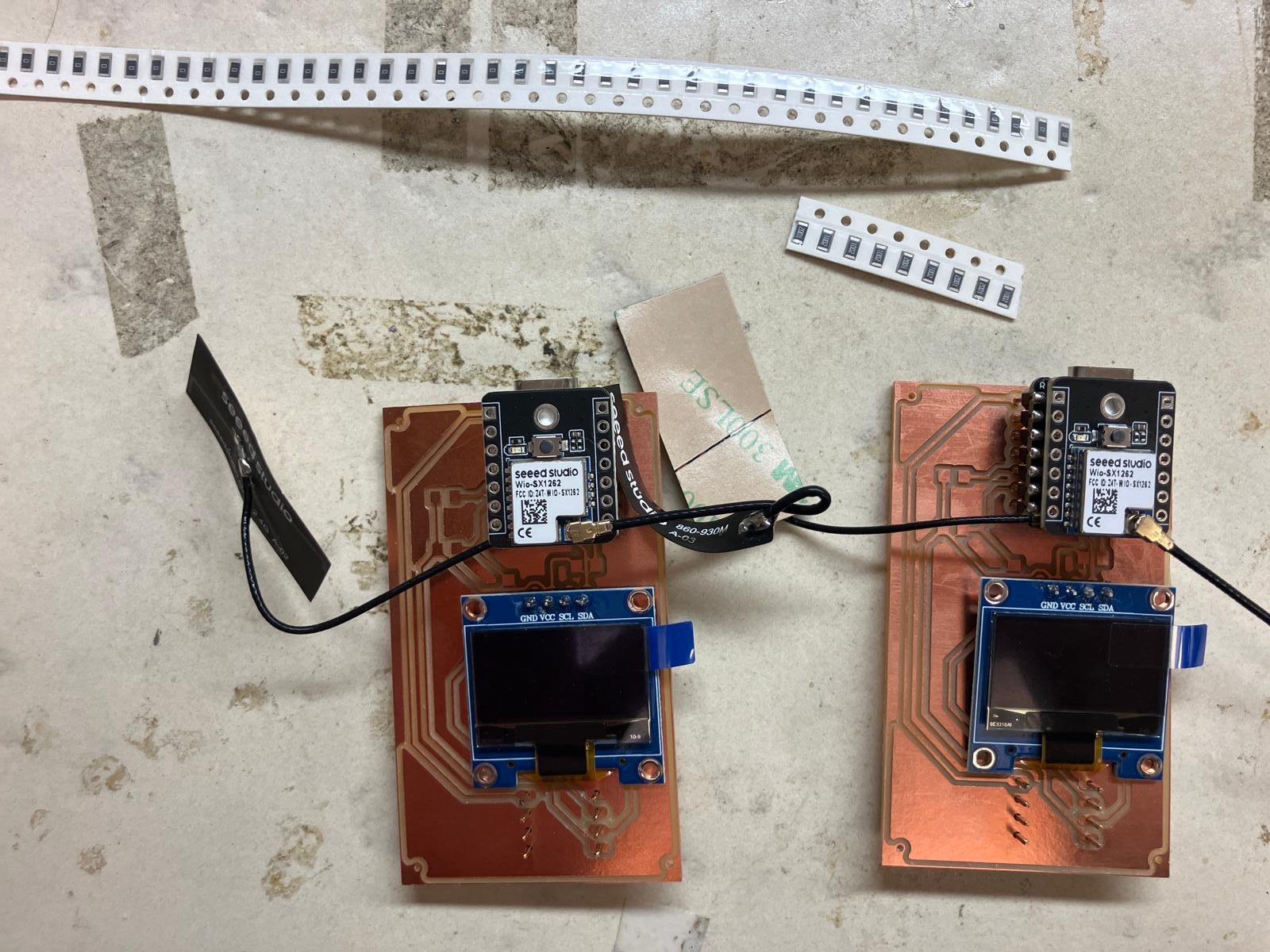
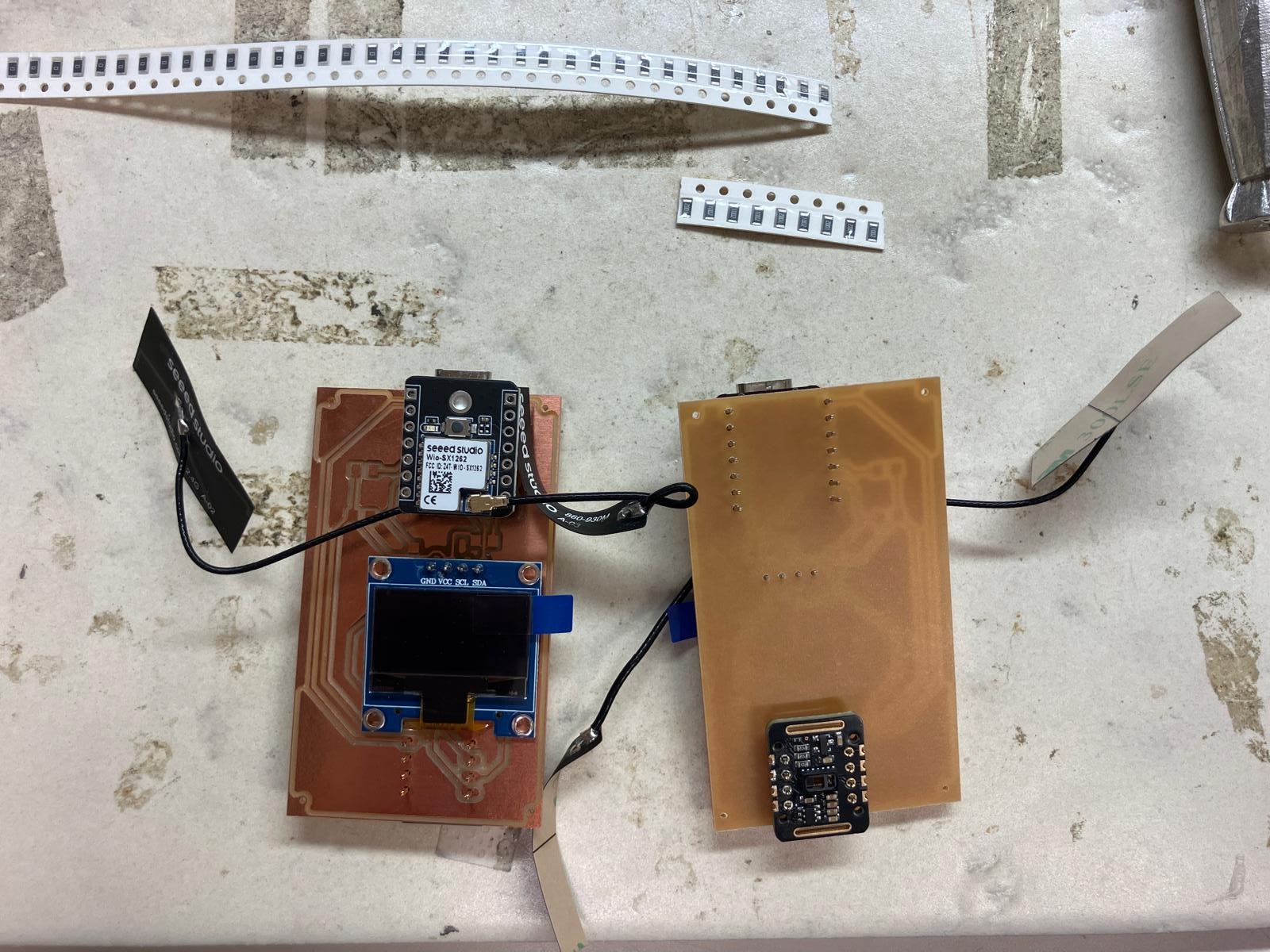
Milling Error Correction
Milling errors resulted in copper "hairs" creating unintended shorts between traces. I used continuity mode on a multimeter to probe for shorts and an exacto knife to carefully cut away the excess copper, restoring proper isolation between traces.
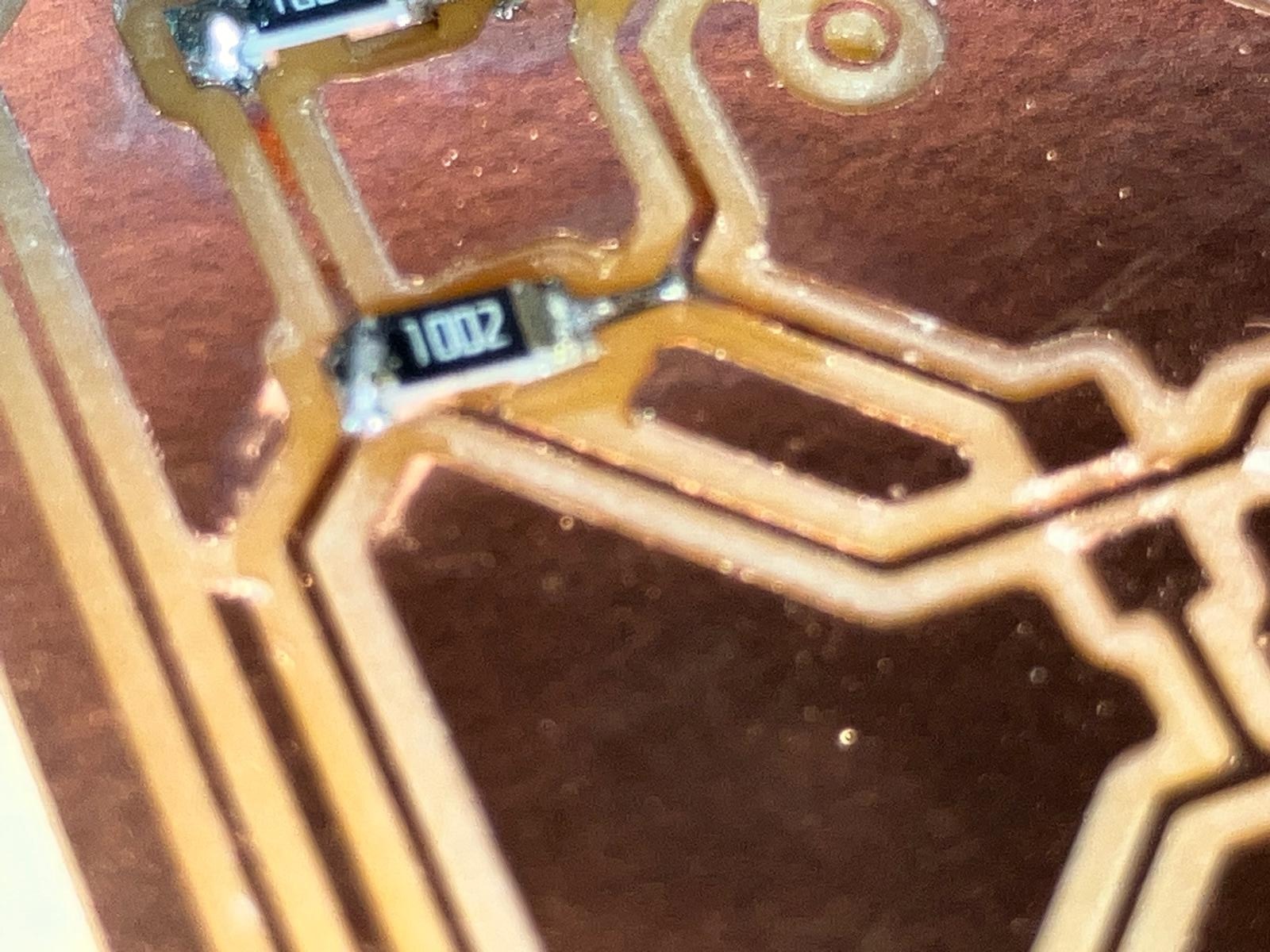
In the end, I had to isolate the common ground on the interrupt side so that RD (red LED) and IRD (infrared LED) grounding terminals are isolated from the rest of the GND plane. This isolation may be necessary for more accurate sensor readings by preventing ground loops and interference.
Network Type & Protocol
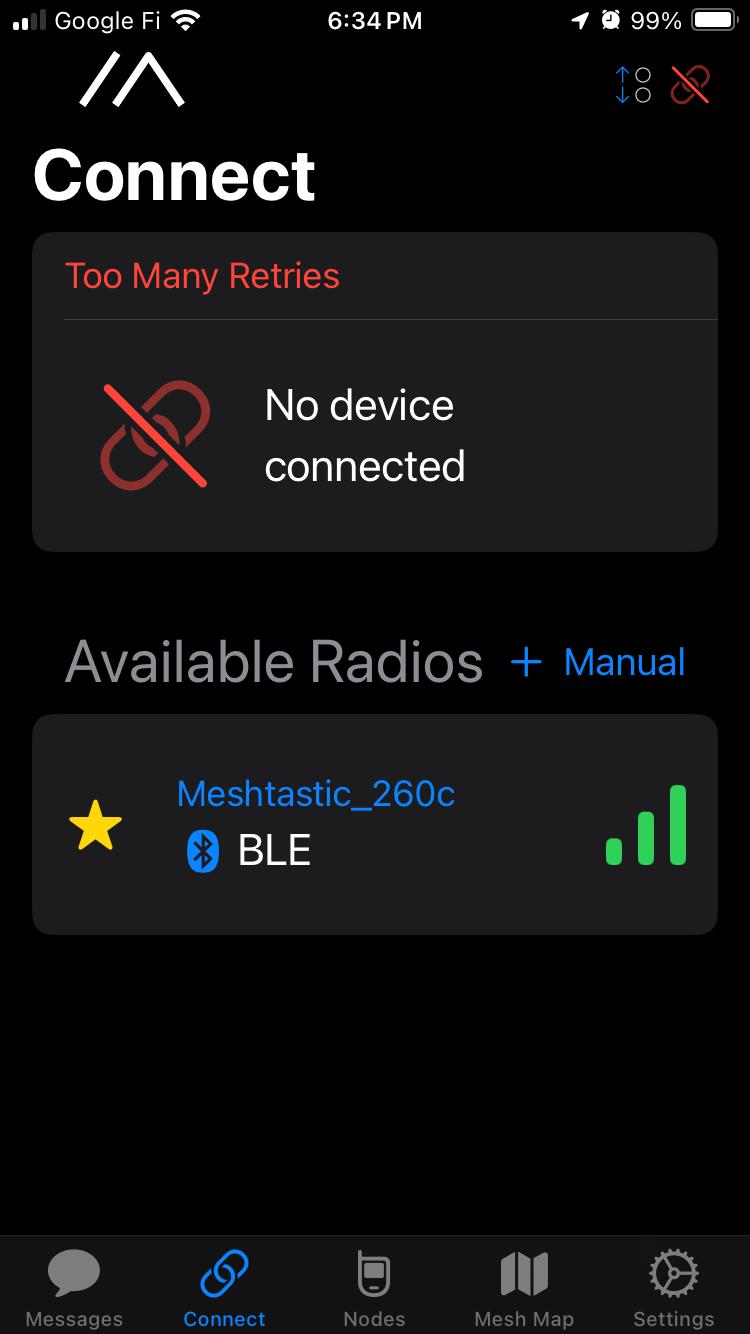
Network Type: Long-range wireless mesh network (LoRa)
Protocol: Meshtastic (open-source mesh networking protocol over LoRa radio)
Radio Module: Wio-SX1262 (Semtech SX1262 LoRa transceiver)
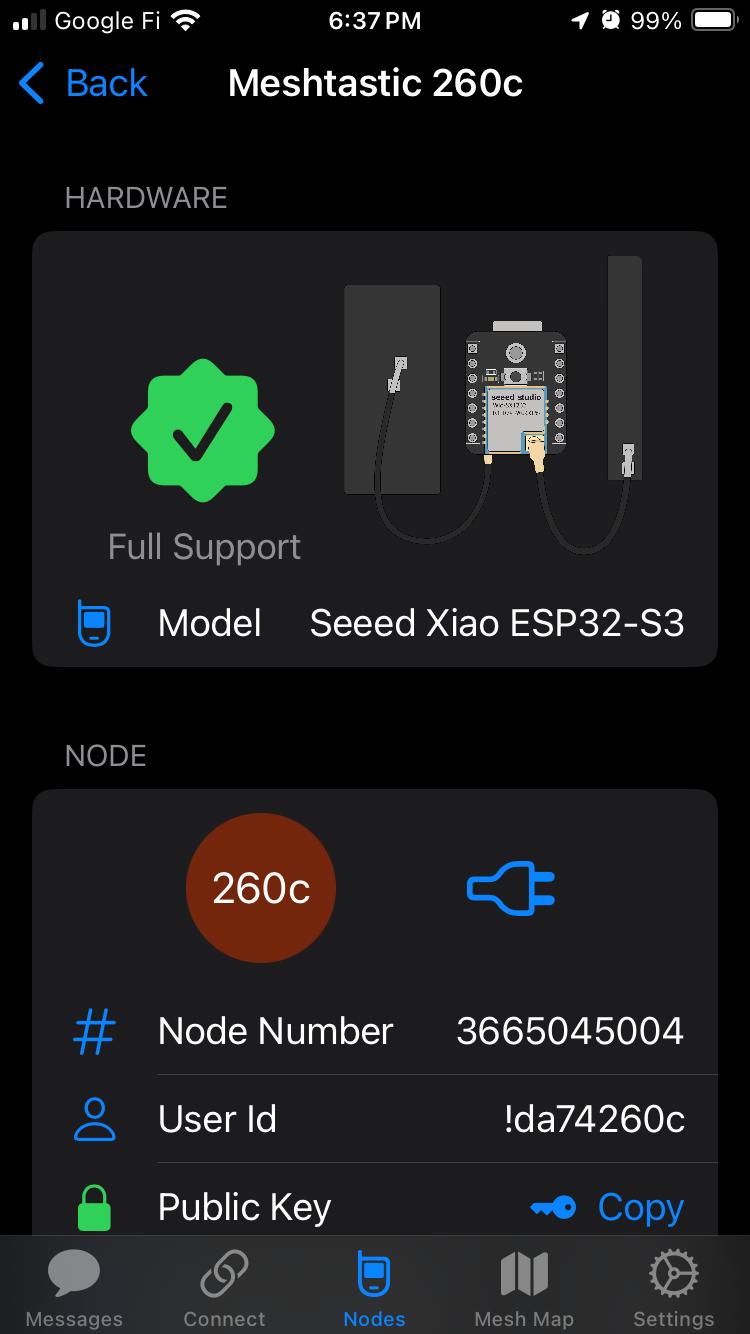
Addressing Scheme: Meshtastic node ID and user ID for device identification
The Wio-SX1262 module provides long-range, low-power wireless communication using LoRa (Long Range) spread spectrum modulation. Meshtastic runs on top of LoRa, creating a decentralized mesh network where devices can relay messages to extend range. The system uses the ESP32-S3 as the main processor, running Meshtastic firmware that manages the LoRa radio and mesh networking protocols.
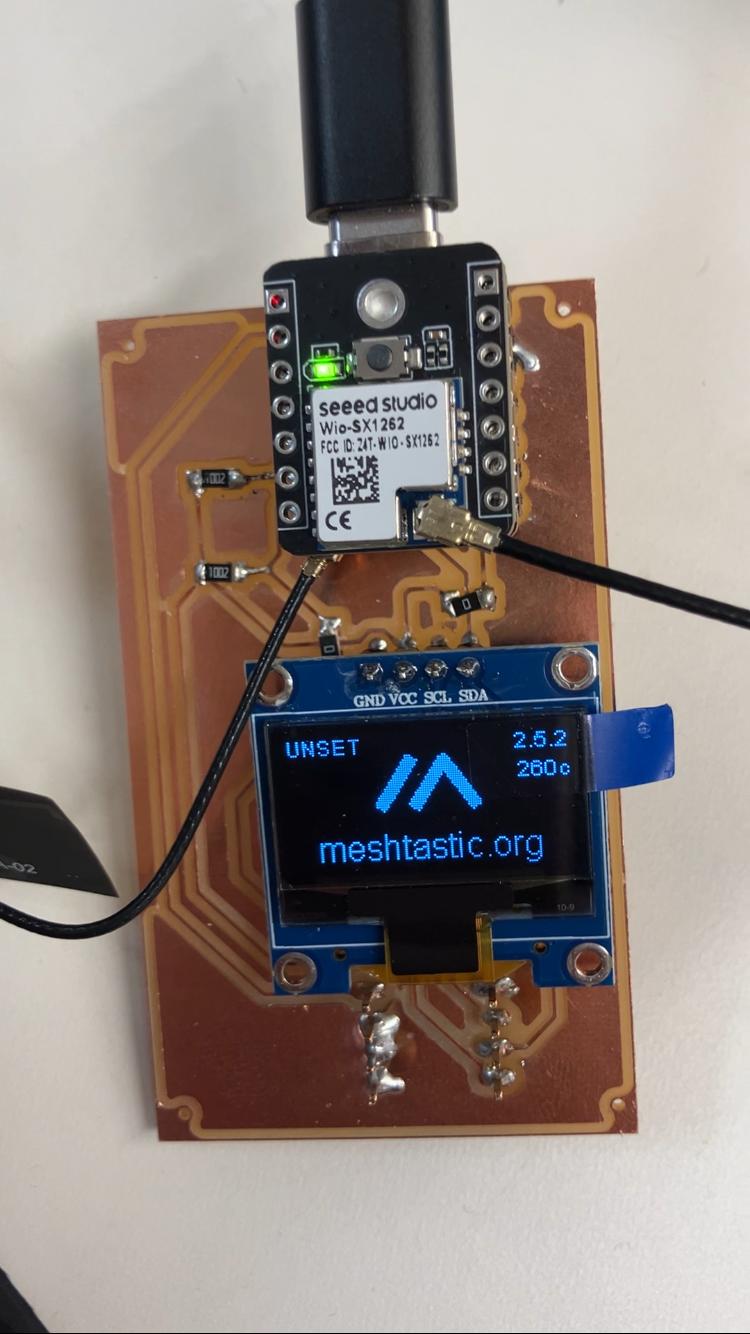

Input & Output Devices
- Input Devices: Heart Rate Sensor Module MAX30102 (pulse detection, blood oxygen concentration measurement) — I²C interface for data communication
- Output Devices: SSD1306 I²C 128×64 OLED display for sensor data visualization and system status
The MAX30102 sensor uses optical reflection (PPG - photoplethysmography) to detect heart rate and blood oxygen levels. It integrates red (660nm) and infrared (880nm) LEDs with a photodetector to measure changes in blood volume through the skin.
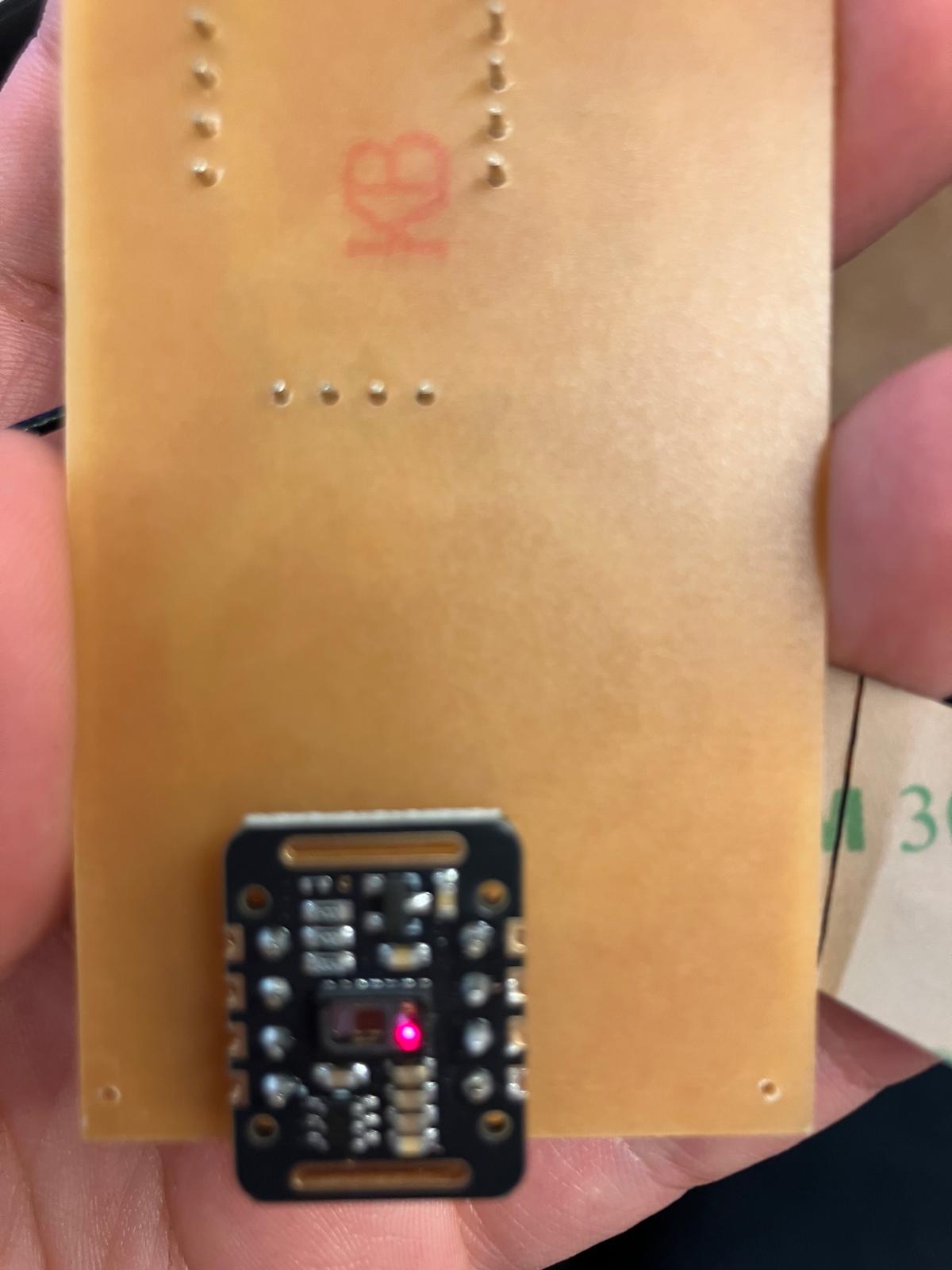

Connections
The XIAO ESP32-S3 connects to the Wio-SX1262 module via SPI interface for LoRa radio control. The MAX30102 sensor connects via I²C (SDA and SCL lines) with pull-up resistors. The OLED display also connects via I²C on the same bus. Power is distributed from the ESP32-S3's 3.3V and 5V rails to all modules. The interrupt pin (INT) from MAX30102 can be connected for event-driven data acquisition, and the RD/IRD pins are isolated from the main ground plane for improved sensor accuracy.
See Network Address Tables for complete device addressing information including Node Number, User ID, and Device Name for the Meshtastic network.
Download Design Files
- invisible_string_schematic.fsch — Fusion 360 Electronics schematic file
- invisible_string_pcb.fbrd — Fusion 360 Electronics PCB layout file
- invisible_string_pcb_brd.brd — Gerber/BRD file for PCB milling
- invisible_string_cad.3mf — 3D CAD rendering of assembled board
Network Address Tables
Complete network addressing information for all connected devices, including MAC addresses (hardware identifiers) and IP addresses (network identifiers) for Wi-Fi-connected devices.
ESP-NOW Network (CircleSquareShapeSongSwingalong)
| Device | Component | MAC Address | Network Type | Input Device | Output Device |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Player 1 | XIAO ESP32-S3 | D8:3B:DA:75:05:AC | ESP-NOW (P2P) | Touch sensors (6 pads) | OLED (SSD1306, 0x3C) |
| Player 2 | XIAO ESP32-S3 | D8:3B:DA:75:E1:9C | ESP-NOW (P2P) | Touch sensors (6 pads) | OLED (SSD1306, 0x3C) |
Wi-Fi Network (Camera Livestream System)
| Device | Component | MAC Address | IP Address | Network Type | Input Device | Output Device |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Camera Node | XIAO ESP32-S3 Sense | [Device MAC] | 192.168.x.x (DHCP) | Wi-Fi (802.11) | Camera module, Button | OLED (SSD1306, 0x3C), HTTP Server |
| Client Device | Web Browser | [Client MAC] | 192.168.x.x (DHCP) | Wi-Fi (802.11) | N/A | Display (receives MJPEG stream) |
LoRa Meshtastic Network (Invisible String)
| Device | Component | Node Number | User ID | Device Name | Network Type | Input Device | Output Device |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Invisible String Node | XIAO ESP32-S3 + Wio-SX1262 | 3665045004 | !da74260c | Meshtastic 260c | LoRa (Meshtastic) | MAX30102 Heart Rate Sensor | OLED (SSD1306, 0x3C) |
Note: MAC addresses are hardware identifiers unique to each ESP32-S3 device. IP addresses are assigned dynamically via DHCP when connecting to a Wi-Fi network. For ESP-NOW communication, only MAC addresses are used (no IP addresses required). The camera system's IP address is printed to the Serial Monitor upon Wi-Fi connection establishment. For Meshtastic networks, devices are identified by Node Number (unique identifier), User ID (hexadecimal user identifier), and Device Name (user-configurable name). The LoRa radio uses spread spectrum modulation for long-range, low-power communication without requiring IP addresses.
Group Assignment: Send a Message Between Two Projects
Send a message between two projects. This assignment demonstrates inter-project communication using wired or wireless networking protocols.
Assignment Description
Send a message between two projects. This assignment demonstrates inter-project communication using wired or wireless networking protocols. The CircleSquareCamera Augmented Reality system extends the ESP-NOW multiplayer game from Week 2 by integrating camera boards that receive game state updates and overlay player positions on live camera feeds.
For detailed documentation of the AI-assisted development process, see AI-Assisted Camera Integration Game Update in the Ethical AI Use section.
CircleSquareCamera Augmented Reality
An augmented reality system that combines the ESP-NOW multiplayer game CircleSquareShapeSongSwingalong (documented in Week 2 and Week 11 individual assignment) with camera subsystems from the final project. The system enables game boards to send player state updates via ESP-NOW to camera boards, which overlay game characters (square and circle) on live camera feeds displayed on OLED screens. Camera code development spans Week 7, Week 8, Final Project, and Week 12 (placeholder link).

Development Note: Initial implementation attempted to send camera data from camera boards to game boards. After two hours of troubleshooting communication issues, the architecture was reversed: the final system sends game state packets from game boards to camera boards via ESP-NOW. This approach proved more efficient for real-time AR overlay visualization, as game state is lightweight compared to camera frame data.
Design & Build
The system consists of two networked subsystems: game boards (XIAO ESP32-S3 with touch sensors and OLED displays) and camera boards (XIAO ESP32-S3 Sense with integrated cameras and OLED displays). Game boards run the CircleSquareShapeSongSwingalong multiplayer game, processing touch input, updating player physics, and broadcasting player state packets via ESP-NOW to both the other game board and all camera boards. Camera boards receive these packets, capture camera frames, process them through Floyd–Steinberg dithering for OLED display, and overlay game character positions (square for Player 1, circle for Player 2) on the live feed.
Network Type & Protocol
Network Type: Wireless peer-to-peer (ESP-NOW)
Protocol: ESP-NOW (Espressif's proprietary low-power wireless communication protocol)
Addressing Scheme: MAC address-based device identification for game boards and camera boards
Communication Pattern: One-to-many broadcast from game boards to peer game board and all camera boards
Input & Output Devices
- Game Boards:
- Input: Capacitive touch sensors (6 touch pads per device) for player controls (left, right, jump)
- Output: SSD1306 OLED display (128x64, I²C address 0x3C) for game rendering
- Camera Boards:
- Input: Camera module (integrated on XIAO ESP32-S3 Sense) for image capture, ESP-NOW packets for game state
- Output: SSD1306 OLED display (128x64, I²C address 0x3C) for displaying dithered camera feed with AR overlay
Connections
Game Boards: Each ESP32-S3 board connects to an OLED display via I²C (SDA pin 5, SCL pin 6) and reads touch sensor inputs from GPIO pins. ESP-NOW communication is handled through the ESP32-S3's built-in Wi-Fi radio, requiring no external hardware connections.
Camera Boards: The camera module is integrated directly on the XIAO ESP32-S3 Sense board, connected via parallel data bus (Y2-Y9), control signals (XCLK, PCLK, VSYNC, HREF), and I²C interface (SIOD, SIOC). The OLED display connects via I²C (SDA pin 5, SCL pin 6) with pull-up resistors. ESP-NOW reception uses the ESP32-S3's built-in Wi-Fi radio in receive-only mode.
Network Address Tables
Complete network addressing information for all devices in the CircleSquareCamera AR system, including MAC addresses (hardware identifiers) for ESP-NOW communication.
ESP-NOW Network (CircleSquareCamera AR System)
| Device | Component | MAC Address | Network Type | Input Device | Output Device |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | XIAO ESP32-S3 | D8:3B:DA:75:05:AC | ESP-NOW (P2P) | Touch sensors (6 pads) | OLED (SSD1306, 0x3C) |
| P2 | XIAO ESP32-S3 | D8:3B:DA:75:E1:9C | ESP-NOW (P2P) | Touch sensors (6 pads) | OLED (SSD1306, 0x3C) |
| Camera A | XIAO ESP32-S3 Sense | B8:F8:62:F9:E2:C0 | ESP-NOW (Receive) | Camera module, ESP-NOW packets | OLED (SSD1306, 0x3C) |
| Camera B | XIAO ESP32-S3 Sense | B8:F8:62:F9:D6:38 | ESP-NOW (Receive) | Camera module, ESP-NOW packets | OLED (SSD1306, 0x3C) |
Note: MAC addresses are hardware identifiers unique to each ESP32-S3 device. Game boards broadcast player state packets to both the peer game board and all camera boards. Camera boards operate in receive-only mode, processing incoming ESP-NOW packets to identify player positions and overlay them on camera feeds.
Download Design Files
Complete Arduino code for game boards and camera boards, including ESP-NOW communication, camera feed processing, and AR overlay implementation.
Design Files
Complete design files for networked systems including ESP-NOW multiplayer game and Wi-Fi camera streaming implementations with Arduino firmware and configuration files.
ESP-NOW Multiplayer Game (CircleSquareShapeSongSwingalong)
Arduino code for ESP-NOW wireless multiplayer game with MAC address-based player identification and synchronized game state management.
Key Features:
- ESP-NOW wireless peer-to-peer communication
- MAC address-based player identification (D8:3B:DA:75:05:AC and D8:3B:DA:75:E1:9C)
- Real-time game state synchronization
- Ready state coordination between players
- Touch-based input controls (left, right, jump)
- OLED display output for game rendering
Wi-Fi Camera Livestream & Edge AI
Arduino code for ESP32-S3 camera livestreaming over Wi-Fi using MJPEG protocol and Edge AI face detection using FOMO models from Edge Impulse.
Camera Livestream Pseudocode:
SETUP:
1. Initialize Serial communication (115200 baud)
2. Configure camera pins (from camera_pins.h)
3. Create camera_config_t structure
4. Initialize camera with esp_camera_init()
5. Connect to Wi-Fi network
6. Start HTTP server with stream handler
STREAM_HANDLER:
1. Set HTTP response type to "multipart/x-mixed-replace"
2. Enter loop: capture frame, send via HTTP, repeat
LOOP:
- Minimal delay to allow other tasksKey Features:
- Wi-Fi HTTP server for MJPEG streaming
- Edge AI face detection using FOMO models
- Real-time camera frame capture and processing
- OLED display output for local visualization
- IP address assignment via DHCP
- MAC address for hardware identification
Video Dithering Stream to OLED
Arduino code for capturing camera frames and streaming them to an OLED display using Floyd–Steinberg dithering for high-quality monochrome rendering. This code demonstrates real-time image processing and display optimization for low-resolution OLED screens.
How the Code Works (Pseudocode):
SETUP:
1. Initialize Serial communication (115200 baud)
2. Initialize I²C bus for OLED display
3. Initialize OLED display (128x64, I²C address 0x3C)
4. Configure camera pins using camera_pins.h definitions
5. Initialize camera with QQVGA resolution (160x120)
6. Set pixel format to GRAYSCALE
7. Display initialization status on OLED
LOOP:
1. Capture camera frame using esp_camera_fb_get()
2. Process frame through showDitheredPreview():
a. Downsample camera frame (160x120) to OLED resolution (128x64)
b. Average pixel values in each downsampled region
c. Store results in gray_buffer array
d. Normalize brightness values to full range
e. Apply Floyd–Steinberg dithering algorithm
f. Render dithered result to OLED display
3. Return camera frame buffer using esp_camera_fb_return()
4. Repeat continuously for live preview
DITHERING ALGORITHM (Floyd–Steinberg):
For each pixel from top-left to bottom-right:
1. Quantize current pixel (0 or 255)
2. Calculate quantization error
3. Distribute error to neighboring pixels:
- Right: 7/16 of error
- Bottom-left: 3/16 of error
- Bottom: 5/16 of error
- Bottom-right: 1/16 of errorKey Features:
- Real-time camera frame capture at QQVGA resolution (160x120)
- Grayscale image processing for efficient monochrome display
- Floyd–Steinberg dithering algorithm for high-quality visual output
- Automatic brightness normalization for optimal contrast
- Continuous live preview stream to OLED display
- Optimized downsampling from camera resolution to OLED resolution (128x64)
What You Need to Know:
This code provides a foundation for displaying camera feeds on OLED displays. The Floyd–Steinberg dithering algorithm distributes quantization errors across neighboring pixels, creating smooth gradients and improved visual quality compared to simple thresholding. The code uses grayscale format for efficient processing, and the downsampling step averages multiple camera pixels into each OLED pixel to maintain image clarity.
This implementation serves as a building block for the CircleSquareCamera AR system, where camera feeds are combined with game state overlays. See Ethical AI Use section for ChatGPT co-development transcript.
Group Assignment: CircleSquareCamera Augmented Reality System
Complete Arduino code for the CircleSquareCamera AR system, including game board code that broadcasts player states via ESP-NOW, and camera board code that receives game packets and overlays player positions on live camera feeds.
Camera Board Code (CircleSquareCamera.ino)
Camera board receives ESP-NOW packets from game boards, captures camera frames, processes them through dithering, and overlays game character positions (square for P1, circle for P2) on the live feed displayed on OLED.
How the Code Works (Pseudocode):
SETUP:
1. Initialize Serial, I²C, OLED display
2. Initialize ESP-NOW in receive-only mode
3. Register ESP-NOW receive callback
4. Initialize camera (QQVGA, GRAYSCALE)
5. Determine camera ID from MAC address (A or B)
6. Display camera ready status
ESPNOW_RECEIVE_CALLBACK:
1. Check if packet is correct size (NetPacket)
2. Extract player state from packet
3. Identify player (P1 or P2) based on sender MAC address
4. Store player state in p1 or p2 variable
5. Set gotP1 or gotP2 flag
LOOP:
1. Capture camera frame (esp_camera_fb_get)
2. Process frame through makeFrame():
a. Downsample camera (160x120) to 64x32
b. Normalize brightness
c. Apply Floyd–Steinberg dithering
d. Rotate 180° for correct orientation
3. Draw camera feed to OLED (2x2 pixel blocks)
4. Overlay game characters if received:
- Draw square at p1.x, p1.y for Player 1
- Draw circle at p2.x, p2.y for Player 2
5. Display frame on OLED
6. Return camera frame bufferKey Features:
- ESP-NOW receive-only mode for game state packets
- MAC address-based player identification (P1: 0xAC, P2: 0x9C)
- Real-time camera frame capture and dithering
- 180° rotation for correct display orientation
- AR overlay of game characters on live camera feed
- Automatic camera ID detection from MAC address
Game Board Code (TwoSquares_XiaoESP32S3_Touch_ReadySplash_MACFix_Camera.ino)
Extended version of the CircleSquareShapeSongSwingalong game that broadcasts player state packets to both peer game boards and camera boards via ESP-NOW. This enables real-time AR visualization of gameplay on camera displays.
How the Code Works (Pseudocode):
SETUP:
1. Initialize Serial, OLED display
2. Set WiFi mode to STA
3. Read self MAC address
4. Initialize ESP-NOW
5. Identify player role (P1 or P2) from MAC address
6. Add peers: peer game board + Camera A + Camera B
7. Register ESP-NOW send/receive callbacks
8. Initialize touch sensors (warm-up readings)
9. Reset player states (left/right positioning)
LOOP:
1. Update touch sensor readings
2. Process player input (left, right, jump)
3. Update player physics (movement, gravity, collision)
4. Create NetPacket with player state and ready flag
5. Broadcast packet to all peers:
- Other game board (peerMac)
- Camera A (camA_MAC)
- Camera B (camB_MAC)
6. Render game state to OLED:
- Draw ground line
- Draw own character (square if P1, circle if P2)
- Draw other player character
- Display "Waiting Player" if other not ready
7. Delay for frame timing (30ms)Key Features:
- ESP-NOW one-to-many broadcast to game boards and camera boards
- MAC address-based player identification (P1: D8:3B:DA:75:05:AC, P2: D8:3B:DA:75:E1:9C)
- Touch-based input controls with threshold detection
- Real-time physics simulation (movement, gravity, collision)
- Ready state synchronization for coordinated gameplay start
- Game state rendering with square/circle character representation
What You Need to Know:
This code extends the original CircleSquareShapeSongSwingalong game by adding camera board peers to the ESP-NOW network. The game broadcasts player state packets (position, velocity, onGround flag) to enable AR overlay on camera displays. The camera boards use these packets to draw game characters at the correct positions relative to the camera feed, creating an augmented reality experience. Player identification is done via MAC address comparison, with P1 using square representation and P2 using circle representation. See Ethical AI Use section for ChatGPT co-development transcript.
Reflections & Learnings
Key insights and learnings from working with networking and communications protocols.
Key Points
- Wireless communication protocols (Wi-Fi, ESP-NOW, LoRa/Meshtastic) each have distinct trade-offs in range, power, and data rate
- Reliable data transmission requires robust error handling and network topology design
- Network topology and data handling strategies are critical for distributed systems
- Integrating communication modules into PCB designs requires careful RF layout considerations
- Real-time synchronization across networked devices demands careful protocol design and state management
Networking & Communications Insights
- Understanding various wireless communication protocols (Wi-Fi, ESP-NOW, LoRa/Meshtastic).
- Challenges in establishing reliable data transmission between multiple devices.
- The importance of network topology and data handling for distributed systems.
- Integrating communication modules into PCB designs for seamless connectivity.
Contributions
Acknowledgements and team roles for networking and communications work.
Developed CircleSquareShapeSongSwingalong multiplayer game with ESP-NOW wireless communication during Week 2. See Week 2 documentation for details.
Developed camera livestreaming and Edge AI face detection system during Week 10. See Week 10 documentation for details.
Ethical AI Use
Transparent documentation of AI assistance used in this week's networking and communications work.
📋 General Guidelines: See General Commands for Cursor on the homepage for standard guidelines and commands used consistently throughout documentation development.
AI-Assisted Camera Integration Game Update
Used ChatGPT for collaborative development of the CircleSquareCamera augmented reality system, integrating ESP-NOW communication between game boards and camera boards. The AI assisted with ESP-NOW packet structure design, camera feed dithering algorithms, AR overlay implementation, and real-time synchronization of player states with camera displays. This extends the original CircleSquareShapeSongSwingalong multiplayer game from Week 2 with augmented reality visualization.
ChatGPT Co-Development Transcript:
AI-Assisted Week 11 Project Documentation Update
Cursor AI assisted with comprehensive updates to Week 11 documentation, including ethical AI use section updates, design files documentation with pseudocode and key features, group assignment CircleSquareCamera AR section development, network address tables, and overall page organization. The AI helped refine technical content, create professional code documentation, add media captions and descriptions, and organize information for optimal readability and aesthetic presentation.
The AI was used to:
- Update ethical AI use section with ChatGPT co-development transcript references
- Create comprehensive design files documentation with pseudocode, key features, and "what you need to know" sections
- Develop group assignment CircleSquareCamera AR subsection with detailed technical explanations
- Add network address tables for CircleSquareCamera AR system with all device MAC addresses
- Implement download links for all code files (zip archives and individual files)
- Add professional captions and descriptions to all images and videos
- Refine and organize content for professional presentation while preserving technical accuracy
Complete AI Assistance Transcript:
AI-Assisted Week 11 Page Creation and Assignment Documentation
Cursor AI assisted with creating the complete Week 11 documentation page, including networking protocols overview, group assignment CircleSquareCamera AR documentation, individual assignment sections summarizing ESP-NOW multiplayer game and Wi-Fi camera streaming systems, network address tables, and all formatting and styling. The AI helped refine and organize content from Week 2 and Week 10 into professional, succinct networking documentation while preserving key technical details.
The AI was used to:
- Create week11.html from the week8.html template structure
- Populate networking and communications resources from the MIT Academy class page
- Summarize and integrate content from Week 2 (ESP-NOW multiplayer game) and Week 10 (Wi-Fi camera streaming)
- Create network address tables with MAC and IP addresses for both networked systems
- Format and style all sections for professional presentation
- Embed images, videos, and design file download links
Complete AI Assistance Transcript:
AI-Assisted Week 11 Recitation Notes Update
Cursor AI assisted with updating the Week 11 recitation notes section with comprehensive system integration content. The AI helped refine and organize raw notes from the recitation session into a well-structured, professional format with proper headings, bullet points, and external links. The updated section includes usability principles from Dr. Jan Borchers's session, failure modes analysis, testing strategies, repair considerations, lifecycle planning, and assignment details.
The AI was used to:
- Organize raw recitation notes into structured sections with proper headings
- Format content with consistent styling matching the rest of the page
- Add external links to resources (Slack message, class pages, GitLab, etc.)
- Create clear bullet points and lists for readability
- Integrate the refined notes into the existing recitation section
- Maintain technical accuracy while improving presentation
Complete AI Assistance Transcript:
AI-Assisted Week 11 Individual Assignment Update
Cursor AI assisted with comprehensive updates to the Week 11 individual assignment section, including MIT Wi-Fi connection instructions, Networked System 3 (Long Range Radio Board Design, Fabrication, and Connection to Meshtastic), and Network Address Tables. The AI helped refine technical content, organize documentation with proper structure, add detailed captions and descriptions to all images and videos, and create professional documentation following the established template format.
The AI was used to:
- Update Networked System 2 (Camera Livestream) with step-by-step MIT Wi-Fi connection instructions
- Add Networked System 3 section documenting the Invisible String long-range radio board design
- Create comprehensive documentation of PCB design process, component selection, routing, and fabrication
- Document soldering techniques, milling error correction, and assembly procedures
- Add Network Address Table for LoRa Meshtastic system with node information
- Add links to Network Address Tables from each networked system section
- Create second row of highlights with links to specific images and videos
- Add professional captions and descriptions to all media throughout the section
- Organize content with proper headings, subsections, and design file download links
Complete AI Assistance Transcript:
 This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License